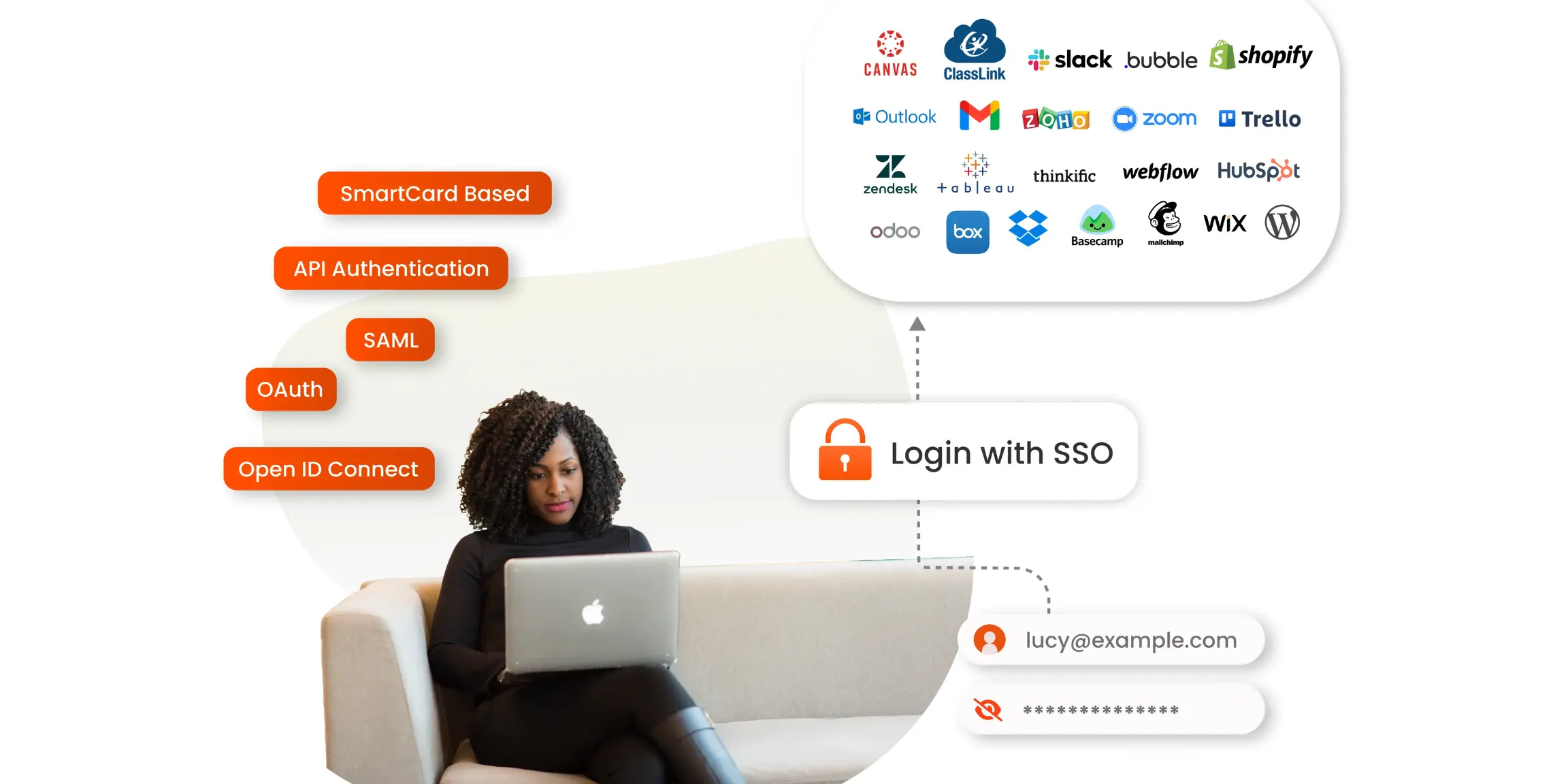
Single sign-on authentication (SSO authentication) has revolutionized the digital landscape by replacing the traditional login process. Gone are the days of asking users to remember passwords of multiple applications; SSO authentication simplifies the login experience. Additionally, it also enhances security and eliminates the frustration associated with password-based logins.
Whether you run websites, develop apps, or run a business, user authentication is essential for both logistical and security reasons. We at miniOrange, understand the limitations of passwords and have come up with an ultra-secure SSO authentication that can streamline user access, bolster security, and offer a better digital experience.
What is the Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication method?
SSO authentication revolutionizes the login experience by allowing users to access multiple applications, services, and accounts with a single login. A notable example is Salesforce's suite of applications, where logging into one grants access to all. This eliminates the hassle of repeatedly entering passwords when switching between applications like Salesforce Sales Cloud and Salesforce Service Cloud.
The advantages of SSO authentication are many such as, users getting a hassle-free login experience while accessing multiple applications, administrators enjoying improved internal security through centralized monitoring of user accounts, and dealing with fewer password management-related responsibilities. SSO authentication also fosters collaboration and efficiency, such as the ease of sharing documents with other user accounts in the same ecosystem.
