Work culture is changing from in-office to remote and hybrid, and so are the businesses. More and more organizations are moving to secure deployment modes such as cloud or hybrid settings.
There’s a need for solid security solutions that can keep an organization’s resources protected from potential cybercriminals. Access gateway gives you that extended level of security.
Unlike VPNs, access gateways are scalable and more secure, making them an ideal solution for hybrid, remote, or in-office work environments.
With this in mind, let’s compare access gateway vs. VPN, and understand why businesses are turning towards more hassle-free solutions like access gateways over conventional VPNs.
Why are Businesses Rethinking VPNs?
According to data presented on Forbes, around 57% of the respondents faced a cyberattack while using a VPN, and around 25 million VPN user records were exposed in 2022.
A significant rise in cyber activities is compelling businesses to rethink using VPN in the long term. A VPN may keep you safe from prying eyes but fails to protect you from phishing, malware, and other malicious activities.
What’s Wrong with the Traditional VPNs Today?
Here’s what you should know about it:
1. Full Network Access: VPNs are designed to offer unrestricted and broad access to the internal network, resources, or apps. This increases the risk of exposing credentials to an unwanted guest.
2. Hard to Scale with Remote/Hybrid Teams: The conventional VPNs were never meant for large workplaces scattered worldwide. So, if you’re using it, then it is time to switch to access gateways, which are scalable.
3. VPN Users are Clunky, Slow, and Error-Prone: Users with VPNs struggle with complex installations, unreliable connectivity, and poor user experience for all the devices.
4. The Perimeter Security Model is Outdated: VPNs use an obsolete ‘castle-and-moat’ approach and trust everyone inside the network, even though their IDs aren’t verified, which is problematic for organizations.
What are the Modern Security Demands?
So, to tackle threats and vulnerabilities in today’s era, businesses need:
1. App-Level Access Control: Here, businesses can grant control to only the required app or resources and not the entire system or the network. This protects the core data from potential harm.
2. Verify User Identity at the Core: Every type of business needs to verify users’ identity for every resource access requested by them. This helps to prevent unauthorized access control.
3. Zero Trust Security Principles: Every time grant least privilege access, and continuously authenticate users via MFA and SSO solutions. This helps to establish the zero trust principle.
Access Gateway vs VPN: Core Differences
What is an Access Gateway?
An access gateway acts as a digital gatekeeper that sits between your internal apps/resources and the users (external aspects).
These gateways validate the users who are trying to access your resources, thereby offering a protective shield to your data.
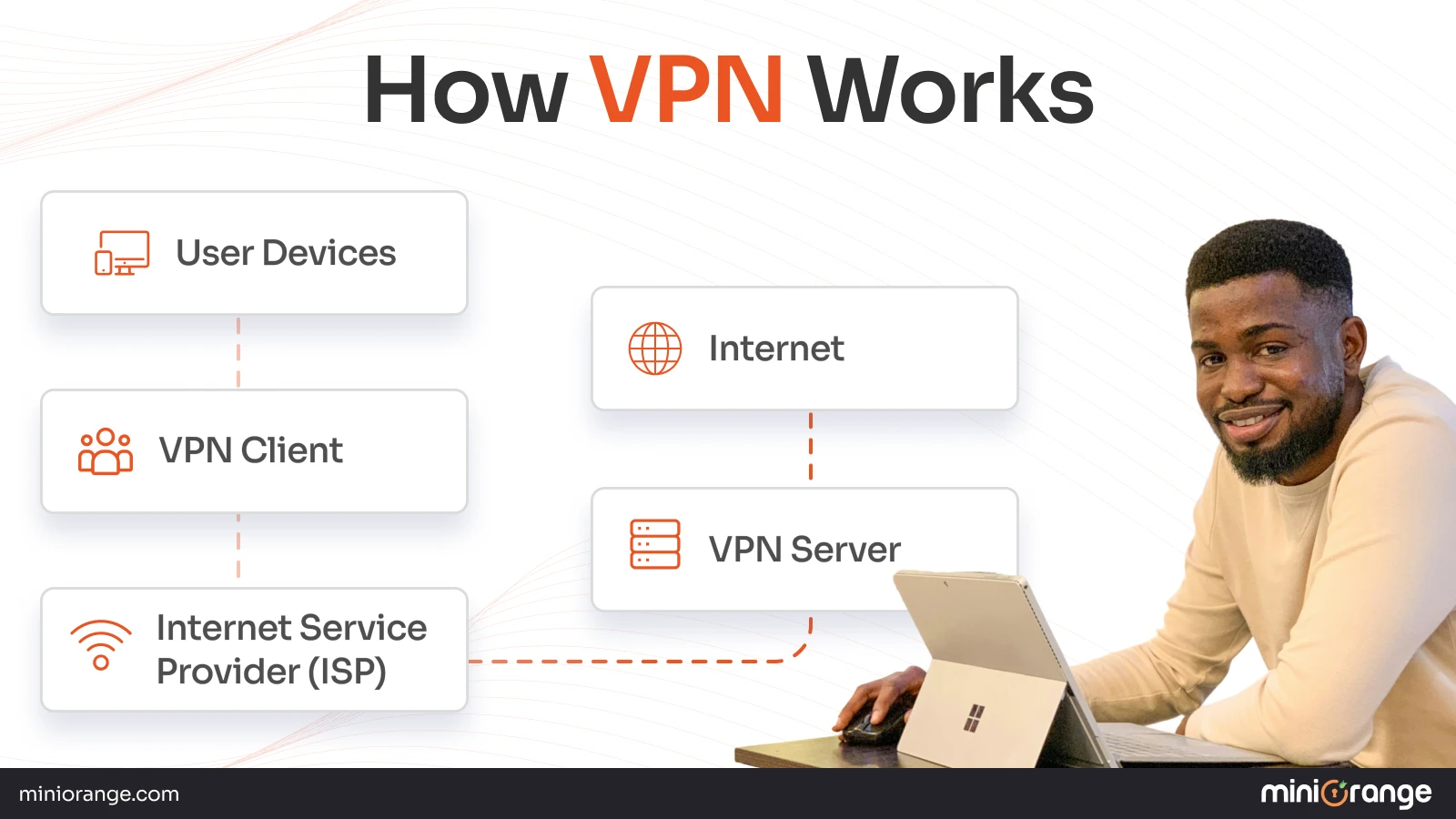
What are VPNs?
A virtual private network (VPN) is a tool or a service that creates a safe connection over the internet.
VPN hides the user’s IP address and protects it from unwanted traffic. It keeps the hackers away by encrypting the data.
