Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a bedrock of cybersecurity tactics used by organizations to safeguard themselves against phishing, credential theft, or brute-force attacks. It is a security measure to protect resources, accounts, and data from unauthorized access.
It is assumed that most of the MFA solutions need an internet connection. This leaves a critical gap for users and devices that operate offline or face network outages - think of freelancers, remote workers, traveling executives, or organizations powering air-gapped infrastructure for security or compliance reasons.
This is where offline MFA steps into the picture, enabling secure authentication on endpoints during outages or zero connectivity, making sure that credentials are protected and compliance is maintained regardless of connectivity.
From backup codes to locally stored verification data, offline MFA vendors like miniOrange offer indispensable security for modern businesses.
Let’s look at the foremost offline MFA providers who are likely to leave a mark in 2026.
Leading Offline MFA Vendors in the Spotlight
Currently, the global Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) market is growing at a CAGR of 14.2% from 2023 to 2030. Let’s look at the vendors who are emerging to be the key contributors to the market growth.
1. miniOrange Offline MFA
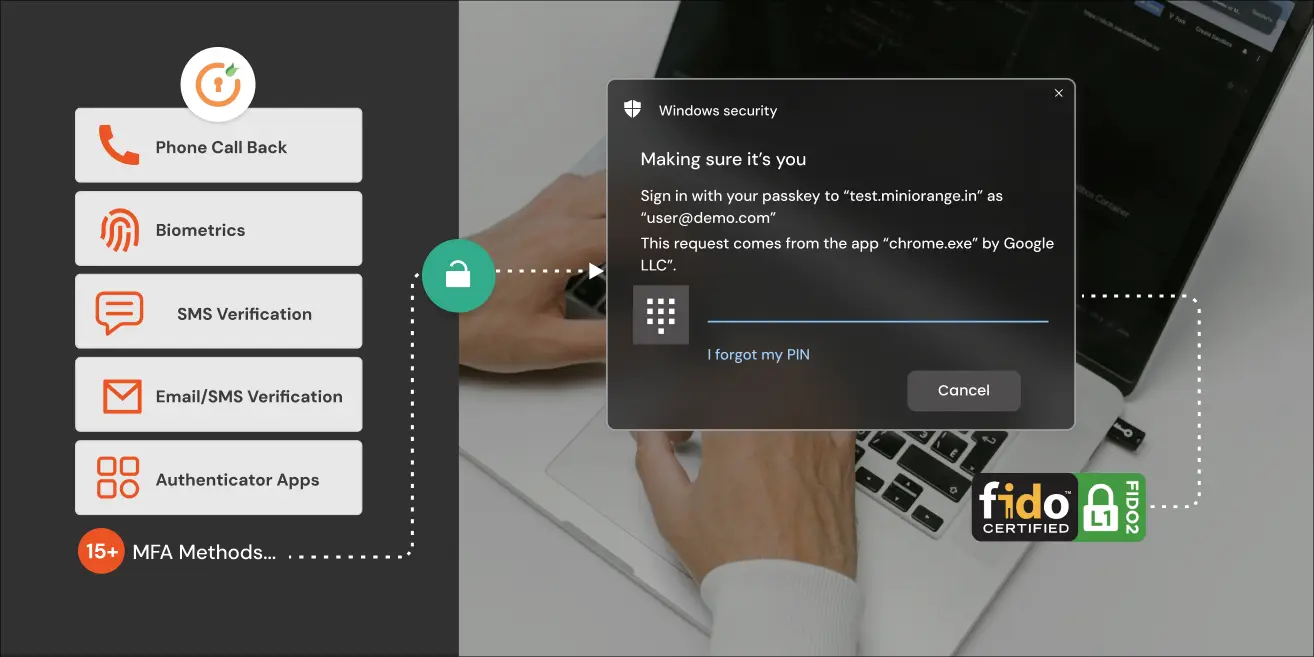
miniOrange, a cybersecurity company with a focus on Identity and Access Management (IAM), offers phishing-resistant Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) products for both online and offline users.
Its offline MFA solutions are a right fit for those working in either remote or hybrid settings, traveling employees, or in places with constant network outages.
Pros
- Compatible with Windows, macOS, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), and VPNs.
- Works with authenticator apps such as Google, Authy, Microsoft, and miniOrange.
