Imagine signing in without ever having to remember a password, and this is possible with the help of passwordless authentication. In 2020, Microsoft recorded over 150 million monthly passwordless logins, clearly showing that frictionless security works. Meanwhile, 90% of organizations face phishing attacks, and nearly 64% plan to switch to passwordless methods to protect their data.
In this blog, explore how passwordless authentication is creating more windows of opportunity to fight against attackers and take digital security to the next level by making logins easier than ever. Also, learn how miniOrange helps your organization with securing your applications and websites using passwordless authentication.
Passwordless Authentication vs. MFA
Passwordless authentication offers significant improvements in terms of security and user experience. In this approach, organizations discontinue the use of traditional passwords and instead utilize authentication methods such as biometrics, security keys, or cryptographic tokens. This method removes vulnerabilities, like phishing and credential stuffing, making the login process relatively easier. Passwordless solutions reduce human error and provide a more intuitive, secure user experience.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a fundamental component of cybersecurity that combines a traditional password with an additional factor, like a single-use code, one-time password (OTP), or a physical hardware token. While MFA enables organizations to effectively defend against various attack vectors, its dependency on passwords as a first line of defense poses security challenges and operational inefficiencies. This means that organizations now need to implement passwordless methods within their MFA frameworks to achieve a more secure and frictionless login experience. Learn more about MFA and its various methods to protect your user accounts.
How Does Passwordless Authentication Work?
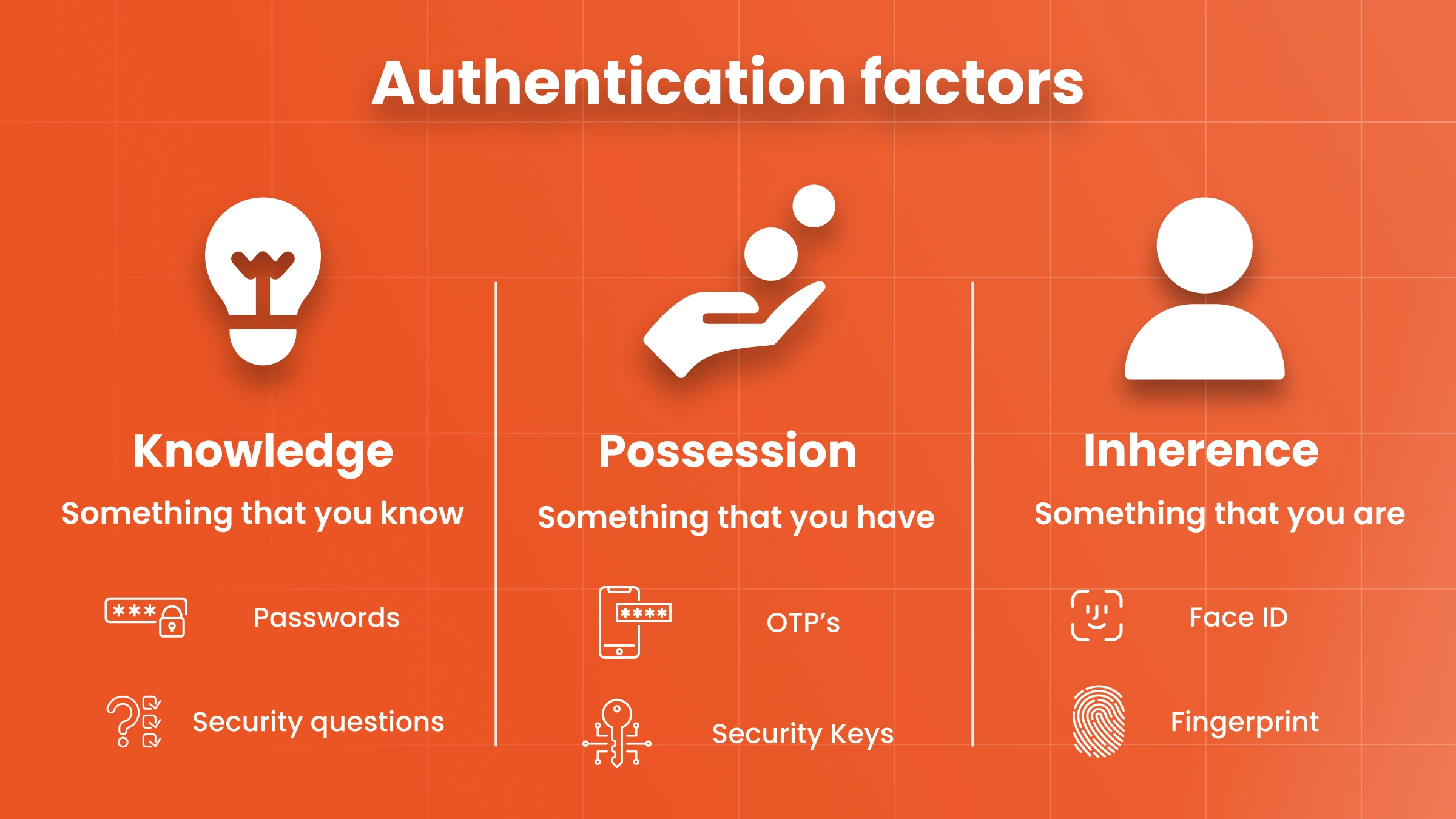
Authentication factors belong to one of the three categories:
- Something that you know i.e., knowledge factor, e.g., PIN or password,
- Something that you have i.e., possession factor, e.g. hardware token or singleuse code,
- Something that you are i.e., inherence factor, e.g.
