Over 93% of organizations are reportedly experiencing two or more identity-related attacks a year due to weak passwords, and at this critical level, organizations are looking out for an additional layer of security with biometric authentication to verify their users. Multi-factor authentication plays an integral role in verifying user identities. It adds an extra security layer on top of classic usernames and passwords and forms one of the factors for verifying users on the basis of ‘who they are’ with biometric authentication. Biometrics reliably verify user identities. In the face of rising identity security risks, miniOrange is at the forefront of providing strong and reliable identity and access security.
Biometrics are the unique biological traits and characteristics that set a person apart and are used to identify who you are. For example, these attributes are your fingerprint, face structure, voice, or more. In this article, you will explore how you can apply biometric authentication to your business to heighten your business security.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security method used to verify user identities of people with the help of their unique physical or behavioral characteristics. These include fingerprints, facial features, irises, retinas, voice recognition, and behavior patterns like your mouse movements and how you type or walk.
A user’s biometrics are an ‘inherence factor’ when a user is logging in. When verifying users, biometrics secure both physical and digital environments. For instance, a person can enter a facility physically using their biometrics, or they can log into the system online with the use of biometric authentication.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work?
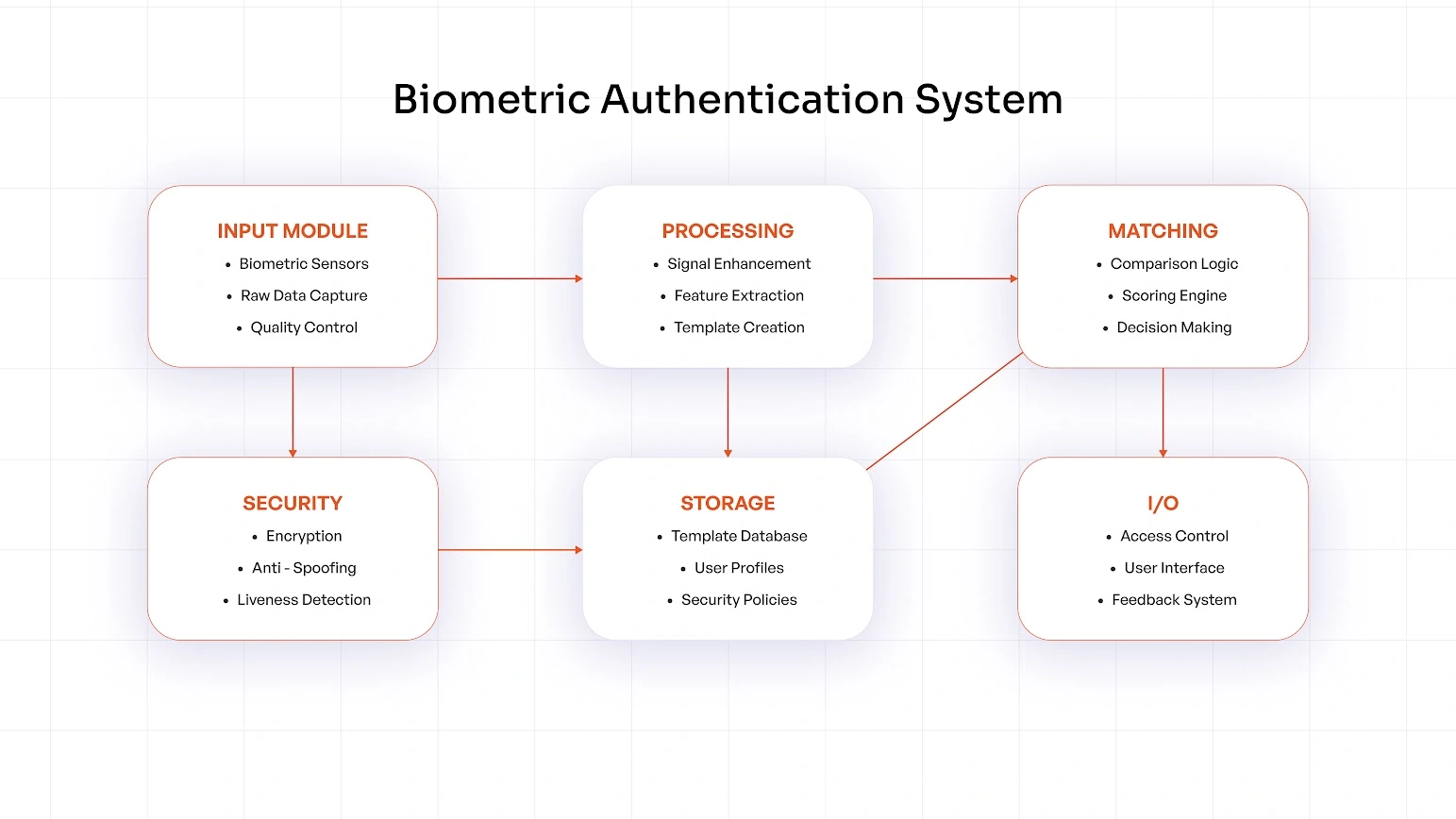
Specialized sensors, including fingerprint scanners, facial recognition cameras, and voice recognition microphones, function as biometric authentication tools to collect distinct physical and behavioral characteristics. The data undergoes preprocessing to eliminate noise before feature extraction transforms unique elements such as fingerprint minutiae or facial landmark distances into secure digital templates. The system stores encrypted templates in secure environments to verify identity through statistical template matching of new biometric samples against stored templates while using liveness detection to prevent spoofing attempts.
