It starts like this: a new employee joins, and your IT team jumps in to create an account, assign access, and configure permissions. Soon after, tickets start pouring in for password resets, group changes, and locked accounts. By the end of the week, your admins are juggling hundreds of small but critical identity tasks.
That’s the everyday reality for IT teams managing enterprise systems. Each account represents a potential security risk if not handled properly, and every manual step adds time and complexity. Active Directory Management brings order to that chaos. It gives IT teams a structured way to create, modify, and secure user accounts, apply policies, and control access, all from one central place.
It’s not just about user management; it’s about control, consistency, and confidence in how your organization handles identity.
What Is Active Directory Management?
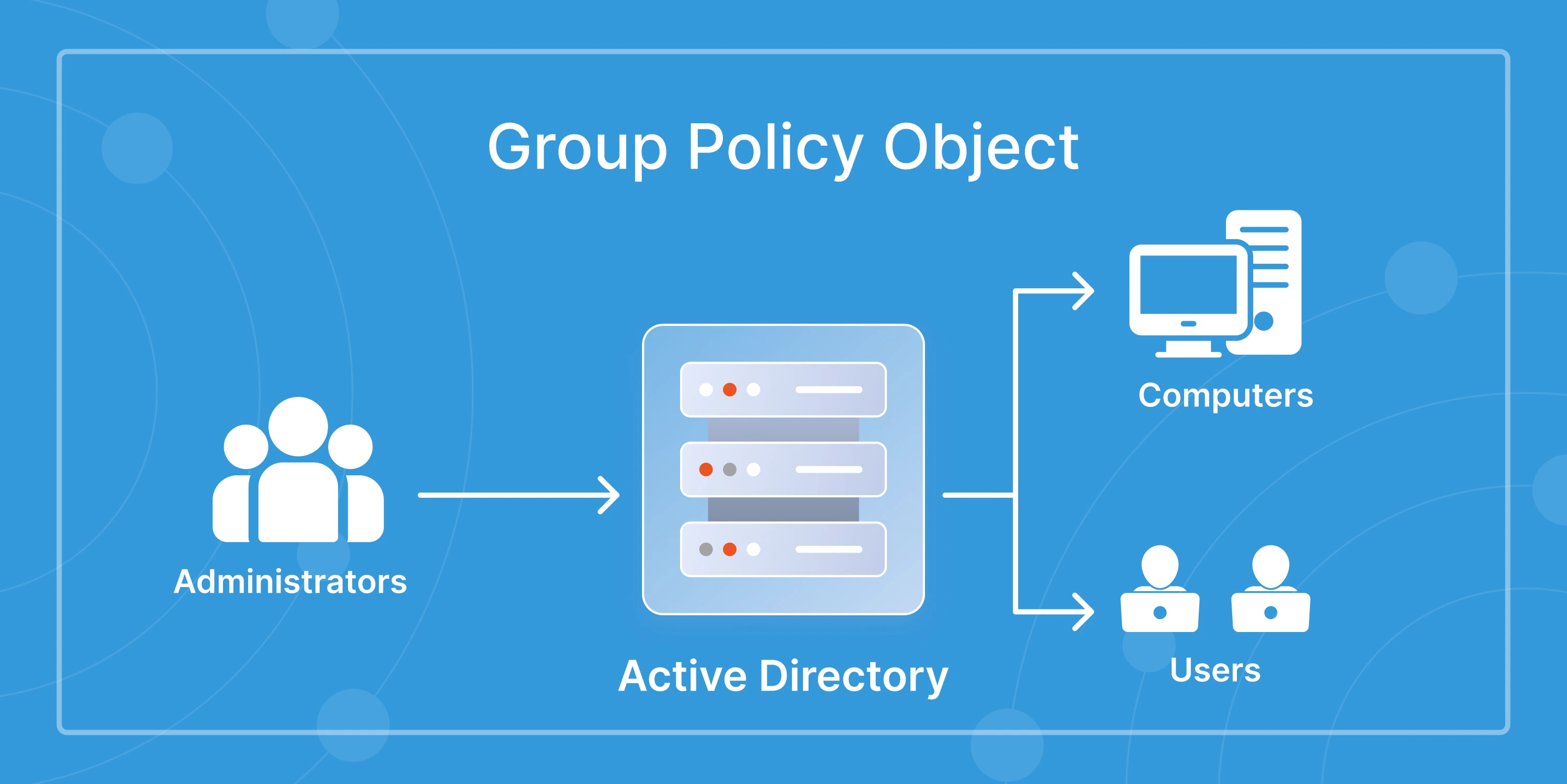
At its core, Active Directory Management is about keeping your digital workplace organized. It’s how IT teams create, update, and control everything that lives inside Microsoft’s Active Directory: users, groups, computers, and policies.
