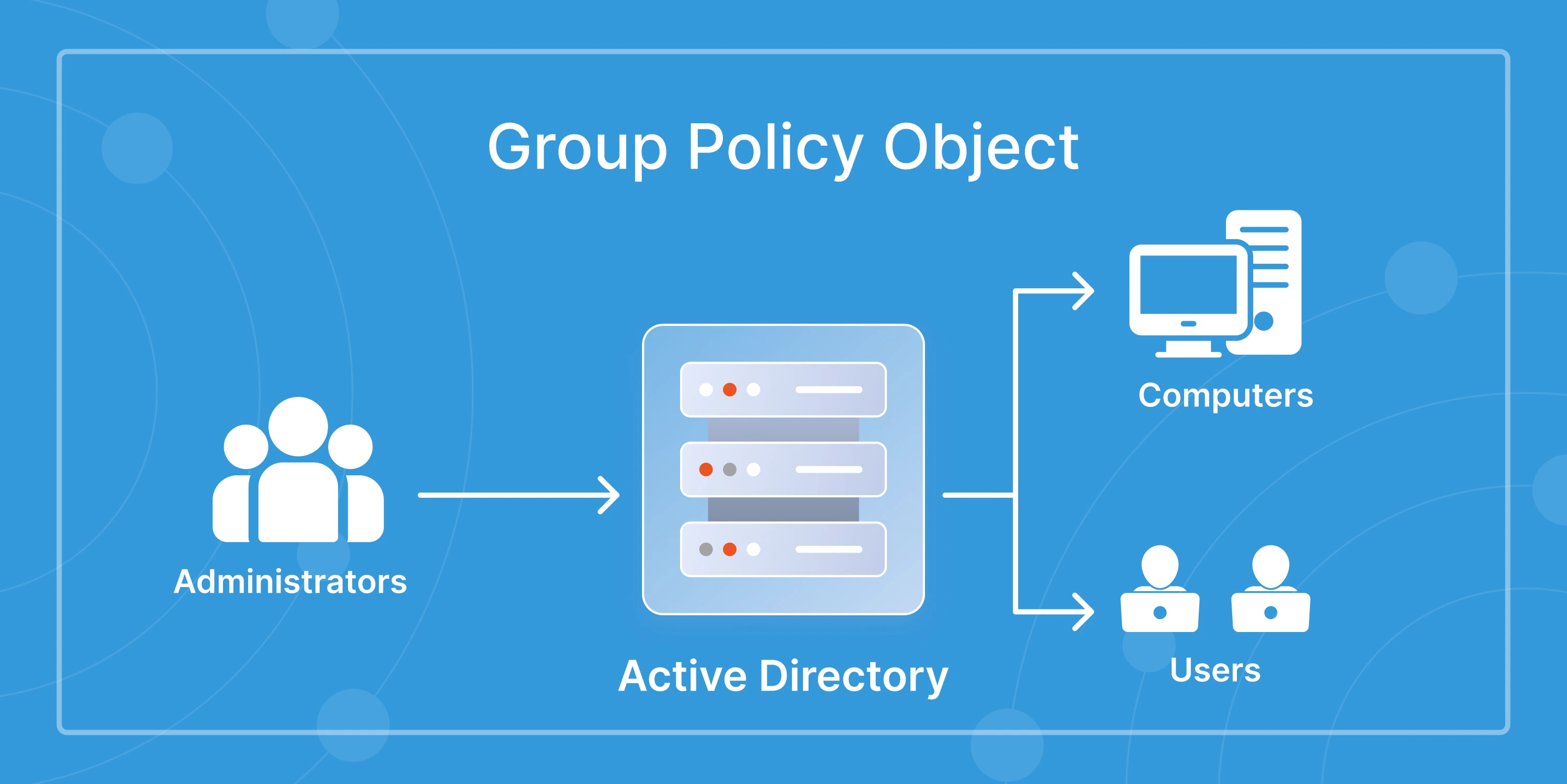
Active Directory (AD) remains the backbone of identity and access management in most enterprises. However, this foundational role also makes it a high-value target for cyber attackers. According to Mandiant's M-Trends 2023 report, 90% of ransomware attacks involve AD at some stage of the attack chain.
With attackers using sophisticated tools like Cobalt Strike, Mimikatz, and BloodHound to exploit AD misconfigurations and escalate privileges, securing your AD environment is more crucial than ever. Following modern best practices can drastically reduce risk, improve detection, and ensure more secure access control across your organization.
This blog outlines the top AD security best practices for 2025 and provides a comprehensive checklist to help IT teams protect their Active Directory infrastructure.
Why Active Directory Security Matters in 2025
Despite being more than 20 years old, Active Directory is still the most widely used identity system in enterprise environments. Its ubiquity also makes it a prime target. When attackers compromise AD, they often gain access to your entire digital ecosystem.