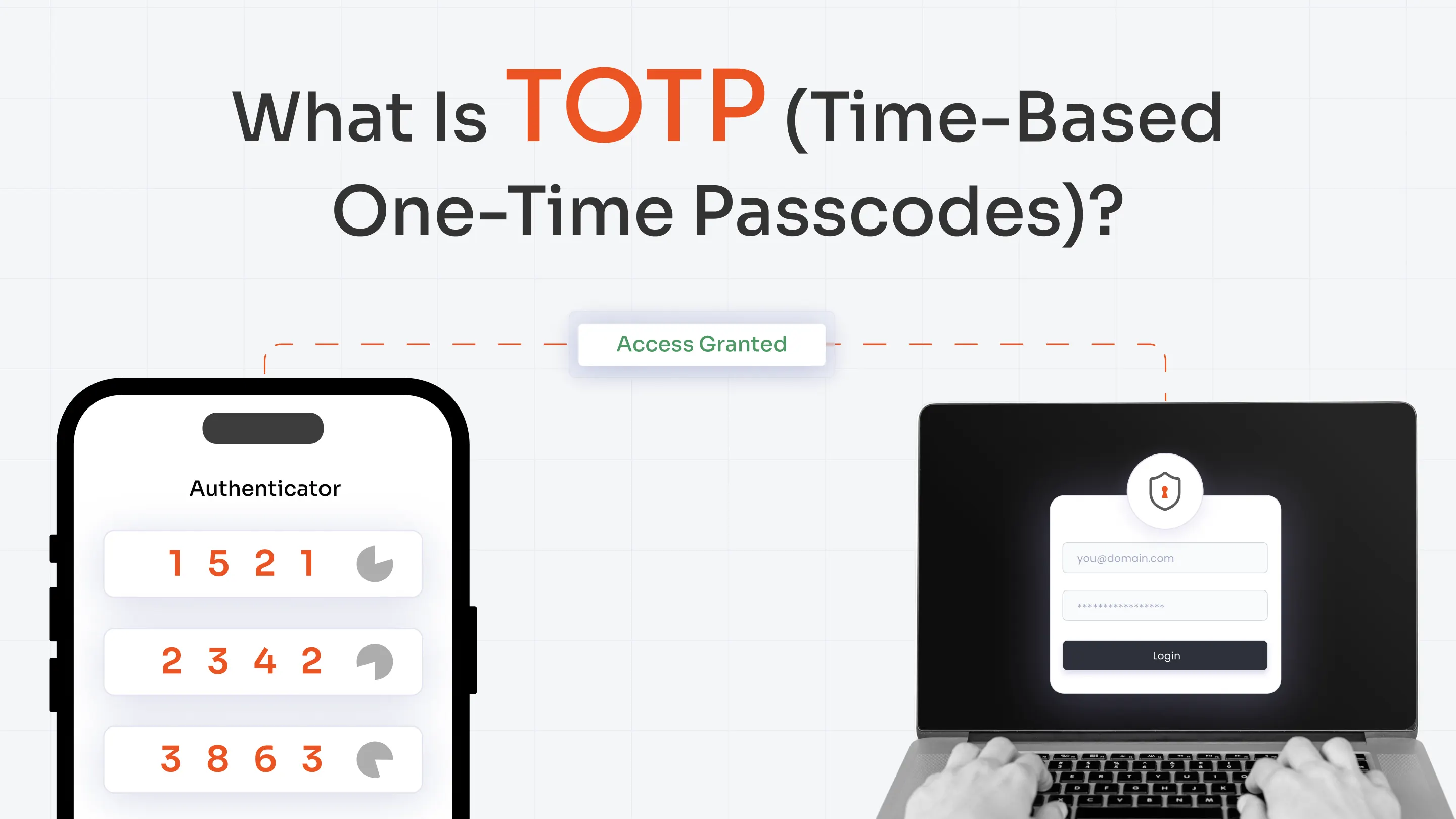
- miniOrange offline MFA features include hardware tokens, offline bypass, and Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP).
- Offers flexible pricing options - Plus package (includes MFA) priced at $2/user/month.
Cons
miniOrange offers TOTP methods, but in case users or organizations require extra authentication methods like biometrics, then the solution can be customized.
2. Duo Offline MFA
Duo offers MFA solutions for cloud, but it also supports offline authentication for Windows login.
Pros
- Ensures user-friendly authentication
- Provides MFA authentication methods such as biometrics, tokens, and Duo Push.
- Easy to manage and set up, without additional IT support.
Cons
- Slightly higher priced than miniOrange - Duo Essentials, priced at $3/user/month.
- Works on a cloud-first approach, with limited offline multi-factor authentication features.
3. ADSelfService Plus by ManageEngine
AdSelfService Plus by ManageEngine supports offline multi-factor authentication for Windows and macOS logins. A must-have product for enterprises aiming to harden endpoint security for hybrid and remote work environments.
Pros
Supports authenticators, such as Microsoft, Google, Zoho OneAuth’s TOTP authenticator, and custom TOTP authenticators for offline MFA.
AdSelfService Plus lets users enroll in offline MFA on varied devices.
