Phishing isn’t just yesterday’s email scam. It’s a multi-billion-dollar menace that exploits human trust at every level, from student inboxes to the C-suite.
According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach report, phishing is the most common data breach vector, accounting for 15% of all breaches. Breaches caused by phishing cost organizations an average of USD 4.88 million.
As a brand trusted worldwide for identity security, miniOrange believes everyone, from developer to decision-maker, deserves clarity (and a defense plan) in today’s phishing-laden digital ecosystem. Explore miniOrange’s authentication solutions to safeguard yourself from phishing attacks.
What is a Phishing Attack?
A phishing attack is a type of cybersecurity threat where attackers use social engineering, deception, impersonation, and psychological tactics to trick users into handing over confidential information or downloading malicious software.
They target individuals or businesses by masquerading as legitimate contacts, adding urgency to their requests, and preying on our instincts to trust recipients that appear familiar.
Common Delivery Methods
- Email: Most prevalent, imitating banks, partners, or well-known services.
- SMS (Smishing): Spoof messages from companies or contacts.
- Phone calls (Vishing): Attackers pose as authority figures or tech support.
Get a detailed insight into Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Phishing Techniques
- Impersonation: Pretend to be someone you know or trust.
- Urgency: “Your account will be locked; act now!”
- Deceptive Links and Attachments: Fake login pages, “invoice” files, etc.
What is the Impact of Phishing if Successful?
- Direct financial fraud
- Serious data breaches and identity theft
- Ransomware or malware infection
- Steep operational downtime and reputational damage to your brand
How Do Phishing Attacks Work?
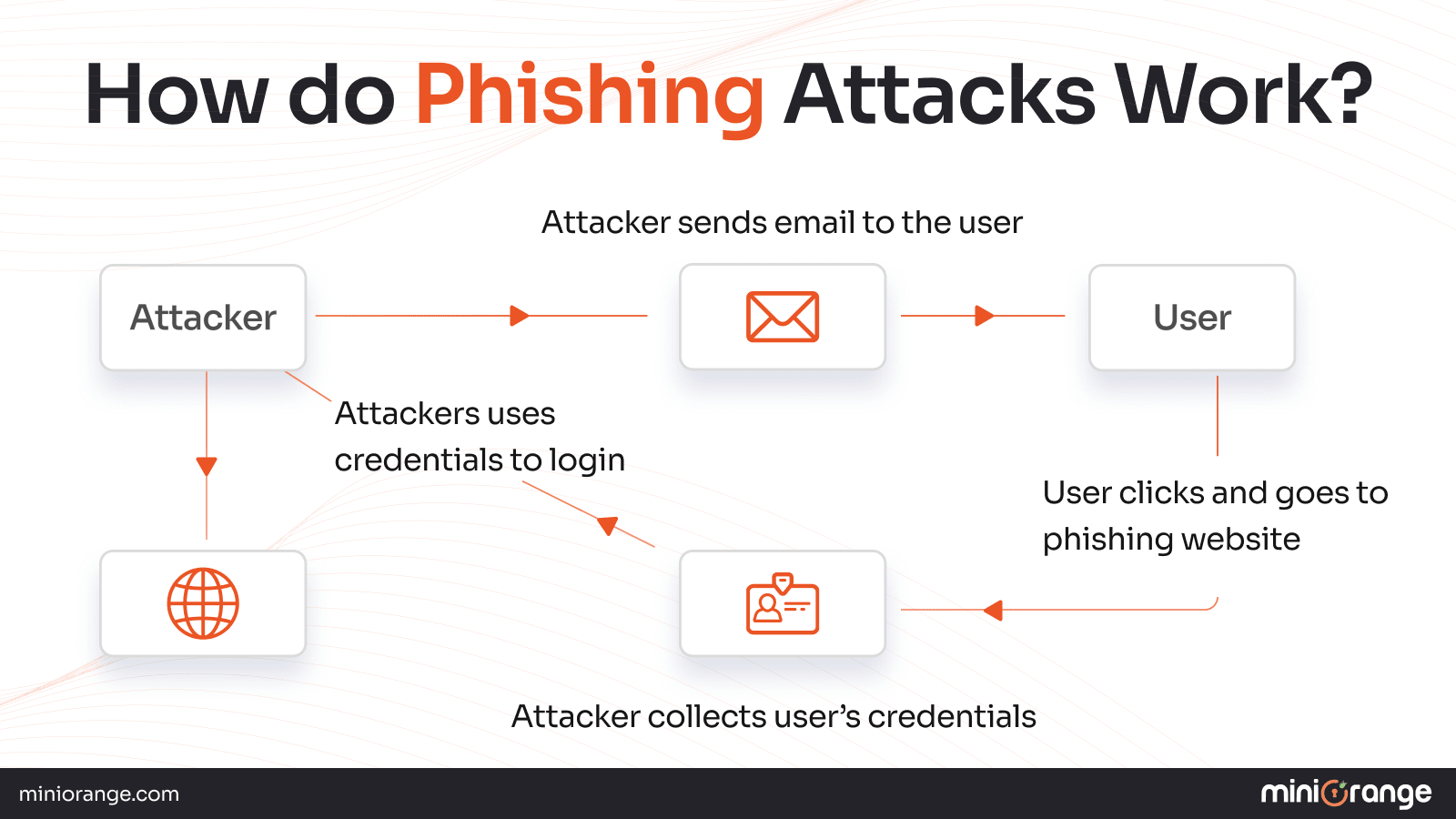
