The SSO (Single Sign-On) protocols are used to offer one-click access to your applications, validate users’ identity, and authorize users to access apps, without compromising security.
They are here to make your life easier and to amplify your organization’s safety and security. Cause no one wants to become the next data breach headline, hampering an organization's reputation.
In this blog, we’ll talk about SSO and explore the key single sign-on protocols that will take your security levels to newer heights. We will also compare different SSO protocols and look at their benefits.
What is SSO and Why is it Important?
To put it down technically, Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication method that allows users to gain access to varied applications or resources with just one set of credentials.
In this method, there is no need to remember multiple passwords for different apps. This aspect ameliorates the user experience.
Additionally, Single Sign-On centralized authentication process improves the overall security of organizations, keeping cyber criminals away.
What are SSO Protocols?
Now that we’ve seen what SSO is, let’s hop into understanding its protocols.
Single sign-on protocols are a set of standards or rules that explain how the authentication and authorization processes are performed between different applications.
There are varied protocols for SSO available, such as:
- OIDC
- SAML
- OAuth
- LDAP
- RADIUS
What are the Different Types of SSO Protocols?
Let’s look at the widely used SSO authentication protocols, their benefits, workings, features, and user cases.
1. OIDC
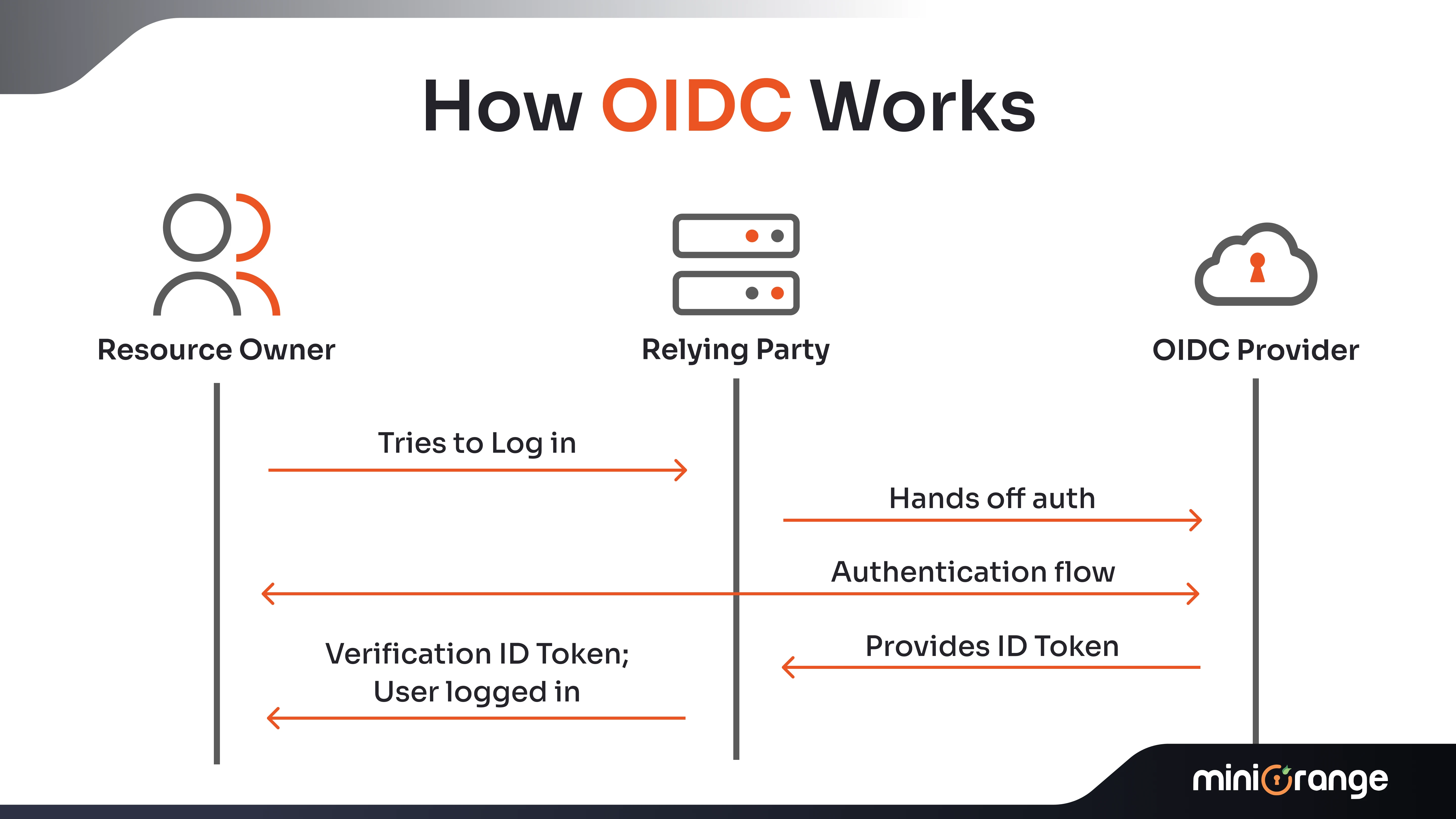
- What it is: OpenID Connect (OIDC) is a user authentication protocol that verifies the identities of users and allows them to access the apps securely.
