We are surrounded by generative AI tools, cloud-based solutions, and AI assistants that often perform functions for us. We tend to share data with them for smoother operations and to automate our work for enhanced productivity.
The non-human tools are a playground for cybercriminals to access the data and damage critical infrastructures. So, it is paramount for us, especially organizations, to protect the shared information, along with the access rights of the non-human entities.
This is carried out with the help of secret management.
What are Secrets?
Secrets hold sensitive information such as passwords, repository credentials, client configuration files, and more. Items that must remain private are stored as secrets.
Moreover, secrets like digital credentials allow non-human entities to communicate and perform some kind of action on a database, service, IT resource, or an app.
Secrets helps businesses solidify their security posture by assuring that only authorized users gain access to confidential data.
What Is Secrets Management?
Secrets management is a method or a practice to keep information confidential and store it securely. This information encompasses SSH keys, API keys, database passwords, credentials, or tokens used for digital authentication, including confidential data stored on the servers.
It also includes better access workflows, a centralized vault, and credential rotation for elevated safety. Furthermore, it eliminates hardcoded secrets and automates governance across DevOps and cloud environments.
The terms ‘secrets’ and ‘secrets management’ are majorly highlighted in IT about the DevOps and cloud native environment, tools, and processes.
What are the Types of Secrets?
Types of secrets (but not limited to) are as follows:
- API Keys: Secret tokens and unique identifiers used by the services, apps, and users to authenticate themselves to an API, for example, a cloud service or a payment gateway.
- Arbitrary Secrets: These are unstructured or structured sensitive data, like certificates, configuration files, etc., which are stored and managed in a secure vault.
- Database Passwords: Credentials used in connection strings to authenticate applications or users to databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or Redis.
- SSH Keys: SSH keys are access credentials used in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol to authenticate users and establish secure, encrypted connections between computers over unsecured networks.
- TLS/SSL Certificates: These are digital certificates that offer encrypted or private channels of communication between a client and a server, using the Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) protocol.
- Encryption Keys: These are used to encrypt and decrypt data in transit or at rest, ensuring that all data is kept confidential.
- OAuth Tokens: Access and refresh tokens issued in OAuth flows that grant delegated access to APIs on behalf of a user or service.
- Service Account Credentials: These are usernames, passwords, Kerberos tickets, and other secrets used by apps and not humans to securely access services or resources and perform actions in systems or cloud environments.
- Authentication and Authorization Tokens: Authentication and authorization tokens are crucial for secrets management, acting as temporary, secure credentials (like JWTs) that prove an identity and grant specific access to secrets (passwords, keys) after an initial login.
- Other Private Keys: These comprise Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) certificates, signing keys, and Hash-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) keys.
All of these are treated as secrets because they are high-value credentials that must be centrally managed, access-controlled, rotated, and monitored to prevent unauthorized use.
Why is Secret Management Essential?
Secrets management matters to organizations because it helps detect, avoid, and remediate unwanted access to sensitive data like the Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
Secrets management is closely related to Privileged Access Management (PAM), a part of the Identity and Access Management (IAM) that solely focuses on protecting and securing privileged accounts.
Why DevOps Needs Secrets Management?
DevOps pipelines rely on many secrets to access databases, cloud services, source control, and third-party APIs during Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) runs.
Without proper secrets management, the development team’s hard-coded secrets are in repositories, scripts, or container images, which greatly increases the risk of leaks and breaches.
Furthermore, secret platforms add audit logs, fine-grained access control, and policy enforcement, helping prove who accessed which secret and when.
Risks of Poor Enterprise Secrets Management
If handled poorly, secrets management can have significant risks as follows:
1. Hardcoded or Embedded Secrets
Secrets like API keys or passwords written directly into code or configurations become public if repos are leaked or scanned, allowing attackers instant unauthorized access to systems and data.
Rotation is nearly impossible without code changes everywhere, prolonging risks even after discovery.
2. Incomplete Visibility
Teams lose track of where secrets exist (code, configs, vaults), creating "secrets sprawl" with millions of unmanaged keys across clouds and tools.
Without unified monitoring, breaches go undetected, enabling attackers to pivot undetected through networks.
3. Stale Secrets and No Rotation
Old, unrotated credentials remain valid indefinitely, turning minor leaks into prolonged attacks even after passwords change elsewhere. Regular, automated rotation is a key security best practice to minimize the impact of a potential compromise.
4. DevOps Pipeline Leaks
Secrets injected into CI/CD logs, builds, or containers get exposed in artifacts or scanners, compromising entire deployment chains. Manual handling slows teams and amplifies human error in fast-paced environments.
5. Third-Party and Vendor Access Risks
Organizations often grant third-party vendors or partners access to systems using shared secrets. The risk here is that the organization cannot enforce its own stringent security practices on the vendor.
If a vendor has poor internal security controls, the shared secret may be compromised, providing an entry point for attackers into the primary organization's systems.
6. Siloed Secrets Across Teams
This describes a fragmented approach where different teams (e.g., development, operations, security) manage their secrets independently using various ad hoc methods (manual sharing, environment variables, different local storage options).