Universal directories integrate with identity and access management (IAM) frameworks to store user identities securely through biometric authentication. The combination of biometric data with organizational access policies through universal directories results in improved security and operational efficiency.
The digital environment uses WebAuthn standards to merge biometric systems for passwordless multi-factor authentication experiences. WebAuthn connects biometric data with web-based security protocols to authenticate digital credentials through real-time template matching of live biometric samples. The combined system strengthens access security while providing easy user experiences through a contemporary, user-focused identity verification method.
Due to advanced sensor technology and sophisticated algorithms, putting in complex biometric physical and behavioral traits into secure digital templates is easy.
Types of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication depends on authenticating identity by using distinctive physical characteristics together with behavioral characteristics. There are different ways to authenticate user biometrics, including:
1. Facial Recognition:
The system uses advanced algorithms to examine facial geometry, which includes eye separation, nose shape and jaw alignment. Real-time processing enables secure applications ranging from mobile devices to airport surveillance.
2. Fingerprint Recognition:
The system reviews distinct finger patterns together with refined minutiae points, which have been developed through decades of forensic practice. Modern implementations blend traditional methods with liveness detection for trusted access control.
3. Eye Recognition:
Eye recognition examines diverse features—contours, movement, and spacing—beyond standard iris or retina analysis. Its inherent ambiguity often leads to reliance on specific methods like iris or retina identification.
4. Vein Recognition:
Near-infrared light reveals the hidden vein patterns in hands or fingers, which produces strong security measures.
The system provides natural resistance to forgery, which makes it suitable for contactless authentication systems that need high security.
5. Voice Recognition:
The system identifies users by measuring vocal characteristics such as pitch and tone together with cadence and speech patterns.
The system uses sophisticated algorithms that overcome environmental obstacles to maintain reliable operation in banking and smart home device applications.
6. Palm Print Recognition:
The system maps the entire hand surface to collect detailed biometric data through the analysis of unique lines and creases and textures.
The system works with multiple identification methods to boost both the accuracy and security of identification systems.
7. Gait Recognition:
Remote monitoring becomes possible through the examination of specific walking patterns, which the technology uses to enable continuous, non-intrusive tracking.
The system works best with additional biometric data to overcome its sensitivity to variations, including footwear and injuries.
8. Retina and Iris Recognition:
- Iris Recognition: This technology leverages the complex, unique patterns found in the colored ring of the eye. Its non-invasive nature and high accuracy have made it popular in national ID programs and border control.
- Retina Recognition: The blood vessel patterns found at the back of the eye serve as the basis for retina recognition to achieve highly precise identification methods. The need for close proximity and the invasive nature of the scan make retina recognition less prevalent than iris scanning.
Both techniques deliver very accurate results and are two of the most secure biometric methods. These are quite useful in environments that require very strong authentication, although cost and user convenience often mean iris recognition gets picked over the other two.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Verifying human identities with the help of biometrics helps more secure and efficient logins over traditional usernames and passwords. It has the potential to streamline processes in various sectors as well. Here are the advantages of biometric security for businesses:
1. Identity insurance:
The identity verification process through biometric logins relies on distinctive characteristics including fingerprints, facial features and retinal patterns. The traits possess such unique characteristics that they become virtually impossible to duplicate, thus providing strong protection against unauthorized access and identity theft.
2. Ease of Use:
Biometric systems get rid of complicated passwords by allowing users to quickly scan their fingerprints or facial features. The system provides efficient access while maintaining security through daily interactions.
3. Fraud Detection:
The distinct nature of biometric data creates an almost insurmountable barrier for impostors to replicate it even when traditional authentication credentials become vulnerable. The system includes liveness detection to confirm that the data originates from a living person, thus preventing spoofing and impersonation attacks.
Risks of Biometric Authentication
As biometric authentication brings in the convenience of faster logins by verifying “who you are,” it poses risks of concerns like privacy, spoofing and the irreversible nature of the biometric data. Here are the risks involved in biometric authentication:
1. Partial Matches:
The matching algorithm of biometric systems can produce near but not perfect matches, which leads to incorrect user authentication. The authentication system may grant unauthorized access to individuals when the matching algorithm lacks precise settings.
2. Prone to Hacking:
Biometric systems maintain security features yet remain exposed to complex spoofing methods and bypass attacks. Attackers can use system vulnerabilities to create fake biometric characteristics, which breaks down authentication security.
3. Data Storage:
Biometric systems store personal information that makes them attractive targets for attackers. The security implications from leaked biometric data become irreversible because these traits are immutable when storage and encryption management are not properly secured.