Passwordless authentication replaces traditional password-based verification with more secure forms of user authentication like biometrics, physical hardware tokens, or cryptographic keys. Organizations are using passwordless authentication with the help of FIDO2 authentication standards compatible with the WebAuthn API, which uses public-key cryptography. In public key cryptography, users register their devices that store private keys on them while sending public keys to authentication servers. When users authenticate, their device signs an MFA challenge with the private key. Thus, preventing credential theft, as no secret keys are made to travel through the network.
Enterprises deploy passwordless solutions with the help of integration with single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conditional access policies that evaluate risk factors before granting resource access. This approach significantly reduces security vulnerabilities by eliminating password-related risks (phishing, credential stuffing, password reuse) while improving user experience through faster logins and reduced friction. Implementation requires careful planning around device management, recovery processes, and legacy system integration but delivers substantial improvements in both security posture and operational efficiency.
Drag and Drop Passwordless Authentication with miniOrange
miniOrange’s drag-and-drop authentication system helps control the hassle of multiple password management. It lets the administrator set up secure and user-friendly login methods—such as biometrics, OTPs, push notifications, and magic links—in an easy-to-use interface. This means your team spends less time around passwords and more time towards productivity.
Our solution provides better security against brute-force and phishing attacks using passwordless authentication methods. It is flexible and reliable and scales easily with your changing business needs while being simple and straightforward.
Password-imposed Problems
Traditional authentication with the help of credentials like username and password impacts the user experience and is mostly unsafe if the user keeps forgetting them. In a recent study, an average person manages nearly over 100 passwords, around 30% of which are weak and repeated, creating a fresh ground for cyberattacks. Organizations need to secure their sensitive information but not at the expense of the user experience. Here are some of the problems a user faces when dealing with passwords:
User friction
Users experience a burden from complex passwords that require frequent resets because they must remember multiple complicated credentials, which leads them to unsafe practices of password repetition. Employees end up spending productive hours resetting forgotten passwords or going through tough login procedures. It is evident from a FIDO report that due to complex login processes, nearly a third of people abandon online services.
The resistance to password entry creates both performance issues and user trust problems, which motivates the development of user-friendly authentication systems. This is one of the reasons why companies are making a shift towards user-friendly alternatives such as biometric and passwordless authentication solutions.
Security headaches
Passwords are one of the primary vulnerabilities in security infrastructures, even though technology has advanced. They pose as the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain. Organizations find that their passwords are inadequately secured (such as "Summer2024!") or their credentials are compromised through social engineering. Once the passwords are breached, it is likely that most of the mission-critical and sensitive information is exposed to attackers, leading to even greater damage.
Security teams expend heavy resources addressing the damage these human tendencies of keeping simple passwords cause, which render vulnerability management and incident response inefficient. Some organizations that keep relying on traditional passwords keep on continuing with the risk. However, with passwordless solutions, they are now finding relief.
High cost
Password management generates high operational costs that organizations are unable to map effectively. In typical enterprise settings, password resets account for around 30% of IT support resources. These calculations do not consider the productivity losses that occur during login process interruptions and the disruptions in operations that follow a password breach.
Also, there is a high irreparable reputation damage when your passwords are involved in a data breach. Adopting either multi-factor or passwordless authentication tightens up the security posture while delivering major cost reductions, enabling organizations to spare resources from maintenance for strategic initiatives.
Benefits of Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication is designed to provide a smooth login experience and enable secure logins. It helps drop the risks of fraud and safeguard accounts from any breaches. Here are the advantages of passwordless authentication:
Reduce fraud and account takeover:
The elimination of traditional password systems removes all their built-in security weaknesses. Organizations reduce their attack risks through the implementation of strong authentication methods, which include biometric and cryptographic token systems.
The streamlined authentication system reduces traditional vulnerabilities while providing personalized security measures that make it extremely difficult for fraudsters to access any account.
Onboard and engage more users:
The passwordless authentication system provides users with an easy-to-use experience that combines security features with user-friendly design. The quick and problem-free registration and login process creates immediate trust and satisfaction among potential users.
The platform attracts more users who stay active because they avoid the password management hassles.
