Some of the most reliable products come from unseen bootstrapped innovators in a time when flashy fundraising rounds dominate headlines. These founders aren't interested in unicorn valuations or Venture Capital (VC) approval; instead, they aim to create long-lasting software businesses that prioritize user needs over investor returns.
Conventionally, investor-led funding has been the go-to route for ambitious entrepreneurs. However, recent trends and the sudden downturn for VC funding over the last year (including a 22% drop in Q1 2025) have started to shift the favor towards bootstrapping.
The two main business models that define the software industry today are investor-led and bootstrapped. While investor-backed software companies depend on outside investment, typically from venture capital firms, to scale quickly, bootstrapped software companies expand using their income and resources.
Although each model has a place, more and more companies are choosing bootstrapped solutions because of their stability, openness, and long-term support. Customer-focused software is becoming more and more popular as buyer priorities shift toward reliability over rapid growth.
How Bootstrapped Companies Prioritize Current User Needs vs. Investor-Led Companies That Focus on Future Market Trends
Bootstrapped software companies build their product development based on active customer feedback and day-to-day usage. They tend to focus on enhancing existing features and refining the product, rather than chasing short-lived market trends. This results in more stable updates and a consistent product experience.
Investor-led companies often build with scalability and market potential in mind. They prioritize features that appeal to enterprise clients or future growth areas. While this can lead to innovation, it sometimes causes a disconnect between product direction and the actual needs of existing users.
Why Product Experience Often Changes After Investor-Led Acquisitions
When investor-led businesses go through mergers or acquisitions, they may introduce new pricing, change support teams, or adjust product features, which can affect the customer experience. The customer support team may change entirely, causing users to lose touch with previous contacts. New teams may lack product familiarity, delay responses, or fail to understand long-term customers, leading to a frustrating experience.
Bootstrapped companies grow without external investors and operate with a long-term product focus. They often provide more personal, responsive customer support, with users receiving direct help from team members who are deeply involved in the product. This stability and attentiveness make bootstrapped businesses a more dependable choice, especially during times of market disruption.
How Bootstrap and Investor-Led Companies Approach Pricing and Customer Support and Users
Bootstrapped businesses sustain operations through customer-generated revenue rather than external capital. Their pricing remains fair, transparent, and structured to support a broad range of users, from individuals to mid-sized businesses. Renewal terms typically remain consistent, and the focus stays on delivering ongoing value rather than pushing unnecessary upgrades.
Investor-backed companies aim to scale quickly and capture market share. They often invest heavily in marketing and promotions to expand their user base and focus on developing new, futuristic products that appeal to emerging market trends. These businesses typically prioritize large enterprise customers, which can lead to higher prices and reduced attention to smaller clients. Customer support often becomes less accessible, as resources are redirected toward onboarding new clients or managing high-value accounts.
| Aspect | Investor-Led | Bootstrapped |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | External investors, such as venture capitalists (VCs), angel investors, or private equity firms | Self-funded by founders, revenue reinvestment |
| Control & Decision-Making | Investors often have a say in business decisions, sometimes influencing strategic direction | Founders retain full control over decisions and business strategy |
| Growth Speed | Typically faster growth due to access to significant capital for scaling operations and marketing | Slower growth, as scaling depends on revenue and careful reinvestment |
| Financial Risk | Lower personal financial risk for founders, but higher expectations for returns from investors | Founders take on higher personal financial risk, but when the company becomes profitable, the gains go directly to them without pressure from external investors. |
| Profitability Focus | Often prioritizes rapid scaling over early profitability | Profitability is a key focus since it funds growth |
Economic Challenges and How They Impact Bootstrapped vs. Investor-Led Software Companies
In global trade tensions, software export tariffs (up by 12–15%), and shifting economic policies are increasing business uncertainty. Bootstrapped companies handle these challenges by staying stable and prioritizing profitability. Their self-funded structure allows them to make decisions with more control and less exposure to external market fluctuations.
The economic environment is creating new obstacles for investor-led software companies. Global venture capital (VC) funding has dropped by 18% compared to 2024, continuing a downward trend since 2023. These pressures often lead to reduced innovation, shifting product focus, or slower updates. This uncertainty often impacts product quality and customer experience.
