In today’s digitally interconnected world, the way we work is changing. Access to privileged resources is an underlying concern in today’s corporate landscape, and it is paramount for modern organizations to understand the nuances of managing and safeguarding privileged access. But, in this quest to protect privileged resources, organizations may find it challenging to figure out the right solution to implement.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) and Privileged Identity Management (PIM) often intertwine within this sphere, leading to confusion. This blog aims to clarify these terms, highlighting their differences, workings, and how they fit within the broader scope of Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Key takeaways from this blog:
- Fundamental definitions of PAM and PIM.
- Uncovering differences between PIM and PAM.
- An overview of how PIM and PAM operate.
- Distinction between IAM, PAM, and PIM.
- PAM or PIM: Guide to choosing the right one.
What is PIM and PAM?
PIM and PAM are interrelated terms used in the Privileged Management space, but both have fundamentally different roles to play in securing the Privileged resources of any organization. To clear up the confusion, it is important to learn the definitions of Privileged Access Management (PAM) and Privileged Identity Management (PIM).
What is Privileged Access Management (PAM)?
PAM or Privileged Access Management refers to implementing cybersecurity mechanisms or strategies that enable organizations to take control over the elevated privileged access and permissions for users, accounts, processes, and systems across the corporate IT environment. PAM is a powerful tool for managing and monitoring privileged access, and it empowers organizations to defend against data breaches to prevent misuse of sensitive information.
What is Privileged Identity Management (PIM)?
PIM or Privileged Identity Management is a strategy or mechanism that is built for managing and securing Privileged User Identities (the identities that have privileged access to critical company resources). It involves the identification, organization, and administration of the roles and access privileges of individual users within or across an organization. The fundamental function of PIM is to ensure adequate authentication, authorization, and audit of privileged identities.
What Is The Difference Between PIM and PAM?
While PIM and PAM are both critical components of a comprehensive privileged management strategy, their primary applications differ significantly. PAM is access-centric, emphasizing the security of privileged access to systems and data. It prevents data breaches with access control capabilities and enables admins to monitor & record sessions. When PAM is in place, any imposter cannot gain unauthorized access to privileged resources. On the other hand, PIM is identity-centric, focusing on the management of users who have privileged access. It ensures that users have privileged access only when it is required for their work. When PIM is in place, the risk of insider threats is minimized and users can only get access to privileged resources based on their roles within the particular organizational setup.
PIM vs. PAM: Side By Side Comparison Table
| Feature | PIM | PAM |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Identity Management | Access Management |
| Goal | Ensure the right individuals have privileged access | Protect privileged access from unauthorized use |
| Strategy | Manage identities to prevent misuse | Control and monitor access to prevent breaches |
| Tools | Identity directories, role management systems | Session monitoring, access control systems |
How do PIM and PAM work?
How do PAM solutions work?
PAM systems work by creating a secure, streamlined way to authorize and monitor all privileged user access to all relevant privileged systems. A PAM solution includes features like:
- Multi-Factor Authentication on privileged access - adding an extra layer of security that hackers or malicious actors cannot bypass,
- Session Monitoring & Recording - For detecting any suspicious activities and taking swift action to curb any attempts of unauthorized access, and
- Secure Vaults for password storage - For enhancing security by safeguarding privileged credentials from falling into the hands of cyberattackers.
Apart from the above features, there are many more features that are employed to ensure a robust Privileged Management strategy to protect privileged resources and sensitive information.
How do PIM solutions work?
PIM systems ensure that only authorized individuals or validated user identities can assume privileged identities within the enterprise network. PIM involves features like:
- Role-Based Access Control - to ensure that only adequate privileges are granted as per the requirement of the role that a particular user is assigned to.
- Identity Lifecycle Management- to elevate and delegate privileges based on the change in roles of the current user and to remove privileged access when the user no longer serves the organization, and
- Comprehensive Auditing - which acts as an instrumental tool to manage privileged identities effectively. To monitor suspicious behaviors and activities or detect any anomalies to render timely responses.