Offline MFA for Windows and macOS generates comprehensive reports of users using offline MFA, including timestamps.
Cons
- Customizable offline MFA features can scale up the price for businesses.
- It may have a steep learning curve for both users and administrators.
4. PingID
PingID offline multi-factor authentication is a product of Ping Identity, and it offers a reliable and convenient method for users to authenticate themselves in the absence of an internet connection.
Pros
- Offline authentication can be configured for a variety of use cases, such as Windows login, PingFederate Single Sign-On (SSO), RADIUS Password Credential Validator (PCV), and more.
- Offers multiple verification options, such as FIDO2, TOTP, or YubiKey.
- Better security for remote working conditions.
Cons
- It may involve administrative complexities, which can be inconvenient.
- Limited policy enforcement, as risk-based policies or adaptive policies may not work for offline scenarios.
5. Okta
Okta is a leading provider of IAM products, and the company is moving towards AI agent security. Okta doesn’t have a dedicated offline MFA product; instead, it relies on its built-in offline capabilities and third-party solutions for offline authentication.
Pros
- Enforces MFA with the Okta Verify solution that generates OTP for offline sign-in on Mac, Windows, and Linux.
- User-friendly interface for convenient logins.
Cons
- Doesn’t have an offline MFA product, but relies on Okta Verify, hardware security keys, and Okta on-prem MFA agent for offline authentication of users. It also depends on third-party solutions like TecMFA by Tecnics, which works on Okta policies to authenticate users for offline devices.
6. IS Decisions
UserLock by IS Decisions is a solution built for offline multi-factor authentication scenarios, such as off-domain environments, air-gapped, and remote working.
Pros
- Protects remote access with VPN-less or off-domain MFA.
- Offline MFA for Windows desktops and laptops, without cloud connectivity.
- Consistent MFA experience for remote employees, the Government, and defense sectors.
Cons
- It may have limited customization options compared to other offline MFA vendors.
- For larger enterprises looking to pursue broader IAM strategies, the interface may feel basic for them.
7. LoginTC
LoginTC is a pioneer in offering MFA and 2-Factor Authentication (2FA) software (online and offline) for firewalls, remote desktops, VPNs, Active Directory, and more.
Pros
- Allows users to log into RDP and Windows with LoginTC offline MFA.
- Offers offline authentication methods, such as QR code, offline passcode grid, offline bypass code, offline hardware token, and offline FIDO2.
- LoginTC is an always-on MFA product, implying that MFA is never bypassed and logins are never rejected, irrespective of the user’s internet situation.
Cons
- Focuses only on MFA products, making it limited for organizations looking to pair offline authentication with Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions.
- May face complexities in policies, so admins need to check into it carefully.
How to Choose an Offline MFA Provider?
Choosing the correct offline MFA vendor isn’t just limited to ticking a compliance box; it is about aligning technology to the real-world business threats and operational realities.
Decision makers should look at the following:
- Effectiveness: Check if the chosen vendor’s products are effective against modern threats like AI-generated attacks.
- Diverse Authentication Methods: Check if the vendor offers biometric authentication, OTP, hardware tokens, or any other form of reliable offline authentication methods.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Check for support, license fees, hidden admin costs, and maintenance expenses.
- Compliance and Auditability: Verify audit logs, reporting, and regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and others.
- Customer Support: Localization, 24/7 support, and accessibility features are the key to enterprise adoption.
Summing Up
Offline MFA is no longer a niche feature; rather, it’s fundamental for organizations with field teams, remote employees, freelancers, or compliance-driven air-gapped networks.
Choosing the right MFA vendor means looking beyond flashy demos and weighing true security depth, user convenience, integration, policies, and business intent.
miniOrange offers crude operational realities and delivers the security outcomes that protect assets without frustrating users or adding unnecessary complexity. Hop on a call with us or try out the 30-day free trial to know the product better. You can also check our competitive and flexible pricing options.
FAQs
Why do organizations need offline MFA?
An organization must inculcate offline MFA because it safeguards credentials and assets even when networks are down or remote teams need to work in a disconnected environment.
Is offline MFA harder to deploy than online MFA?
Offline MFA needs more upfront planning, as users need to be present online to be enrolled beforehand in an authenticator app or any other offline MFA feature. But it is quite a smooth process and doesn’t hamper workflows.
Which MFA authentication methods work offline?
Popular methods include authenticator apps (Google, Microsoft, miniOrange authenticator, etc.), hardware tokens, push notifications with local approval, biometric authentication, offline bypass/backup codes, and more.
Can offline MFA help with compliance?
Several regulatory frameworks require strong authentication systems for all settings, especially regulated industries (defense and government). Having an MFA that works only on the internet creates a loophole for compliance, and an offline MFA solves it.

Leave a Comment