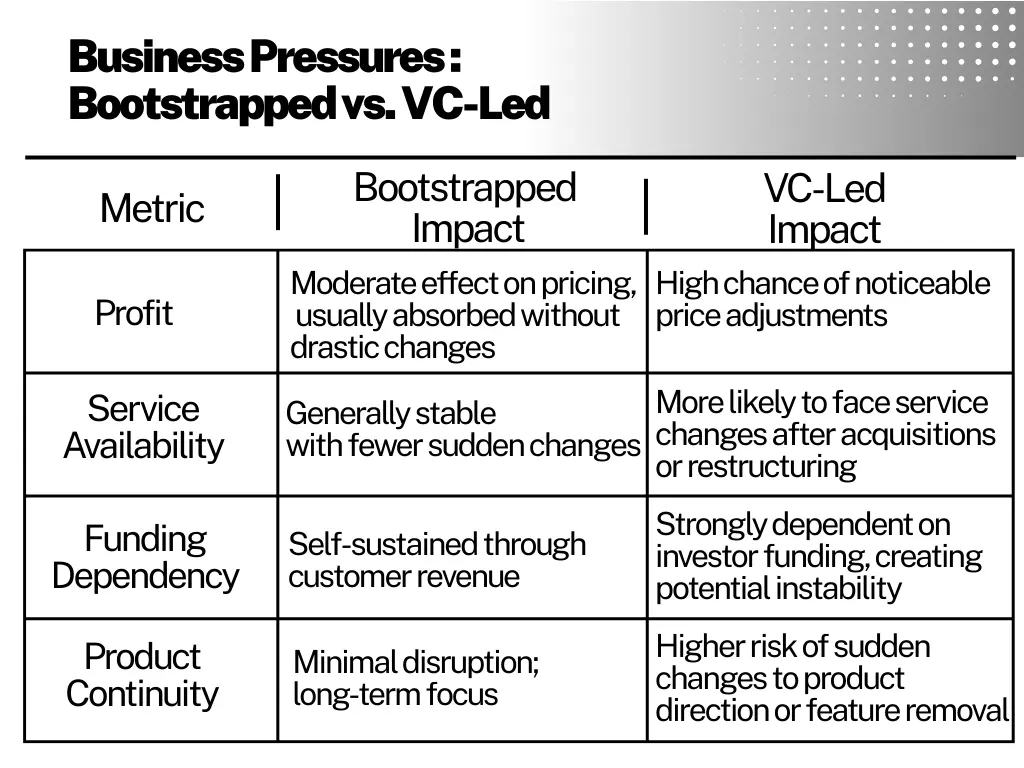
Pros and Cons of Bootstrapped and Investor-Led Companies from a Business Impact Perspective
Bootstrapped businesses led by their founders maintain full decision-making control and produce goods guided by a clear, well-defined vision. Because they’re not driven by investor demands, they prioritize consistent development, stable pricing, and customer retention. Their financial discipline results in lower churn rates, and their decision-making is guided by user needs, not investor timelines.
Investor-led companies rely on external funding to pursue fast business expansion. They often target large clients and focus on fast results. In many cases, founders have less control over decisions, as investors influence the company’s direction. This can lead to unexpected changes in pricing, features, or ownership, which may create confusion or instability for users.
Reasons to Bootstrap in Today’s Economy
- 1: No pressure to meet investor timelines; You set the vision, culture, and pace for your business
The bootstrapping approach allows founders to work towards their vision without having to manage external pressures. You get to decide how you want to scale and build a company culture that aligns with your values, without any influence from investors or pressures to deliver returns before you’re ready.
- 2: No dependency on raising capital and more flexibility to weather downturns, tariffs, etc.
Trade wars, recession risks, and other global uncertainties can cause disturbance across the business ecosystem, but bootstrapped businesses are slightly less vulnerable. Since this business approach doesn’t rely on funding from external investors, bootstrapped companies are generally focused on lean operations from the get-go. This means they are better positioned to adapt faster to any disruptions caused by economic slowdowns, making bootstrapping a path worth considering if your focus is on sustainable growth.
Conclusion
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to funding a startup. Both bootstrapping and investor-led funding have created billion-dollar companies. The key is understanding which approach aligns with your business goals and personal values.
If you prefer independence, can sustain initial growth through revenue, and are patient with scaling, bootstrapping may be your best bet. Bootstrapping your business in today’s economy offers more than just ownership – it gives you freedom.
Freedom to grow on your terms, build authentic customer relationships, and create long-term value without the constant pressure to scale fast. In an economic environment defined by uncertainty, this self-reliant model could be the most resilient path forward.



Leave a Comment