Attackers research their targets by listing out names, phone numbers, or email addresses from public data. Then, they send personalized bait (emails, texts, calls) designed to slip past systems.
Once a victim clicks a rogue link or downloads a malicious attachment, they’re directed to a counterfeit login page or site, where entering credentials sends data straight to cybercriminals.
Take a deep dive into What is MFA.
Common Types of Phishing Attacks
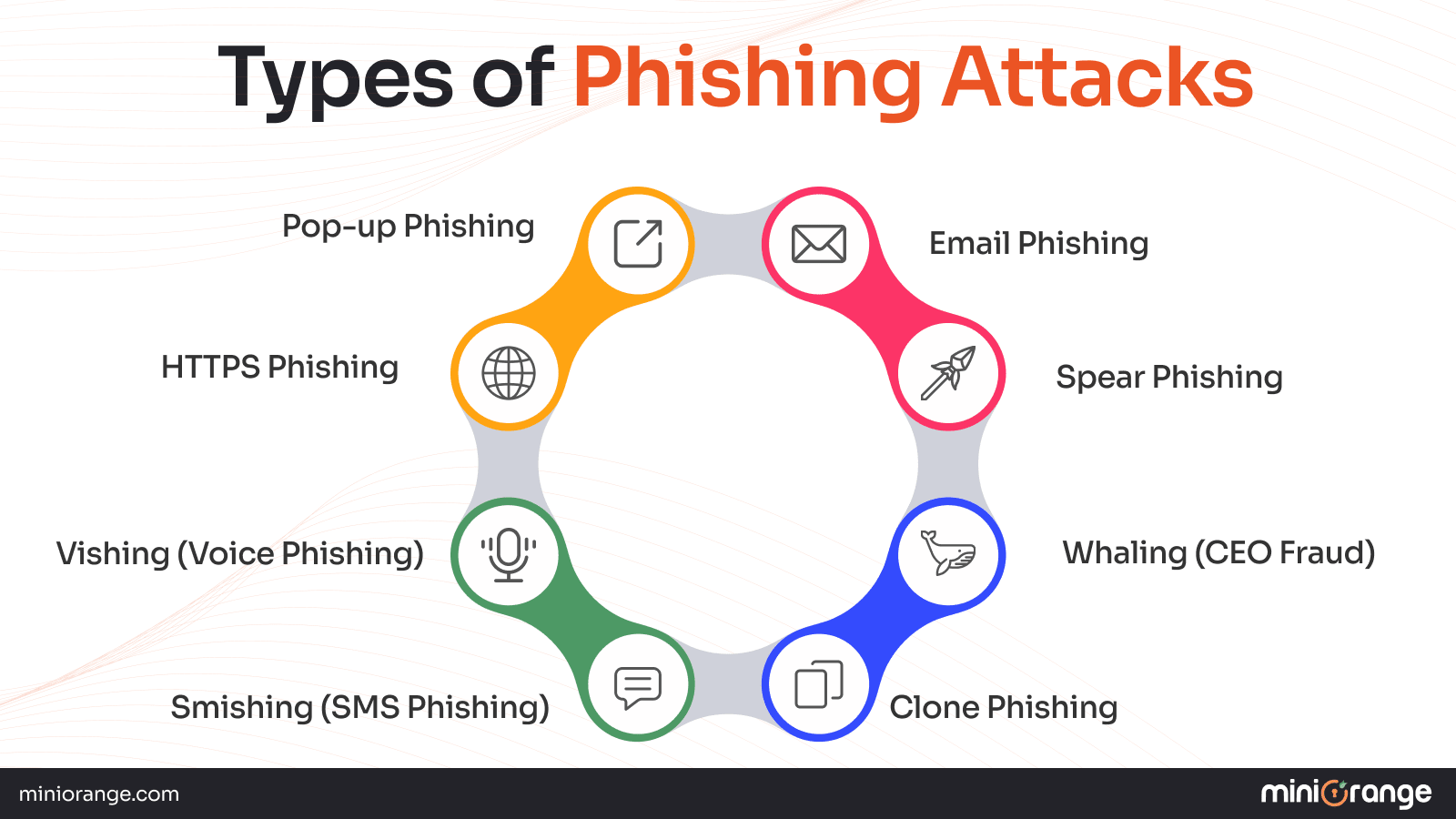
Email Phishing Attack
What is a phishing email? This is the most common form of phishing, where attackers send emails that appear to come from trusted sources like banks, colleagues, or popular services.
These emails often contain urgent messages to lure recipients into clicking on malicious links or downloading harmful attachments.
Spear Phishing
Unlike broad email phishing, spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations. The attackers research their victims carefully, using personalized details such as the recipient's name, position, or interests.
The goal is usually to gather sensitive information, gain network access, or execute a fraud scheme.
Whaling
Whaling is a form of spear phishing aimed at high-profile targets like CEOs, executives, or other influential personnel.
Attackers impersonate these leaders to trick employees or partners into making large financial transactions or revealing confidential data.
Clone Phishing
In this attack, a legitimate, previously delivered email is copied and altered by replacing attachments or links with malicious versions.
The attacker then resends the email to the victim, hoping they will trust the familiar content and unknowingly interact with the harmful elements.
Explore in-depth on ‘Push Notifications’ - to counter phishing scams.
Smishing or SMS Phishing
Smishing involves phishing attempts via text messages. Attackers send SMS that appear to be from legitimate sources, prompting recipients to click on malicious links or provide personal information over the phone or via forms.
