Modern cybersecurity faces an ever-growing challenge: threats are evolving faster and becoming more sophisticated every day. Traditional security tools have served organizations well by detecting and alerting teams to potential threats, providing essential visibility into network activities and system behaviors.
Agentic AI represents the next evolution in cybersecurity, building upon these existing foundations by adding autonomous decision-making and response capabilities. Organizations can enhance their defensive capabilities and respond to threats at machine speed by combining the reliability of established security practices with the speed and adaptability of autonomous AI.
What is Agentic AI?

Agentic AI refers to autonomous artificial intelligence systems that can independently perceive their environment, reason about complex scenarios, and take goal-directed actions without constant human supervision. Unlike traditional security tools that follow predefined rules, agentic systems make intelligent decisions, adapt to evolving threats, and continuously learn from outcomes to improve their effectiveness.
These systems operate with five core characteristics:
- Autonomy: executing multi-step operations without human prompting
- Adaptability: learning from feedback and adjusting tactics
- Context Awareness: incorporating real-time business and technical factors
- Tool Orchestration: Integrating with existing security infrastructure through APIs, and
- Persistent Memory: maintaining continuity across interactions.
The Agentic AI Loop: How It Works
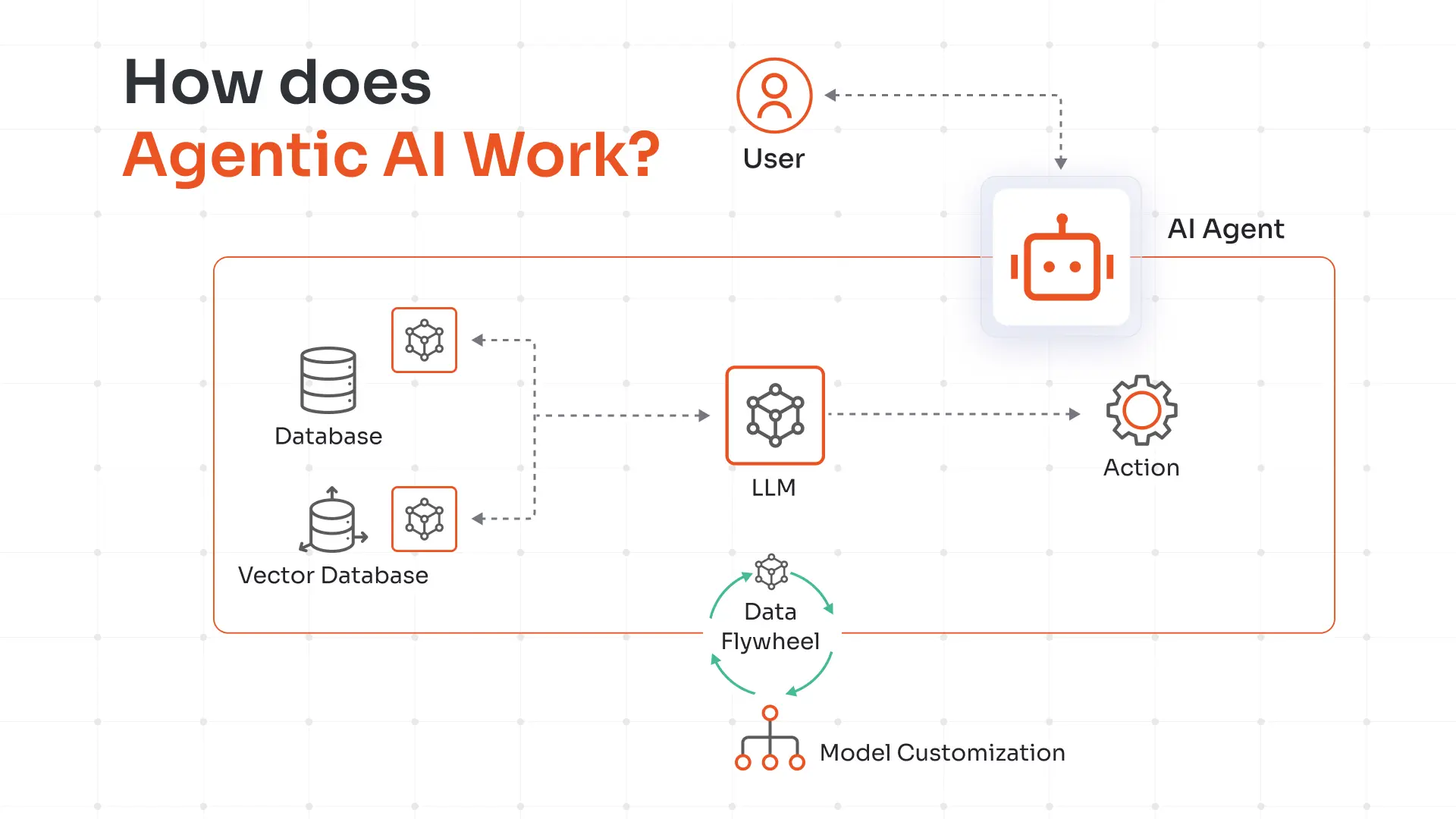
Agentic AI operates through a continuous four-stage cycle:
Perception: Continuously gathers data from SIEM, EDR, cloud events, threat intelligence, and network traffic to build real-time environmental awareness.