This lack of a centralized system leads to inconsistent policies, difficulty enforcing controls, secrets sprawl, and makes it almost impossible to manage the secret lifecycle effectively.
How Secrets Manager Tools Work?
Secrets manager tools centralize, secure, and automate the handling of sensitive credentials like passwords and API keys to prevent leaks and simplify access. They replace risky practices like hardcoding with encrypted vaults, dynamic generation, and strict controls.
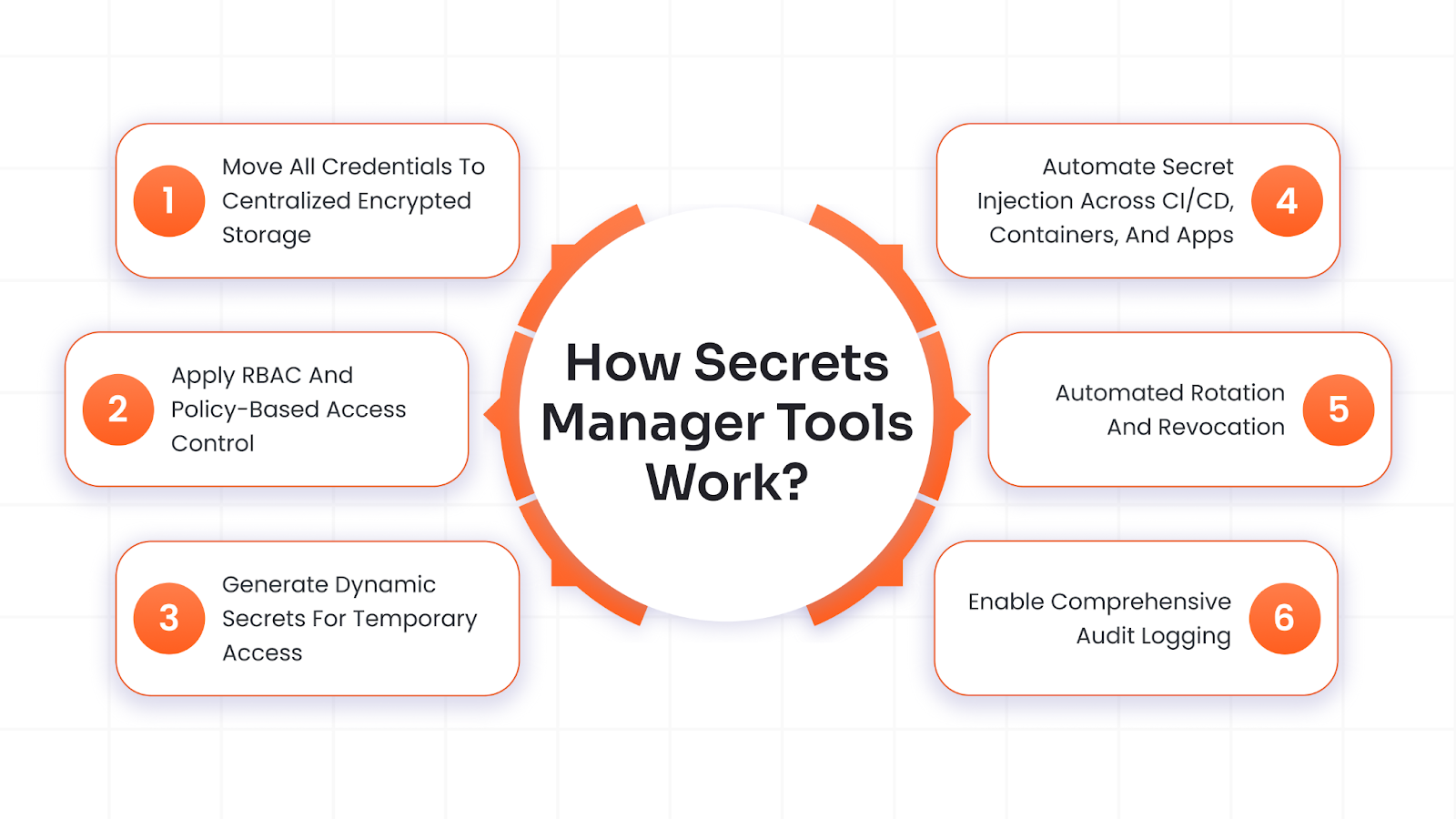
1. Move All Credentials to Centralized Encrypted Storage
This is a fundamental step, where all the sensitive data, such as passwords, certificates, API keys, and more, are stored in one secure digital vault.
They are encrypted at rest with AES-256 (a cryptographic standard) and managed by a Key Management Service (KMS) for top protection against theft.
2. Apply RBAC and Policy-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) assigns permissions by job function, like developers get read-only views, while ops teams handle updates.
Policies enforce rules like time limits or IP restrictions, ensuring no one gets more access than needed. They also enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), so apps receive only the minimum credentials necessary to do a task.