Let’s understand the difference between access gateways and VPNs so you can choose which works best for you.
What Sets Access Gateways Apart from VPNs?
| Feature | VPN | Access Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Access Level | VPN offers full network access. Here, users can access any type of resource inside the network. This broad level of access increases security risks in case devices or credentials are exposed. | Compared to VPNs, access gateways allow only app/resource-specific access to the users. This reduces the exposure to the internal network and boosts security levels. |
| Security Model | Works on a perimeter-based model, where all the users inside the network are trusted. This creates an assumption that any user who is inside the network is safe. | Works on a zero trust model, where identity and context is verified for all the users, irrespective of the network location or the device. |
| User Experience | Requires users to install and handle a VPN client, which can prove to be problematic as it may work slowly and show errors. | Offers browser-based access with a built-in SSO and MFA solution, which adds extra layer of security. |
| App Support | Limited for legacy apps only, and struggle with compatibility issues, with recurring complex configurations. | Provide complete app support, including header injection methods, which allows legacy apps to implement SSO and MFA solutions. |
| Deployment | Have a static setup, meaning they’re deployed on-premise with little to no chance to scale. | Have cloud and hybrid deployment options, making them suitable for today’s IT needs. |
From the above table, it is clear that access gateways provide smarter, safer, and more scalable access than VPNs.
So, now is the time to switch to a better solution like the miniOrange access gateway to keep your organization protected.
Understanding Access Gateway in Cybersecurity
Here’s what you need to know about access gateway in cybersecurity.
1. Acts as a Bridge
As mentioned above, access gateway is a smart digital gatekeeper for your organization’s resources.
So, instead of opening the gate for all the users, the access gateway verifies the users, then lets them into the specific space they’re allowed to access, thus acting as a bridge.
2. Enforces Role-Based and Contextual Access Policies
Not every user needs access to everything, and sometimes permits depend on who the user is. So, access gateways allow you to set the right level of access based on users’s roles (employee, manager, HR, etc.) and real-time context (time, location, or security status of the device).
3. Integrates with Identity Providers (IdPs)
Access gateways are designed to work with the leading IdPs such as Okta, Google Workspace, Microsoft Entra ID, and more. The IdPs manage your users’ authentication for multiple apps.
Plus, it is easier to boost security layers with solutions such as Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Why Does It Matter?
So, poorly handled resources can lead to grave consequences for your organization, such as financial losses, identity thefts, and closure of an entire company altogether.
Unmanaged accounts are easy entry points for hackers to steal private data. In the latest report released by the FBI in April 2025, more than $16 billion was lost due to data breaches.