Vishing or Voice Phishing
Vishing uses phone calls instead of digital messages. Attackers call pretending to be from banks, IT departments, or government agencies to extract sensitive information by creating a sense of urgency or authority.
HTTPS Phishing
To improve their deception, attackers use HTTPS websites that appear secure (with the padlock symbol) but are fake.
This minimizes suspicion, as users see what looks like a secure, legitimate site, making them more likely to enter credentials.
Pop-up Phishing
Pop-up phishing involves malicious pop-up windows that prompt users for login information or other sensitive data while browsing trustworthy websites.
These pop-ups mimic legitimate login forms or security alerts, tricking users into providing information.
What are the Reasons for Phishing Attacks?

- Financial Gain: Tricking FinTech organizations into fraud and scams.
- Targeted Phishing: Attacking only certain organizations or individuals through whaling or spear phishing methods.
- Fake Technical Support: Posing as IT support to extract passwords from users.
- Cloud-Based Services: Exposing SaaS login for gaining access.
- Filesharing Compromises: Threats via suspicious-looking files.
- Social Media Exposure: Credential stuffing or sending unknown links to users via social media accounts.
- Misdirected Information: Confusing organizations with false information/data.
- Identity Theft: Using user data to impersonate their identity and conduct fraud.
These phishing attacks can be prevented through solid cybersecurity tactics such as the phishing-resistant MFA solution offered by miniOrange.
Phishing Trends Today
2025’s phishing landscape is more dynamic (and dangerous) than ever:
- Vishing: Also known as voice phishing attacks, is surging, capitalizing on the rising use of remote IT support.
- CAPTCHA Shielding: Attackers integrate CAPTCHAs on phishing sites to appear trustworthy and bypass automated detection.