- How it Works: The user logs in with an Identity Provider (IdP) such as Microsoft or Google Workspace. The IdP authenticates the user and then issues an ID token that contains the user’s data. This data is used for authentication purposes.
- Features: Get the UserInfo endpoint to acquire additional user details, and also JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for the ID tokens encompassing user details.
- Benefits: The OIDC protocol supports Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) methods and offers protected user ID verification. It makes web and mobile app authentication easier.
- Use Cases: Used extensively in mobile apps and cloud, especially for customer-facing single sign-on.
2. SAML
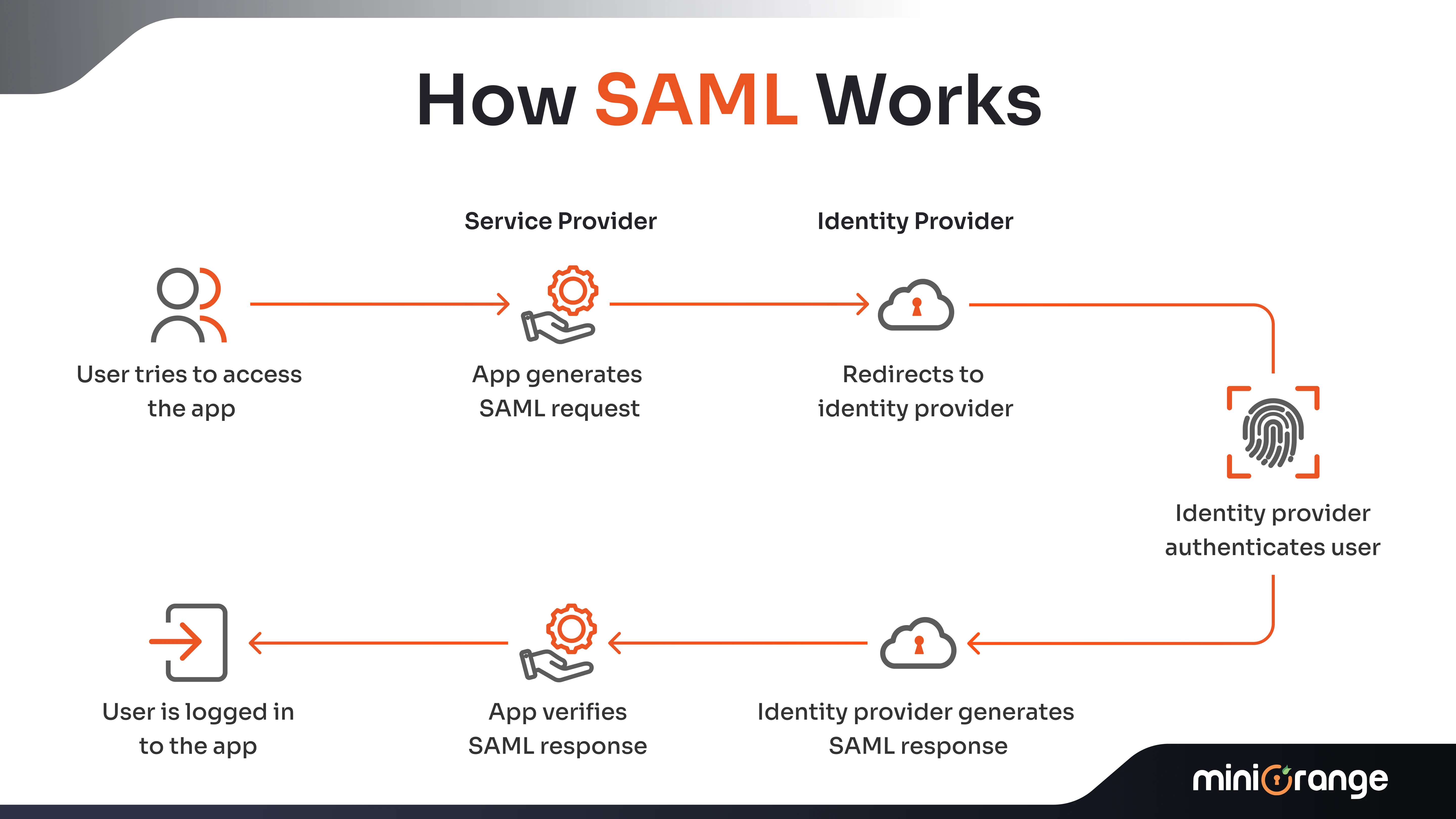
- What it is: Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-driven authentication protocol that enables the IdPs to authenticate users and grant them access to the Service Providers (SPs)/applications, without asking the users to authenticate themselves again by reentering the credentials.
- How it Works: A user tries to log into a SP such as ‘Notion’ or any other cloud app. The SP redirects the user to an IdP ( e.g., Google Workspace), where the user is authenticated, and a SAML assertion is issued. The user is permitted to access the SP without the need to re-login.
- Features: You can leverage XML-based messaging, federated identity management, and authorization and authentication abilities.
- Benefits: With SAML, there’s no need to use multiple passwords; it supports web-based authentication and makes use of encrypted authentication to boost security.
- Use Cases: Commonly used for enterprise systems to maintain secure authentication between the web apps.
3. OAuth 2.0
- What it is: Unlike SAML, which is an authentication protocol, OAuth 2.0 is an authorization standard that lets users access apps or data with limited permissions.