Think of it as the control center for your organization’s access and identity. Instead of managing users and permissions manually, AD Management lets you set rules, automate tasks, and monitor changes in one place.
With proper management, IT teams can quickly onboard new employees, enforce password and access policies, and make sure no inactive or risky accounts are left unattended. In short, it’s the foundation that keeps your network secure and your operations efficient.
Why Does Active Directory Management Matter for IT Teams?
Active Directory isn’t just a user directory; it’s the heart of how your organization manages access, devices, and security. For IT teams, managing it effectively can mean the difference between control and chaos.
Poorly managed directories lead to problems like duplicate accounts, weak passwords, and inconsistent permissions. Over time, these small issues grow into major risks that affect productivity and compliance. That’s why structured Active Directory Management is essential. It helps IT teams:
- Save time on routine tasks by automating password resets, onboarding, and group assignments.
- Enhance security by implementing consistent password policies and controlling permissions.
- Ensure compliance with proper access documentation and audit trails.
- Reduce human error by standardizing how users and groups are managed.
- Improve visibility across all accounts, devices, and policies within the network.
When management becomes proactive instead of reactive, IT teams can focus on what really matters: scaling systems, improving uptime, and strengthening the organization’s security posture.
Common Challenges in Active Directory Management
Active Directory is powerful, but it isn’t easy to manage, especially when user activity grows across departments, devices, and hybrid environments. IT teams often face a long list of challenges that can drain time and increase security risks. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Too many privileged accounts: Admin access often spreads wider than it should, increasing the chance of accidental or unauthorized changes.
- Manual user provisioning: Creating and updating accounts one by one leads to delays and inconsistent permissions.
- Password fatigue: Constant reset requests slow down helpdesk teams and frustrate users.
- Lack of visibility: Without centralized monitoring, tracking who changed what and when becomes difficult.
- Compliance pressure: Meeting audit requirements is hard when logs and reports aren’t standardized or easily accessible.
- Hybrid complexity: Managing users across on-prem and cloud directories adds another layer of maintenance and syncing challenges.
Each of these issues adds friction to IT operations. Over time, they lead to slower support, higher security risks, and more administrative overhead, all problems that effective Active Directory Management can solve.
How Automation Helps in Active Directory Management?
Manual directory management might work for a small team, but as your organization grows, the workload scales faster than the team can handle. Automation turns what used to be repetitive, error-prone tasks into smooth, rule-based workflows that save time and improve accuracy. Here’s how automation changes the game for IT teams:
- Faster onboarding and offboarding: Automatically create, disable, or update user accounts based on HR or project data, ensuring access is always in sync.
- Reduced human error: Replace manual data entry with predefined templates and policies that maintain consistency across departments.
- Smarter access management: Assign permissions dynamically based on roles or departments, reducing the risk of over-privileged accounts.
- Proactive password handling: Set automated reminders and policies that reduce password reset tickets.
- Real-time visibility: Automated reports and alerts help track every change across users, groups, and OUs.
When automation handles repetitive work, IT teams can focus on higher-value goals like optimizing infrastructure, improving user experience, and strengthening security.
Key Components of Active Directory Management
Active Directory Management brings multiple functions together to help IT teams maintain control, consistency, and compliance across their network. Here are the core components that define a well-managed AD environment:
- AD Object Management:
Create, modify, or delete Active Directory objects like users, groups, computers, and contacts in a centralized way. This helps maintain data accuracy and saves time during routine operations. - AD Access Management & Delegation:
Assign permissions with precision. IT admins can delegate specific tasks, such as password resets or group updates, to helpdesk staff without giving full administrative control. - AD Bulk Management:
Perform actions like user creation, modification, or password resets for hundreds of accounts at once, reducing repetitive manual work and keeping processes consistent. - AD Workflow & Automation:
Build automated workflows that handle onboarding, offboarding, password expirations, and access reviews. Automation minimizes human error and improves response time. - AD Reports:
Generate detailed reports on user activity, password status, and policy changes. These insights support audits, compliance checks, and better visibility across your AD environment. - GPO Management:
Manage and monitor Group Policy Objects to enforce security settings, configure devices, and maintain consistent system behavior across all users and computers.