So, organizations need to take proactive steps to prevent attacks and reduce overall risks.
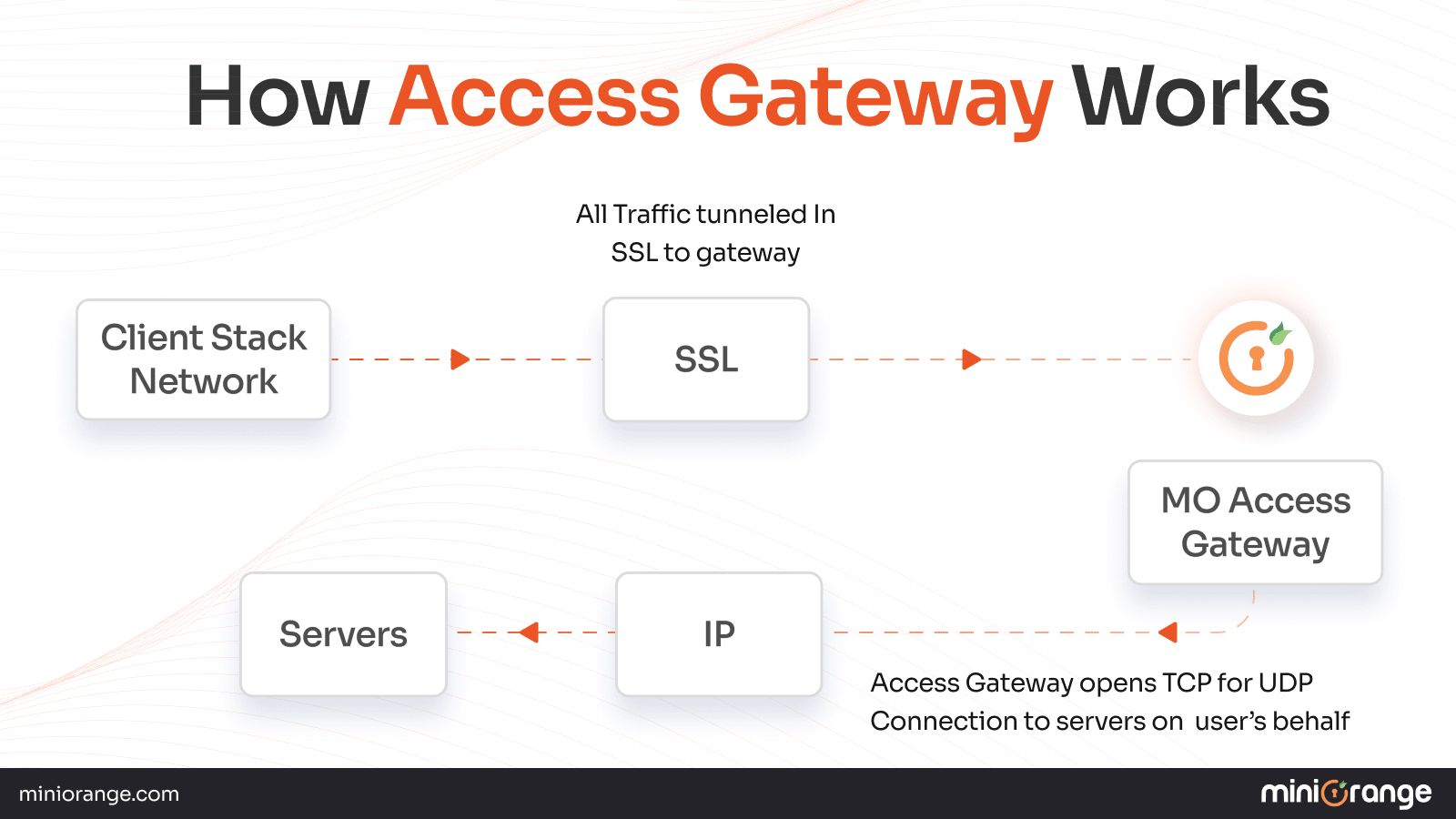
How Does Access Gateway Work?
Here’s what you should know about the workings of the access gateways:
Typical Access Flow
1. User Requests App Access
The user requests to access an app (hosted on a cloud or on a legacy system) and makes a request by clicking on the link or by entering a web address. The access gateway understands this request and sends it ahead for further processing.
2. Redirect to IdP for Authentication
Before validating the user and granting entry to resources, the access gateway redirects the user to an Identity Provider (IdP) such as Google Workspace, Microsoft, or Okta. The IdP verifies user identity with the existing user credentials like password and username.