In 2025, cyber threats have become more sophisticated and automated. Tools like Cobalt Strike, Mimikatz, and BloodHound make it easier for attackers to discover AD misconfigurations, elevate privileges, and move laterally across systems. Even nation-state actors and ransomware groups are now adopting these tactics in bulk attacks.
Real-world incidents like the SolarWinds breach and Colonial Pipeline attack demonstrated how adversaries exploit unsecured AD environments to escalate access and maintain persistence. A single overlooked misconfiguration, such as an overprivileged service account or an inactive user, can become an entry point for full domain compromise.
That’s why following AD security best practices is no longer just an IT hygiene task, it’s a business-critical responsibility. Proactive security measures in an AD environment can mean the difference between stopping an attack at the doorstep or having your entire infrastructure held ransom.
Common Active Directory Security Mistakes to Avoid
Even organizations that invest heavily in cybersecurity often overlook simple missteps that leave their Active Directory environment exposed. These common mistakes can significantly weaken your overall security posture and are frequently exploited in real-world attacks.
1. Overusing Domain Admin Privileges
One of the most dangerous practices is assigning Domain Admin rights too broadly. Many administrators operate with elevated privileges even for routine tasks, increasing the attack surface. Follow the Principle of Least Privilege to avoid unnecessary exposure.
2. Neglecting Inactive Accounts
Inactive user and service accounts that go unnoticed are a ticking time bomb. Attackers often exploit these accounts because they’re unmonitored and may retain unnecessary access rights. Regular audits and automated cleanup policies are essential.
3. Weak or Reused Service Account Passwords
Hardcoded or poorly managed passwords in service accounts are a favorite attack vector. These accounts often have elevated access and rarely get updated, making them a prime target for brute force or credential stuffing attacks.
4. Lack of Monitoring and Alerting
Without proper logging, it's impossible to detect privilege escalation, group changes, or unauthorized logins. Many organizations fail to configure audit policies or centralize their event logs with SIEM tools.
5. Not Reviewing Group Memberships
AD groups, especially ones like Domain Admins or Enterprise Admins, must be reviewed frequently. It’s common to find users added temporarily and never removed, violating access control policies.
Avoiding these mistakes is just as important as implementing new security features. These pitfalls often undo even the best security planning and are essential to address in any Active Directory security best practices checklist.
Best Practices for Securing Active Directory
To protect your organization from privilege escalation, lateral movement, and ransomware attacks, it's critical to follow a structured and regularly updated Active Directory security best practices checklist. Below are the most recommended practices for 2025:
1. Limit Privileged Access with the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Avoid assigning Domain Admin rights unnecessarily. Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and tiered administration to ensure users only get the access they need — and nothing more.
2. Separate Administrative Accounts
Ensure IT administrators use dedicated admin accounts for performing administrative tasks. Daily activities like checking email or browsing should be done through separate, non-privileged accounts.
3. Implement Secure Tiered Administration Model
Follow Microsoft's Tier Model to segment administrative control:
- Tier 0 – Domain Controllers, AD FS, and schema masters
- Tier 1 – Application and server administration
- Tier 2 – User workstation management
This limits the blast radius in case of a breach.
4. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for All Privileged Users
Requiring MFA significantly reduces the risk of credential-based attacks. Integrate MFA with administrative tools and remote access gateways.
5. Regularly Audit and Clean Up Inactive Accounts
Dormant accounts are a goldmine for attackers. Set up automated tools or scripts to flag inactive users and service accounts, and follow a routine cleanup schedule.
6. Monitor for Privilege Escalation and Lateral Movement
Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools and Active Directory audit logs to detect abnormal activity such as group membership changes or Kerberoasting attempts.
7. Keep Domain Controllers Up to Date
Ensure your Domain Controllers run supported OS versions and are regularly patched. Vulnerabilities in these systems can expose the entire AD infrastructure.
8. Enforce Strong Password Policies and Lockout Rules
Use complex passwords and enable account lockout policies to deter brute force attacks. Consider integrating with password protection tools like Azure AD Password Protection for real-time breach detection.
9. Protect Domain Controllers with Network Segmentation
Isolate Domain Controllers on separate VLANs and restrict access to only required administrative systems.
10. Maintain an Active Directory Security Baseline
Use tools like Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit or CIS Benchmarks to establish and regularly review your AD security configuration baseline.
Tools to Strengthen Active Directory Security
Active Directory is often the gateway to your organization’s most critical systems, which is exactly why attackers target it. In 2025, relying on outdated configurations and manual oversight simply isn’t enough. By following the Active Directory security best practices outlined in this blog, IT teams can significantly reduce their attack surface, detect threats faster, and maintain better control over user access.
But securing AD isn't a one-time effort. It requires continuous monitoring, policy enforcement, and the right tools to back your strategy. That’s where solutions like miniOrange AD Tools come in, offering real-time account management, automated alerts, and granular access controls designed to help you implement these best practices efficiently and at scale.
Strengthen your AD environment before it becomes a liability. Explore how miniOrange AD Tools can help you stay secure, compliant, and in control.



Leave a Comment