- How it Works: The user is granted permission to access some data on an app (e.g, a management app to access the dashboard). The app requests an access token from the authorization server. This server issues a token that is used by the app to grant access to the user.
- Features: The Main feature is user authorization and utilizes an access token to manage permissions. It is compatible with various authorization flows such as implicit, PKCE, authorization code, etc.
- Benefits: OAuth 2.0 offers secure access to the app without exposing the username and password. This protocol supports granular access control to the data/resources.
- Use Cases: A perfect fit for web and mobile applications, API access, and third-party integrations.
4. RADIUS
- What it is: Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a networking protocol that authenticates and authorizes users trying to access a remote network. It works on a client-server model.
- How it Works: The user signs in using a password, a PIN, a token, or any other authentication method. The credentials are sent to the server via the client for validation. The RADIUS server then either accepts or denies the login.
- Features: The Main functionality of RADIUS is Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) of users accessing a remote network, such as Wi-Fi or a VPN. It can keep track of all the user activities.
- Benefits: Centralized access system via AAA framework, enforces policies for secure app access. Detailed auditing and logging keep track of users’ sessions, preventing cyber activities.
- Use Cases: Used for security in the wireless networks, Network Access Control (NAC), VPN, and more.
5. LDAP
- What it is: Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is used for authentication and user management in a network. It lets organizations store and retrieve information from an Active Directory (AD).