Focus resources on core initiatives:
Organizations can use their resources more effectively after removing password maintenance responsibilities, which include both frequent resets and extensive IT support. IT teams gain the ability to work on strategic projects and innovations because they no longer need to handle routine security matters.
The realignment of resources leads to reduced operational costs while improving organizational agility, which enables more impactful and forward-thinking initiatives.
Passwordless Authentication Methods
Passwordless logins are the most efficient way to authenticate users. Some of the methods have innovative approaches such as email magic links, biometrics and push notifications. Here are some of the most useful passwordless authentication methods:
Biometric Authentication (Face, Fingerprint, Iris)
Biometric authentication (face, fingerprint, iris) provides passwordless authentication through individual physical characteristics, which provides smooth user experiences. The system needs dedicated hardware together with protected template databases and active detection of living users. The main obstacles to implementation stem from privacy risks and the need to develop backup authentication protocols when biometric verification fails.
Magic Links and Email-based Login
The authentication method of magic links and email-based login eliminates password management by sending temporary authentication URLs to user email addresses. The system's security depends on both the protection of email accounts and proper encryption methods for links. The main drawbacks of this approach include delayed email delivery and the risk of email account breaches.
One-Time Passcodes via Trusted Devices
The authentication system generates short-lived codes (valid for 30-60 seconds) that users receive on their registered devices. The system integrates both possession factor and knowledge factor to achieve better security. The implementation requires solutions for synchronization problems as well as secure seed protection and device recovery protocols for situations when devices become unavailable.
Security Keys and FIDO2-based Devices
Security Keys and FIDO2-based Devices operate as hardware tokens that use cryptographic challenge-response protocols to stop phishing attacks and protect user credentials from theft. Users must possess the device physically to authenticate because private keys stay confined within the device. The implementation requires complete provisioning systems and revocation procedures and cross-platform compatibility planning.
Push Notifications to Authenticator Apps
The miniOrange Authenticator provides enterprise-focused features with offline capabilities and customizable policies, while Microsoft Authenticator uses number matching to prevent MFA bombing attacks with cloud backup options, and Google Authenticator generates TOTP without cloud synchronization while focusing on security through simplicity with recent device-to-device transfer capabilities.
How miniOrange Helps with Passwordless Authentication
The miniOrange authentication solution provides optimal security and user convenience through its implementation. It protects enterprise environments from compromised credentials by using FIDO2-compliant methods such as biometrics and hardware tokens together with contextual risk analysis. The solution provides flexible deployment through cloud, on-premise, and hybrid environments, which enables smooth passwordless authentication integration without disrupting existing infrastructure or user workflows.
The miniOrange authentication solution stands out because of its adaptive authentication engine. The advanced system assesses continuous contextual elements such as device posture, user behavior patterns, and location data to enforce customized risk-based security policies that meet organizational requirements. Security teams can use miniOrange MFA product orchestration features to create sophisticated authentication processes that combine strong security protocols with user-friendly experiences according to current risk evaluation results.
The deployment of passwordless solutions by miniOrange for Fortune 500 companies demonstrates its ability to scale and maintain reliability across various environments. The solution delivers detailed authentication event monitoring and fulfills complex security requirements and compliance standards, which establishes miniOrange as a reliable partner for contemporary enterprises. Try miniOrange passwordless authentication for free along with multi-factor authentication with a suitable login method for your business.
Conclusion
The security-conscious industry has adopted passwordless authentication as a transformative solution during recent times. Businesses have finally eliminated password-related security issues through their adoption of fingerprint and face scan authentication and security key solutions using FIDO2 using WebAuthn API. Multiple clients have adopted miniOrange's robust MFA solutions to defend against continuous phishing attempts and credential stuffing attacks, which disturb security teams throughout the night.
The most advanced organizations achieve better security while simultaneously enhancing their operational efficiency. Learning the differences, i.e., authentication vs. authorization, is crucial too. The implementation of miniOrange's intelligent adaptive authentication has reduced password reset help desk tickets and recovered valuable time for employees. Any business that wants to protect its critical assets must implement miniOrange's flexible MFA because attackers operate without rest in today's threat environment.
FAQs
Is passwordless better than password?
Yes. Passwordless authentication removes password-related vulnerabilities such as password reuse, weak passwords, and phishing attacks while decreasing user friction.
Is passwordless authentication better than MFA?
Not necessarily. Passwordless is one form of MFA. The most secure method requires passwordless authentication (something you have/are) alongside additional verification factors.
What are the disadvantages of passwordless authentication?
The implementation of passwordless authentication requires substantial initial capital expenditure and intricate technical setup. The system depends on particular devices, which could result in access restrictions when devices go missing, and it raises privacy issues about biometric information, while fallback systems might bring back traditional security vulnerabilities.
Is going passwordless more secure?
Yes, when properly implemented. Passwordless authentication removes password-based security risks while implementing possession-based or biometric authentication methods, which provide stronger security than passwords.




Leave a Comment