How does SSO authentication work?
To initiate the access process for a desired application or website, the user follows these steps within the SSO framework:
- The user attempts to access a specific application or website provided by the Service Provider.
- The application or website (Service Provider) directs the SSO request to the Identity Provider (IDP) for authentication.
- The user provides their credentials associated with the Identity Provider to sign in.
- Upon successful authentication by the IDP, a Single Sign-On response is sent back to the Service Provider.
- With the received SSO response, the user is granted access to log in and securely utilize the desired resource or application.
- Within the Service Provider's ecosystem, the user gains the ability to seamlessly access other pre-configured applications or websites through the SSO functionality.
Is SSO authentication secure?
SSO systems are secure when implemented properly and used alongside other cybersecurity measures. They enhance internet security by reducing the reliance on weak passwords and centralizing systems for easier management and protection. However, centralization also presents some risks, as a breach in the central system could grant unauthorized access to all connected apps and tools.
And hence to overcome this issue and for enhance security, adding a two-factor login, such as miniOrange’s 2FA solution, provides an added layer of identity verification without significantly impacting the user experience. Two-factor login is becoming increasingly common, and users generally don't mind the added step for the benefits of prolonged secure access.
Advantages of Single Sign-On (SSO) Authentication
A. Enhanced user experience and convenience:
- Simplifies access to multiple applications and services through a single login.
- Eliminates the need to remember and manage multiple passwords.
- Streamlines user experience, thus saving time and effort.
B. Improved security and reduced password fatigue:
- Reduces reliance on weak or reused passwords.
- Enables stronger password policies
- Minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
C. Centralized user management and access control:
- Simplifies administration and maintenance of user accounts.
- Allows for easy provisioning and deprovisioning of user access.
- Enhances control over user access privileges and security policies.
Single Sign On Authentication methods
Let us have a look at some of the advanced and indispensable Single Sign-on authentication methods for your organization.
1. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language):
SAML is a widely adopted standard for implementing Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication, offering several advantages. With SAML-based SSO, users are relieved from manually entering credentials and the burden of remembering and changing passwords. Weak passwords become less of a concern as SAML leverages existing identity information. It seamlessly integrates with existing identity systems like Active Directory, enabling a smoother authentication process. SAML-based SSO provides a secure and convenient method for accessing applications, leveraging existing identity information for an improved user experience and enhanced security.
2. API Authentication:
In today's digital landscape, APIs have gained immense popularity due to their ability to manage and process vast amounts of data efficiently. APIs have introduced a new realm of possibilities in the realm of online security. Among the numerous API authentication methods available, some of the most widely used are HTTP Basic Auth, API keys, and OAuth.
3. OAuth:
OAuth, a widely used API authentication method, provides a comprehensive solution for both authentication and authorization processes. By defining the scope, OAuth enables the API to authenticate and gain access to the requested system or resource.
4. OpenID Connect:
Its an authentication method that builds upon the OAuth 2.0 framework. It serves as an identity layer and enables applications or websites to authenticate its users and verify their identity. This is done by leveraging an authorization server, which performs the authentication process. Overall, OpenID Connect enables applications to verify the identity of users by relying on an authorization server's authentication.
5. Smartcard Based:
Smartcard SSO authentication uses smartcards as secure authentication token. Each user has a smart card with a digital certificate and private key. Users insert the smartcard into a reader, authenticate with a PIN or biometric, and gain access to authorized resources without further authentication. It enables users to access multiple resources, simplifying the authentication process and enhancing user convenience. This method offers strong security, eliminates the need for multiple passwords, and simplifies the authentication process.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving technology landscape, prioritizing security is essential to differentiate yourself from competitors and deliver a seamless experience to end-users.
Compromising security exposes your company to various risks, including phishing attacks and data breaches. To mitigate such risks, it's crucial to select an authentication system that aligns with your budget and ensures a seamless user experience. As a trusted provider of Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions, miniOrange can help you identify the most dependable authentication solution for your organizational needs. We also provide solutions for WordPress to perform WordPress SAML SSO or OAuth SSO using SAML and OAuth protocols. If you have any inquiries regarding the SSO authentication process, feel free to reach out to us at idpsupport@xecurify.com.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between SSO and SSO authentication?
In Single Sign-On, users can access multiple systems or applications using a single set of login credentials. It eliminates the need for users to remember and manage separate usernames and passwords for each system. It enables users to authenticate once and give access to various systems seamlessly.
Whereas SSO authentication emphasizes the authentication aspect of SSO, where user's identity is verified using a single set of credentials across multiple systems. SSO authentication ensures that the user's login information is securely validated and grants them access to the authorized systems.
In summary, SSO is the overarching concept of using a single login across multiple systems, while SSO authentication focuses on the authentication mechanism that allows for this seamless access.
2. What does SSO authentication stand for?
SSO authentication stands for Single Sign-On authentication, which is a method that allows users to log in once with a single set of credentials to access multiple applications or services.
3. What is the difference between single sign-on and MFA?
The difference between single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) is that SSO is a method where users can access multiple applications with a single set of login credentials, while MFA is an additional security layer that requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a verification code.
Author