- How it Works: When a user enters credentials, they are verified against the AD. After successful authentication, the user can access applications.
- Features: Supports integration with OpenLDAP, Active Directory, Azure AD, and more. It is designed for both Intranet and Extranet networks.
- Benefits: Offers centralized authentication management, amplifies security by storing user data in a secure directory, and integrates with enterprise identity management systems.
- Use Cases: Enable Single Sign-On (SSO), manage network resources such as files, media, etc., and manage user identities.
6. NTLM
- What it is: New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) is a set of protocols provided by Microsoft to verify users and safeguard the privacy of their activities. It relies on a challenge-response protocol to validate users without needing them to submit a password.
- How it Works: Authenticates users via a challenge-response method. The process involves three messages: a negotiation message from the client, a challenge message from the server, and the authentication message from the client.
- Features: Enables SSO, proxy support, offline authentication, and integration with identity management systems such as Active Directory for frictionless user management.
- Benefits: NTLM helps in backward compatibility with legacy systems.
- Use Cases: Used in Windows for maintaining compatibility between the old servers and clients. It secures SMB and remote desktop access and cross-domain authentication.
7. Kerberos
- What it is: Kerberos is developed to offer authentication for the clien/server applications by utilizing secret-key cryptography.
- How it Works: Users log in and get a Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT) from a centralized server that lets them access services without entering their credentials repeatedly.
- Features: Works with Windows and ascertains strong authentication with the tickets.
- Benefits: Protection against password replay cyber attacks, and allows SSO for Windows-based apps/systems.
- Use Cases: Performs well for internal enterprise networks that need top-notch security for on-premise apps.
SAML vs. OAuth vs. OIDC: Key Differences
Here are the key points that separate the three SSO protocols from one another.
| Property | OIDC | SAML | OAuth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authentication (built on OAuth 2.0) | Authentication & authorization (esp. enterprise SSO) | Authorization (delegates resource access) |
| Use Case | Web/mobile login with social IdPs (Google, Facebook) | Enterprise SSO across multiple internal apps | Granting 3rd-party app access (e.g., APIs) |
| Technology | JSON, REST, JWTs | XML, browser redirects, SAML Assertions | JSON, tokens, REST |
| Tokens | ID Token (JWT), Access Token | SAML Assertion (XML) | Access Token, Refresh Token (often JWT) |
| Scenarios | Consumer apps, social logins, API security | Enterprise, legacy, internal SaaS SSO | API authorization, secure data sharing |
| Actors | End user, Client (Relying Party), IdP (Auth Server) | End user, Service Provider, Identity Provider | Resource Owner, Client, Authorization Server |
This table highlights each protocol’s main function, data format, and role in authentication or authorization workflows. OIDC is best for modern, web/mobile app authentication; SAML for enterprise SSO; and OAuth for delegated authorization without exposing user credentials.
Explore more on SAML vs. OAuth
What are the Benefits of SSO Protocols?
Here are the benefits of using the different SSO protocols.
- Improved Access Control: A centralized authentication server helps to easily establish access control methods based on the user roles and attributes.
- Centralized Auditing and Authentication: A crucial aspect to keep track of the user’s sessions, so anomalies can be easily detected, and makes reporting simple. Centralized authentication helps to manage user data effortlessly.
- Little to No Human Error: Human errors are one of the biggest security concerns, especially when they have to juggle between multiple passwords and usernames. SSO makes it possible for them to have one-click access to applications.
Choosing the Right SSO Protocol for Your Organization
Choosing the right SSO protocol depends on several major organizational factors. These include:
- Future scalability conditions
- Security requirements
- User experience
- Compatibility with the systems, especially legacy applications.
The best way forward would be to list out your apps and databases, then define your compliance policies, such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc.
After this, check the number of users who will be accessing the apps, and then draw out an estimated cost for the SSO integration and maintenance expenses.
If you’re still feeling doubtful, then integrate a combination of SSO protocols for flexibility and better compatibility with your systems.
Want an SSO for your organization? Drop a mail at idpsupport@xecurify.com, and we will get back to you.

Leave a Comment