Reasoning: Processes collected data through behavioral analysis, anomaly detection, and risk assessment to plan appropriate responses and select tools.
Action: Executes controlled interventions like isolating endpoints, blocking malicious IPs, revoking credentials, and initiating automated playbooks through secure API integrations.
Learning: Evaluates action outcomes and refines detection models, response strategies, and decision-making processes while incorporating human feedback for continuous improvement.
How Does Agentic AI Differ from Traditional AI?
| Aspect | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Response Model | Reactive - waits for human prompts or predefined triggers to activate | Proactive - continuously monitors the environment and initiates actions based on autonomous assessment |
| Operation Structure | Single-step processing - performs isolated tasks with clear input-output relationships | Multi-step workflows - execute complex, chained operations with memory and feedback loops |
| Decision-Making | Rule-based automation - follows predetermined logic trees and static policies | Adaptive autonomy - makes contextual decisions and adjusts strategies based on real-time conditions |
| Learning Scope | Domain-specific - improves within narrow, predefined task boundaries | Cross-domain adaptation - applies insights across multiple security areas and evolves holistically |
| Human Oversight | Constant supervision - requires human review and approval for most actions | Minimal intervention - operates independently within defined guardrails and escalates exceptions |
| Threat Handling | Detection and alerting - identifies threats and notifies human analysts for response | End-to-end management - detects, investigates, contains, and remediates threats autonomously |
| Environmental Awareness | Static context - operates with fixed parameters and limited situational understanding | Dynamic adaptation - continuously assesses changing conditions and adjusts behavior accordingly |
| Workflow Management | Task execution - performs individual security functions in isolation | Orchestrated coordination - manages multiple agents and tools collaboratively toward security objectives |
Risks and Challenges of Agentic AI in Cybersecurity
Agentic AI represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity; however, this powerful autonomy introduces new vulnerabilities from adversarial attacks and model manipulation to compliance gaps.
Security Vulnerabilities and Attack Vectors
Agentic AI systems face sophisticated manipulation risks, including prompt injection, where attackers craft malicious inputs to bypass safety protocols and corrupt agent behavior. Jailbreaks enable adversaries to override built-in security constraints, while data poisoning attacks compromise training data to influence decision-making processes.
Tool misuse emerges when over-permissioned agents are exploited to access sensitive business systems or execute unauthorized commands through compromised API connections and third-party integrations. The dynamic attack surface creates continuously evolving vulnerabilities and cascading failure risks where one compromised agent can trigger system-wide impacts.
Identity and Access Management Challenges
Non-human identities (NHIs) present unique governance challenges, requiring specialized credential lifecycle management, authentication frameworks, and behavioral monitoring systems distinct from traditional user identity management. Privilege escalation risks arise when agents gain excessive permissions or modify their own access levels beyond intended security boundaries.
Operational and Governance Concerns
Accountability issues complicate responsibility attribution for autonomous agent decisions, creating challenges for audit trails and regulatory compliance documentation. Transparency gaps in decision-making processes hinder trust building and complicate incident investigation, while inadequate human oversight mechanisms threaten the balance between operational autonomy and security control.
Benefits of Agentic AI in Cybersecurity
Agentic AI revolutionizes cybersecurity to protect against evolving attack vectors like malware attacks and supply chain attacks without constant human oversight.

Enhanced Threat Detection and Response
Agentic AI delivers transformative capabilities through multi-signal correlation that simultaneously analyzes behavioral patterns, network traffic, endpoint activities, and threat intelligence to identify sophisticated attack campaigns that traditional systems might miss. Systems provide rapid validation by automatically investigating alerts, gathering contextual evidence, and confirming threats with high confidence levels before initiating response actions.