Together, these components give IT teams the control and agility they need to manage large-scale environments without losing visibility or security.
Best Practices for Managing Active Directory
Active Directory works best when it’s managed with structure and discipline. A few simple practices can make a big difference in how secure, efficient, and reliable your environment stays. Here’s a quick checklist that every IT team should follow.
- Use role-based access (least privilege):
Give users only the permissions they need to perform their jobs. Limiting admin rights reduces the impact of accidental or malicious actions. - Automate routine tasks:
Automate password resets, user onboarding, and account updates. This not only saves time but also ensures consistency across the directory. - Schedule regular AD health checks:
Review unused accounts, outdated policies, and permission structures. Regular audits help you catch issues before they turn into risks. - Monitor account and group changes:
Track who made what change and when. Real-time alerts and reports strengthen accountability and improve compliance. - Enforce password and MFA policies:
Combine strong password rules with multi-factor authentication to protect user accounts from unauthorized access.
Following these best practices helps IT teams keep Active Directory secure, up to date, and ready to support organizational growth without unnecessary complexity.
How Active Directory Management Supports Compliance and Security
Strong security and compliance start with knowing who has access to what, and ensuring that access stays under control. Active Directory Management plays a central role in maintaining that visibility and enforcing policies that meet regulatory standards. Here’s how it supports both security and compliance goals:
- Audit-Ready Records
Every change in AD, from password updates to group modifications, can be tracked and reported for internal or external audits. - Controlled Access:
By assigning permissions through defined roles and policies, IT teams prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems or data. - Policy Enforcement:
Centralized password rules, account lockouts, and MFA ensure consistent security standards across all users. - Automated Compliance Checks:
Scheduled reports and alerts help detect risky accounts or policy violations early. - Regulatory Alignment:
Proper AD management supports frameworks like ISO 27001, GDPR, and SOX by providing accountability and secure identity handling.
When AD management becomes part of your organization’s security workflow, compliance isn’t an afterthought; it’s built into everyday operations.
Future of Active Directory Management – Smarter, Automated, Secure
The future of Active Directory Management is moving beyond manual updates and static policies. As IT environments grow more dynamic, the focus is shifting toward automation, intelligence, and continuous monitoring. Here’s what’s shaping the next phase of AD management:
- AI-Driven Insights
Machine learning will help IT teams predict potential account risks, detect unusual login patterns, and recommend proactive actions. - Context-Aware Automation:
Automated workflows will adapt based on user behavior, device type, or location, keeping access both secure and flexible. - Zero Trust Adoption:
AD will become a key enabler for Zero Trust architectures, verifying every user and device before granting access. - Unified Hybrid Identity:
On-prem and cloud directories will continue merging into one management layer, allowing centralized control across environments.
The direction is clear: smarter automation and security intelligence will define how organizations manage access and identity. For IT teams, this means less manual effort and more time spent on building secure, scalable systems.
miniOrange AD Tools – Simplify and Secure Your Active Directory
Managing Active Directory should empower IT teams, not overwhelm them. miniOrange AD Tools turn complex directory tasks into simple, automated workflows, helping you manage users, enforce policies, and maintain security at scale. With miniOrange, IT teams can:
- Automate What Matters
Handle onboarding, password resets, and account updates automatically, freeing admins from manual work. - Control Access With Confidence:
Delegate responsibilities safely, track every change, and maintain clear accountability. - Stay Compliant Effortlessly:
Generate detailed reports for audits, monitor policy violations, and maintain consistent password standards. - Empower the helpdesk:
Give limited access to frontline staff to manage common requests without risking system-wide privileges.
miniOrange AD Tools bring structure, visibility, and control back to Active Directory, allowing IT teams to spend less time troubleshooting and more time strengthening their organization’s security posture.
FAQs
What is Active Directory Management, and why is it important?
Active Directory Management is the process of controlling users, groups, and access within Microsoft’s directory service. It’s important because it helps IT teams maintain security, prevent unauthorized access, and manage user lifecycles efficiently.
How does Active Directory Management help IT teams?
It reduces manual work by automating repetitive tasks like password resets and user provisioning, while improving visibility, compliance, and overall security across the network.
What are the best practices for managing Active Directory?
Use least-privilege access, automate routine tasks, review permissions regularly, monitor changes, and enforce strong password and MFA policies.
How does automation simplify Active Directory Management?
Automation replaces repetitive manual steps with predefined workflows, ensuring consistent execution and reducing the chance of human error.


Leave a Comment