4. Failed Recognition:
The combination of environmental conditions and hardware constraints leads biometric systems to fail to identify authorized users. The system's failure to recognize authorized users would result in denied access and potential disruptions of work activities.
5. Privacy Concerns:
The permanent nature of biometric data creates distinct privacy concerns because it stands as an unalterable aspect of personal identity, unlike changeable passwords. Severe breaches of personal privacy occur when unauthorized parties access or misuse biometric data because such data cannot be easily restored.
Passwords vs. Biometrics: Which One is Stronger?
Digital security relies on passwords as its fundamental authentication method because they provide flexible and cost-effective protection. Users frequently select simple passwords that are easy to guess, and they tend to reuse passwords throughout different platforms, while attackers use brute-force methods and phishing attacks to break them. The requirement for users to remember their passwords as secrets creates vulnerabilities that modern cyber threats actively exploit despite best practices that include password updates and complex password policies.
The use of biometric authentication through physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial recognition and iris patterns provides a stronger authentication system because these traits cannot be easily duplicated or attacked. The advantages of biometric authentication exist, but users cannot reset biometric data after a breach, and the protection of stored biometric data remains a challenge. Cloud security measures that include multi-factor authentication and strict protocols make biometric systems stronger than traditional passwords to provide high assurance for identity verification in secure environments. Organizations can enhance security through MFA software by integrating biometric authentication with other verification factors to create a stronger system while delivering a better user experience.
Biometric Authentication Myths Busted
As a popular method of verifying a user, biometric authentication has a few misconceptions that people think undermine its capabilities. Here are the myths about biometric authentication revealed with their realities:
1. Biometrics are easy to fake
Myth - Some people believe that simple molds or high-resolution images enable easy reproduction of fingerprints and facial features. Actual - Modern biometric systems employ advanced liveness detection and anti-spoofing technologies, which make it very difficult to duplicate the authentic biological characteristics of a person.
2. Biometric systems are perfect
Myth - Many people believe that biometric systems produce no errors while delivering absolute security through perfect performance.
Actual - Every authentication system contains weaknesses because biometric systems produce quantifiable errors during verification processes yet function best when paired with multiple security protocols.
3. Biometric data can be stolen easily
Myth - Many people believe that biometric data faces the same easy theft risks as passwords and would result in permanent security breaches.
Actual - Biometric data exists in practice as encrypted templates instead of raw data during storage. The secure management of biometric data minimizes risk because stolen data remains unusable even after a breach occurs.
4. Biometric authentication is expensive
Myth - The common perception exists that biometric authentication requires excessive costs, which restricts its deployment to premium applications.
Actual - The rapid development of technology has made biometric solutions more affordable so they now appear in everyday devices including smartphones and laptops, which provides accessibility to various users and applications.
Biometric Authentication Use Cases
Applying biometric authentication in digital and physical environments is on the rise. It is one of the most secure ways to identify the person logging in and helps streamline processes. It has many applications across diverse industries, including
1. Healthcare
- Patient Identity and Data Protection:
The system uses fingerprint, iris or facial recognition technology to guarantee that the correct patient receives their medical records. - Access Control:
The system controls entry to areas that are restricted, such as operating rooms. - Remote Monitoring:
The system links wearable data to the correct patient for accurate telemedicine.
2. Travel
- Streamlined Check-ins and Border Control:
The system uses facial/fingerprint authentication to expedite the processes. - E-Passports & Kiosks:
The system enables quick and contactless identity verification. - Service Verification:
The system improves security in hotels, car rentals and other travel services.
3. Law Enforcement
- Identification:
Fingerprints, facial recognition or DNA is used to identify suspects and missing persons. - Surveillance:
Real-time monitoring helps to identify persons of interest. - Securing Sensitive Data:
The system protects access to forensic databases and evidence storage.
Conclusion
The technology of biometric authentication functions as a transformative solution that provides strong protection for sensitive data. The system uses unique personal identifiers to enhance access control while enabling contemporary security practices. Our complete cybersecurity blogs offer additional insights about emerging trends and best practices, while you can discover the latest types of authentication that transform security practices.
Your organization should implement biometric solutions through its existing framework. Our team provides personalized expert guidance through our contact page, which serves clients who need digital security solutions for their on-premises architecture projects or their next security evaluation steps.
FAQs
1. What are biometrics?
The unique physical and behavioral characteristics known as fingerprints, iris scans, and voice recognition serve as reliable biometric data that advanced biometric technology uses for identity verification.
2. What does biometric authentication mean?
The authentication process using biometric methods checks identity through personal biological characteristics, which replaces traditional passwords to provide a secure alternative for access control.
3. What are the main problems with biometric authentication?
The implementation of biometric authentication faces multiple challenges because it raises privacy issues, exposes data to permanent breaches, allows spoofing attacks and produces inaccurate results in different environmental conditions.
4. How does biometric verification work?
Specialized sensors record individual unique traits, which become digital data that gets compared to stored information to confirm identity through biometric verification processes.
5. What is included in a biometric screening?
The biometric screening process collects fingerprints and facial or iris scans as essential biometric data, which serves as the foundation for secure identity verification through advanced biometric technology.



Leave a Comment