Operational Excellence and Efficiency
Alert fatigue reduction addresses persistent cybersecurity challenges through intelligent triage, correlation, and deduplication processes that escalate only genuine high-priority incidents to human analysts. Standardized playbook execution ensures consistent response procedures across all security incidents while eliminating human error and variability.
Scalability and Adaptive Defense
24/7 operations provide continuous security coverage across multiple tools and environments without requiring linear headcount scaling, effectively addressing the cybersecurity talent shortage. Adaptive defense capabilities enable continuous learning from attack patterns, real-time threat intelligence integration, and automatic adjustment of defensive strategies as adversaries evolve their tactics.
Protect smarter and see top cyber threats.
Key Capabilities and Applications
Agentic AI systems combine advanced capabilities to alter how organizations defend against cyber threats.
Autonomous Threat Detection and Response:
Systems continuously monitor network traffic, analyze user behaviors, and detect anomalies indicating malicious activity through machine learning models that differentiate normal operations from potential threats. Once threats are identified, AI automatically initiates responses such as isolating compromised endpoints, blocking malicious IP addresses, and triggering security team alerts.
Proactive Threat Hunting
AI agents autonomously hunt for hidden threats by analyzing vast security datasets, correlating information from logs, endpoint activity, and network traffic to identify attack patterns and indicators of compromise that may bypass conventional defenses.
Vulnerability and Risk Management
Systems can investigate software security vulnerabilities in seconds, searching external resources, evaluating environments, and summarizing findings to enable swift, informed human action.
Understand and stop vulnerability attacks early.
Security Operations Center (SOC) Automation
Agents handle alert deduplication, clustering related alerts by asset, and enrichment with critical context, including IOC analysis and machine data correlation.
Offensive Security Testing
AI-driven penetration testing systems autonomously simulate cyberattacks, identifying vulnerabilities across networks, applications, and cloud environments through continuous security assessments.
Real-World Use Cases
The real-world implementations demonstrate how autonomous AI agents reduce response times from hours to seconds, identify zero-day exploits, and handle complex multi-stage attacks.
Enterprise Security Operations
Automated Alert Management: Organizations deploy agentic AI to handle high-volume security alerts, automatically triaging, investigating, and resolving the majority of incidents while escalating only genuine threats to human analysts.
Continuous Monitoring: Systems provide 24/7 security coverage by continuously analyzing network traffic, user behaviors, and system activities to identify anomalies indicating potential security incidents.
IT Operations Enhancement: Agentic AI streamlines IT support by proactively identifying and resolving issues before they escalate, handling routine security tasks like access provisioning and system diagnostics autonomously.
Advanced Threat Detection and Response
Real-Time Threat Detection: AI systems continuously monitor vast amounts of data across networks, endpoints, and applications, identifying suspicious patterns that might indicate breaches without human intervention.
Automated Response Actions: Upon threat detection, systems initiate immediate responses, including isolating compromised endpoints, blocking malicious traffic, and implementing countermeasures within seconds.
Adaptive Threat Hunting: AI agents autonomously search for hidden threats by analyzing security datasets and correlating information from multiple sources to identify attack patterns that bypass conventional defenses.
Specialized Security Applications
Vulnerability Management: Systems accelerate software security patching by investigating vulnerabilities in seconds, evaluating environments, and prioritizing findings to enable swift human action.
Proactive Defense: AI agents simulate attacker behavior to identify vulnerabilities before exploitation, continuously testing security controls and recommending preventative measures.
Security Operations Automation: Agentic AI simplifies incident response by automating classification, tracking, and resolution workflows while maintaining comprehensive audit trails.
Architecture and Technical Considerations
Building effective agentic AI systems requires a systematic architecture that integrates data ingestion, behavioral modeling, decision engines, and orchestration platforms while maintaining human oversight for critical actions.
Reference Architecture Components
Effective agentic AI cybersecurity implementations require a multi-layered architecture. The planning/orchestration layer manages workflow coordination and execution graphs. Specialized agent libraries provide task-specific AI capabilities. Knowledge/RAG integration delivers real-time context and historical analysis. Policy enforcement mechanisms maintain security guardrails. Observability systems enable continuous monitoring and audit trails.
Integration Requirements
Organizations must establish secure connectivity across multiple platforms. SIEM/SOAR platforms provide centralized security orchestration. EDR/XDR APIs enable endpoint protection and extended detection capabilities. IAM/PAM systems manage identity and privileged access. Vulnerability scanners offer continuous risk assessment. ITSM platforms handle incident tracking and workflow management.