3. Challenge Posed by MFA If your organization has a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) in place, then the IdP will ask the user to provide extra proof of identity, such as biometrics, OTP, or a hardware token.
4. Access Policy Validated
After successful authentication, the gateway checks for policies tied to the user’s ID and session. This could include role-based access, contextual access, and more.
5. Reverse Proxy Delivers App Securely
The access gateway sits between the internal resources and users, but there’s a reverse proxy in place, which the users aren’t aware of.
The gateway doesn’t handover access to users directly; instead, the traffic is redirected to a reverse proxy, which sends the traffic to the backend.
Advantages of Using the miniOrange Access Gateway
The miniOrange access gateway solution can be easily integrated with powerful Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) security solutions. These cybersecurity tools work on all types of apps: cloud, on-premise, and legacy, without the need to handle multiple credentials.
At the core, the access gateway solution enables zero trust principles and is compatible with header-based login for legacy apps.
miniOrange is known for its quick deployment and integration and is trusted by over 25000+ customers across the globe.
Real-World Use Cases: When Access Gateway Wins?
Access gateways are developed to solve real-world scenarios where VPNs fall short.
Problems Solved Better than VPN
1. Secure Remote Access for Global Teams
For organizations present across the world, or employees working from homes, access gateways are used to assign permissions based on users’ departments or roles.
Unlike VPNs, which slow down as the number of remote users increases, gateways can be scaled easily. This bolsters the speed of work, keeping the productivity high all the time.
2. Temporary Access for Vendors and Partners
With access gateways, you can grant temporary access to your partners and vendors. These accesses can be given to specific resources or apps only.
Limiting permissions to internal apps and resources helps to reduce the risk of lateral movements made by hackers.
3. Adherence to Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliances such as HIPAA, GDPR, and more are necessary to maintain the privacy and security of sensitive data. Your organization can suffer legal penalties or charges in the absence of these compliances.
Compliant access gateways help to adhere to policies, auditing, reporting, and other data privacy requirements.
What Does miniOrange Access Gateway offer?
1. Time-Bound and Geo-Restricted Access: With miniOrange access gateway, you can control login timeframes and restrict permissions based on locations.
2. Conduct Full Audit Trails and Access Logs: Every authentication is tracked and audited, so anomalies can be detected beforehand.
3. No Re-Architecture Needed for Legacy Systems: Legacy apps aren’t built for modern security. But the miniOrange product supports header-based authentication, which means that the apps receive identity data through the HTTP headers inserted after the user verification.
Why VPNs Fall Short in the Zero Trust Architectures?
Implement a strong zero trust architecture to protect your business.
Zero Trust Requires
1. Always Verify: All devices, users, and traffic must be cross-checked before granting permissions to any apps/resources.
2. Least-Privileged Access: The users should be allowed only the minimum level of access needed to perform their duties.
3. Evaluate Risks: This point is applicable on the assumption that a breach has occurred or will occur. This mindset will help businesses to mitigate risks beforehand, thus minimizing the risks.
But VPNs fall short of all the above mentioned points. So, businesses need to reconsider their choice of using a VPN.
Here are certain limitations to virtual private networks that you should know.
Limitations of VPNs
1. Overly Broad Access: So, VPNs cannot limit their exposure to certain data, resources, or apps.
2. Lack of Visibility and Policy Control: Virtual private networks make it complicated to see who accessed what and also to make fine-tuned access policies.
3. Poor Integration with Modern IAM Systems: You cannot integrate modern Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions such as MFA, 2FA, or SSO with VPNs. They’ll crash before showing results.
If you ever have to consider an alternative to VPN, go for the miniOrange Access Gateway solution, which is built for Zero Trust from the ground up.
Choosing the Right Tool: Why Access Gateway Is the Future?
The access gateway market was valued at around $5.67 billion in 2024, and is projected to reach approximately $12.34 billion by 2033, rising at a CAGR of 9.2% from 2026 to 2033 timeframe.
The substantial increase in the need for efficient and secure remote access solutions is driving the access gateway market growth.
Furthermore, as companies are migrating heavily to the cloud, there is a need for access gateways to protect the resources in the cloud.
Rapid advancements in technology such as AI, machine learning, and LLMs are bound to expand the abilities of access gateways, so they’re safer.
Top regions where the access gateway market is booming are North America, followed by Europe, then China, India, and lastly the Middle East and Africa.
Final Thoughts: Say Goodbye to VPN Hassles
If you haven’t already, now is the time to modernize your access strategy. By choosing access gateway over VPNs, you tend to put identity verification first and also enable least-privilege access.
Ditch the legacy VPN and move to identity-first, application-aware access control today.


Leave a Comment