- AI Lures: Fake “AI bot” portals mimic trendy platforms, enticing users to submit credentials or pay scammers.
- Crypto Scams: Fraudulent “exchange” or “wallet” signups proliferate during cryptocurrency news cycles.
Know how to Prevent Cybersecurity Threats with MFA Solutions
What are the Examples of Phishing Attacks?
Phishing attacks have been causing disruptions across the world. Let’s look at some of the top phishing attacks that shook the globe.
US Government Agency Impersonation
In 2023, a US government agency finance employee fell victim to a phishing scam and transferred $218,992 to the attacker's account.
The criminal, impersonating a genuine supplier, convinced the employee to update the contractor's genuine banking details to fraudulent ones.
Twilio Phishing Attack
This case study is presented as per the post published by Twilio. In mid-July 2022, malicious actors sent hundreds of smishing text messages to the mobile phones of current and former Twilio employees (the “Smishing Incident”).
The malicious actors posed as Twilio IT or other administrators and urged users to click on what appeared to be password-reset and other links. The links led to fake Okta login pages for Twilio.
These fake pages were hosted on domains created by the malicious actors, such as twilio-sso.com, twilio.net, twilio.org, sendgrid-okta.org, twilio-okta.net, and twilio-okta.com.
Some Twilio employees entered their credentials on these fake pages. The malicious actors then used the credentials of these Twilio employees to access internal Twilio administrative tools and applications to access certain customer information.
The threat actor’s access was identified and eradicated within 12 hours. Customers whose information was impacted by the June 2022 Incident were notified on 2nd July, 2022.
Booking.com Phishing Attack
The Guardian reported, the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) said 363 people reported scams mentioning Booking.com in 2023, up from 53 reports the previous year.
“Fraudsters may attempt to mimic our emails to phish your username and password for the purposes of taking over your account. These phishing emails can lead to a webpage that looks very similar to the Booking.com Extranet login page–but if you look at the URL address bar, you’ll notice differences,” Booking.com explains in its warning (FODORS).
How Can Businesses Reduce Phishing Risk?
- Security awareness training that’s ongoing and practical and includes simulated phishing tests.
- Secure email gateways to filter out suspicious messages and links before employees see them.
- Limiting user access with Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions, so in case an account is breached, the rest of the system remains safe as it lacks access.
- Real-time threat monitoring via advanced SOC tools: don’t just react; proactively find threats as they emerge.
- Regular internal simulations to test employee vigilance and “muscle memory.”
- A prompt reporting culture so potential incidents are spotted and stopped early.
- Using modern Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions to counter identity theft.
Stay Secure with miniOrange’s Phishing Defense
miniOrange offers a layered approach, combining user-friendly MFA products, advanced email security, SSO Product, and tailored awareness programs.
Our real-time threat intelligence and policy-driven controls give organizations the agility to stay ahead of ever-evolving phishing schemes, whether you’re a Fortune 500 or just starting your cybersecurity journey.
Check out our flexible pricing options that are crafted to suit your business needs.
Conclusion
In today’s hyper-connected world, phishing is the persistent threat that unites technical and human vulnerabilities.
Ongoing education, robust email security, proactive cyber hygiene, and the right partners like miniOrange are the foundation to prevent phishing attacks, no matter your organization’s size or role. Get in touch with us to know more.
FAQs
Is phishing illegal?
Absolutely. Phishing is a criminal activity prohibited by cybercrime laws worldwide, leading to prosecution and heavy penalties for perpetrators.
How many phishing emails are sent daily?
Estimates show over 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent worldwide every single day, making email the primary delivery channel for cyber threats.
What percentage of phishing attacks are successful?
While success rates vary, targeted spear phishing attacks have succeeded at rates up to 30%, especially when organizations lack robust awareness and defense programs.
How many phishing emails are sent each day worldwide?
Globally, billions of phishing emails range from 3 to 4 billion daily floods in inboxes.
What can a hacker achieve with a successful phish?
A successful phish can net hackers access to:
- Corporate networks
- Sensitive customer data or trade secrets
- Financial accounts (for direct theft)
- Means to install further malware (like ransomware)
- Even the ability to spread laterally to partners, clients, suppliers, and any connected ecosystem.




Leave a Comment