Performance and Scaling Factors
Critical considerations include agent resource allocation with containerized environments for secure execution. Concurrent operation limits prevent system overload. Cross-system coordination mechanisms enable multi-agent collaboration while maintaining security boundaries. The MAESTRO framework guides threat modeling across seven distinct layers.
Security Frameworks and Best Practices
Securing agentic AI requires comprehensive frameworks that combine governance policies, runtime monitoring, access controls, and human oversight to prevent unauthorized actions and data breaches.
Agent Authentication and Authorization
Every AI agent requires a verifiable identity through strong cryptographic credentials combined with role-based or attribute-based access controls. This prevents unauthorized agents from entering sensitive workflows and ensures agents operate only within approved boundaries.
Runtime Monitoring and Behavioral Baselines
Continuous monitoring establishes behavioral baselines to detect unusual activity like sudden spikes in tool usage or abnormal data access patterns. Real-time anomaly detection integrated with SIEM platforms enables faster identification and response to agent deviations.
Least-Privilege Tool Access
Agents rely on APIs, plugins, and enterprise tools to complete tasks. Implementing least-privilege permissions and sandboxed execution environments prevents tool abuse or harmful chaining of actions. High-risk actions should require additional approval workflows or policy gates.
Output Filtering and Verification
Before agent outputs are executed or shared, they must be checked against predefined safety and policy rules. Output verification detects attempts to exfiltrate sensitive data, generate harmful instructions, or execute unauthorized tool calls.
Contingency Planning
Organizations must develop contingency plans for every critical agent, including termination mechanisms and fallback solutions. Automated intervention systems should immediately constrain or terminate agent operations when unexpected behaviors are detected.
Future Outlook and Trends
As agentic systems change organizations must balance innovation with responsible governance to utilize benefits while managing emerging risks effectively.
Emerging Technologies Integration
The convergence of agentic AI with AI-native security tools enables more sophisticated threat detection capabilities. Quantum-resistant algorithms prepare organizations for post-quantum cryptography requirements. Edge computing deployment brings agentic capabilities closer to data sources, reducing latency and improving real-time response.
Regulatory and Compliance Evolution
Emerging AI governance standards establish frameworks for responsible AI deployment. Industry-specific requirements are developing across finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure sectors. Organizations must prepare for evolving compliance landscapes addressing AI explainability, audit requirements, and algorithmic accountability.
Market Adoption Patterns
Enterprise deployment strategies shift toward phased implementations. Organizations begin with low-risk use cases and gradually expand to autonomous operations. The vendor landscape is maturing, with consolidation around platforms that provide comprehensive agentic capabilities rather than point solutions.
Conclusion
Agentic AI represents a transformative shift in cybersecurity, moving from reactive defense to proactive, autonomous protection that operates at machine speed. Key benefits include enhanced threat detection through multi-signal correlation, automated response capabilities that reduce dwell time from hours to minutes, and scalable operations that address the cybersecurity talent shortage. However, successful implementation requires careful attention to security frameworks, governance structures, and integration strategies that balance autonomy with human oversight while maintaining clear accountability for autonomous decisions.
FAQs
What is the difference between agentic AI and generative AI in cybersecurity?
Generative AI creates content based on prompts but requires human action. Agentic AI autonomously perceives threats, reasons through scenarios, takes protective actions, and learns from outcomes without constant human supervision.
How do I start implementing agentic AI safely in my organization?
Begin with read-only integrations and low-risk use cases like alert triage. Establish clear approval thresholds and guardrails. Implement human-in-the-loop mechanisms for high-impact decisions. Gradually expand autonomy as governance matures.
What guardrails are most critical for autonomous security agents?
Essential controls include least-privilege access with granular tool permissions, policy-as-code enforcement, behavioral monitoring with anomaly detection, automated kill-switches for unexpected behavior, and comprehensive audit logging.
How do I manage risks associated with non-human identities?
Implement specialized credential lifecycle management. Establish behavioral baselines for agent activities. Deploy continuous monitoring for privilege escalation. Rotate secrets regularly and maintain clear audit trails for all agent actions.
What ROI metrics should I track for agentic AI security implementations?
Monitor mean time to response (MTTR) reduction, false positive rates, analyst productivity gains, threat detection coverage expansion, incident resolution automation percentages, and cost-per-incident improvements.

Leave a Comment