Apart from the above features, there are many more features that are employed to ensure robust Identity management of Privileged user accounts and to protect these accounts from falling into the wrong hands.
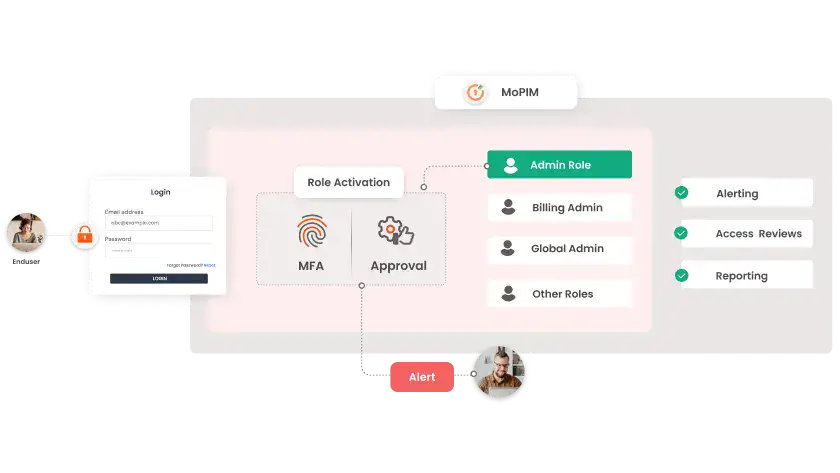
What is IAM? And How is it different from PAM and PIM?
In the world of cybersecurity, Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the umbrella that covers both PAM and PIM. Privileged Management strategies as a whole are a critical part of IAM strategies.
Understanding the IAM solution
IAM is a framework of policies and security mechanisms, which are implemented in any modern organizational environment to ensure that the right users have the appropriate access to different company resources. The IAM solution empowers organizations to manage user identities, their authentication, authorization, roles, and privileges within or across different systems and enterprise environments.
“IAM serves as the foundation for both PIM and PAM.”
IAM Vs. PAM Vs. PIM
PAM is a subset of IAM focused specifically on privileged access. PIM is also a subset of IAM, focusing on managing privileged identities.
Which One Should You Go With?
Deciding between PAM and PIM depends on your organization's specific needs:
- If your primary concern is controlling and securing access to your systems and data, PAM might be the right focus.
- If you're more concerned with managing who has privileged access and ensuring they are the right individuals, PIM will serve your needs better.
- In reality, most organizations will benefit from implementing both PAM and PIM strategies to ensure a comprehensive security posture.
- Balancing both access and identity management ensures not only that the right people have access, but also that this access is securely managed and monitored.
PIM and PAM share the goal of securing privileged access within an organization. A robust cybersecurity strategy will often include both PIM and PAM to ensure not only that access is protected, but also that the identities holding that access are properly managed.
miniOrange Privileged Management Solution
The miniOrange, a vital player in the Identity & Access Management space, offers a holistic Privileged Management Solution that includes both PAM & PIM functionalities to empower organizations aiming to bolster their defense against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. The solution ensures Granular Access Control, strictly adhering to the Principle of Least Privileges. By integrating standout features such as Privileged Remote Access, Automated Password Rotation, and Real-time oversight via Privileged User Session Monitoring & Recording, the solution strengthens account protection. With stringent password policies in place, combined with periodic rotations, the system ensures secure authentication for all high-level accounts.
Key Features and Offerings of miniOrange PAM:
- Comprehensive Password Vault for Machine and User Credentials Management.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Privileged Access.
- Detailed Privileged Session Audit Trail
- Robust Privileged Access Control.
- Streamlined Privileged Access for Web Applications.
- Central Console with Multi-Tenant Support.
You can see the miniOrange PAM in action and test all the features for free in your enterprise environment by claiming your 30-day free trial with POC.
Author