3. Generate Dynamic Secrets for Temporary Access
On request, the tool creates temporary, unique credentials tailored to the task, such as a short-lived database token valid for one hour. These auto-expire, slashing the time attackers have to exploit stolen ones.
4. Automate Secret Injection Across CI/CD, Containers, and Apps
Automated secret injection securely delivers credentials to apps, pipelines, and containers right when needed, skipping risky manual steps.
Furthermore, secrets managers push credentials directly into runtime environments via APIs, ensuring they never hit files, logs, or human hands. This happens instantly as services start up, like during a container launch or pipeline stage.
The secrets manager directly connects with Docker (injects env vars at build), Kubernetes (mounts as volumes in pods), Jenkins/GitLab CI (fetches per job), and Terraform (provides on apply).
Developers code against APIs instead of copying secrets, automating everything end-to-end.
5. Automated Rotation and Revocation
Automated credentials rotation is when the tool changes secret values on a schedule, like daily or monthly, updating both the central vault and the target system (e.g., a new password pushed to AWS IAM or MySQL). This limits damage if a secret leaks, as attackers get locked out after expiry.
Revocation is when, on alerts like breaches or employee exits, the manager instantly invalidates the secret across all systems via APIs, blocking all use without delay. No manual hunting needed; access dies in seconds.
6. Enable Comprehensive Audit Logging
Comprehensive audit logging creates an unchangeable record of every secret access, essential for security monitoring, breach investigations, and regulatory compliance.
Every interaction, successful or failed, gets logged automatically with details like user ID, secret name, timestamp, IP address, and action type, stored in a tamper-proof central system.
Security teams analyze logs for anomalies (e.g., unusual access spikes), trace attack paths during incidents, and generate reports proving adherence to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2 without manual effort.
Secrets Management Best Practices
Secrets management best practices minimize risks by automating security, limiting exposure, and ensuring traceability across DevOps and enterprise environments.
- Automate Secret Rotation: Schedule automatic changes to secrets (e.g., daily or weekly) in the vault and target systems like databases or cloud IAM, reducing breach windows from leaked credentials.
- Enforce Least Privilege and RBAC: Grant access only to what's needed via roles (e.g., read-only for devs, full for admins) and policies that restrict by time, IP, or context, preventing overuse.
- Use Dynamic Secrets: Generate short-lived, on-demand credentials for sessions or tasks instead of static ones, auto-expiring them to slash attack opportunities dramatically.
- Segregate Secrets Across Environments: Keep development, staging, and production secrets isolated in separate vaults or namespaces to avoid test data leaks impacting production systems.
- Integrate Secrets in CI/CD Workflows: Fetch secrets via APIs during builds, tests, and deploys in tools like Jenkins or Kubernetes, avoiding hardcoding or log exposure entirely.
- Frequent Auditing and Monitoring: Review immutable logs regularly for anomalies, set alerts on suspicious access, and conduct scans to detect unmanaged secrets across code and infrastructure.
- Use Encryption At Rest and In Transit: Protect stored secrets with AES-256 and keys from a KMS, plus TLS for all API calls, ensuring data stays secure even if storage is compromised.
Choosing the Best Secrets Management Tool
Choosing the right secrets management tool requires evaluating your organization's scale, cloud setup, compliance needs, and DevOps workflows against key criteria like integration ease, security features, and cost.
Prioritize tools with strong audit logs, API/CLI compatibility for CI/CD (Kubernetes, Jenkins), and developer-friendly UIs like Doppler or Infisical, while checking pricing models, open-source options like HashiCorp Vault suit self-hosted control, but managed SaaS (Akeyless, Keeper) reduce ops overhead.
Solutions like miniOrange PAM extend secrets management with enterprise-grade privileged access controls, session auditing, and policy-driven access, making it more suitable when secrets protection must align with broader PAM and compliance objectives.
Finally, validate vendor lock-in risks, compliance certifications (GDPR, SOC 2), and scalability via POCs, ensuring seamless secret injection without exposure in pipelines or code.
miniOrange PAM: Ultimate Protection for All Your Secrets
miniOrange PAM comes with an integrated privileged password management system, which goes beyond just managing privileged user accounts, to managing all kinds of secrets - SSH keys, service scripts, etc.
With the miniOrange PAM solution, you can:
- Auto-Discover Privileged Assets: Scans and identifies sensitive accounts, keys, and data across endpoints, servers, clouds, and apps for full visibility without manual effort.
- Granular RBAC Access Control: Role-based permissions enforce least privilege, with policies for just-in-time access, approvals, and contextual restrictions.
- Automatic Secrets Injection: Delivers credentials securely into apps, containers, and pipelines via APIs, supporting app-to-app communication without exposure.
- Password and Secret Rotation: Automates regular rotation and resets for passwords, keys, and vaults.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective secrets management transforms a hidden vulnerability into a strategic advantage, enabling secure, and scalable DevOps while thwarting breaches that cost millions.
By centralizing credentials, automating rotations, enforcing least privilege, and providing full visibility, organizations can eliminate hardcoded risks, support dynamic cloud-native workflows, and meet compliance demands effortlessly.




Leave a Comment