Businesses must protect sensitive information because cyber threats continue to grow, and billions of data records are exposed each year.
So, there is a need for secure access to the data, which can be achieved with advanced authentication and authorization solutions such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Single Sign-On (SSO), adaptive security, and more. But what exactly is the meaning of authentication and authorization? Well, basically, authentication verifies identity ("Who are you?"), and authorization controls permissions ("What can you do?").
These two components help to mitigate security risks better for businesses. The following blog explains authentication and authorization, along with the differences between them. We will also understand how miniOrange can defend your organization against contemporary cyber threats.
What is Authentication (AuthN)?
Authentication is the primary and foremost step of verifying users’ identity, who are trying to gain access to their accounts, business data, or web applications. An authentication solution helps your business to fulfill data privacy regulations and protect resources from fraud, scams, data breaches, and other malicious cyberattacks.
Additionally, user authentication is carried out through Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) methods, which include biometric authentication, SMS/email-based OTP, push notifications, and more. These are exclusively offered by the miniOrange authentication solution.
How Does User Authentication Work?
User authentication is essential because it serves the purpose of confirming that a person or entity matches their declared identity. It is also an essential function in accountability systems because it establishes user-specific action tracking, which supports security and compliance audit trails.
At the core, user authentication is simply making sure that the system knows who the person is.
User Authentication Workflow
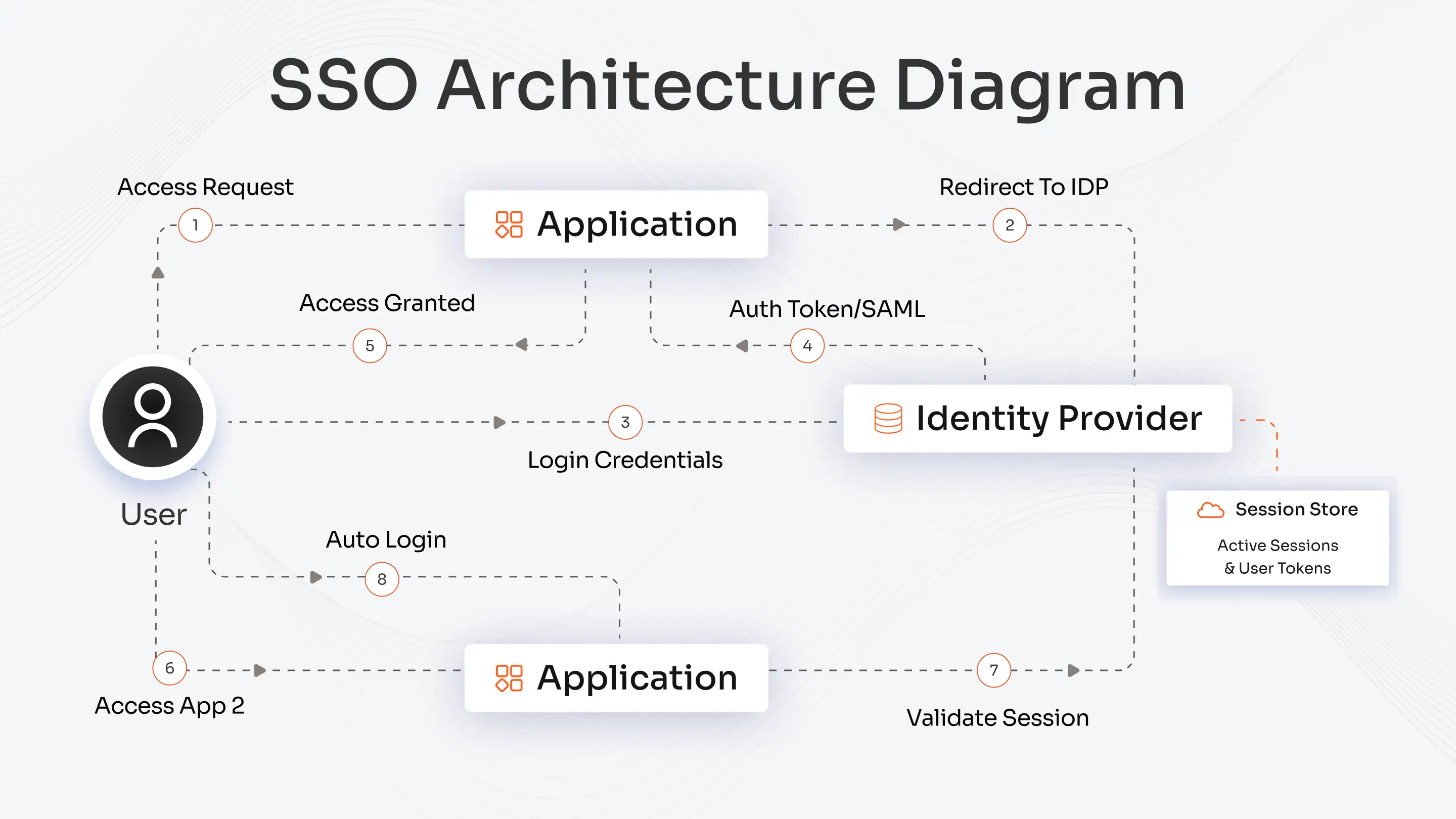
- Credential Input: The user authentication process begins when the user enters credentials (username and password) into the system/server/Identity Provider (IdP).
- Credential Verification: The system or an IdP (Google Workspace, Microsoft, or Okta) checks these credentials against the pre-stored user data in the directory (e.g., Active Directory or LDAP).
- Validation: If the credentials are correct, then the IdP sends a session confirmation.
- Access: After this, the user is granted access to the apps or resources.
Token-Based Authentication Workflow
This authentication workflow can be taken a notch higher with the token-based authentication, where a JSON Web Token (JWT), an encrypted token, is issued once and used till it expires. Usually, JWT is stored in the user’s app and sent for every request to verify identities.
- User Login: The user enters their username and password in the client application. Credential Verification: These credentials are sent securely to the IdP or authentication server, which verifies them against stored user records.
- Token Issuance: Upon successful verification, the IdP generates and signs a JSON Web Token (JWT) containing the user’s identity, roles, and permissions.
- Token Storage: The client application securely stores the JWT, typically in secure HTTP-only cookies or session storage (local storage is generally discouraged due to XSS risk). Requesting Resources: For every subsequent API request, the client includes the JWT in the Authorization header using the Bearer format.
- Token Validation: The server validates the JWT’s signature, issuer, expiration time, and claims to ensure it’s authentic and current.
- Access Granted: If the JWT is valid, the server processes the request and grants access to the requested resource. If invalid or expired, the server denies access or requests reauthentication.
- User enters username into the system or server
- The system sends magic links, push notifications, or an OTP to a verified device
- The user confirms their identity by entering the OTP or code, clicking on the magic link, or approving the push notification
- The system confirms the user action and grants permission to access the app or resources
- Authentication: Firstly, the user’s identities are confirmed (as we discussed above).
- AuthZ Request: Post authentication, the user can request access to applications/resources. The request encompasses username, attributes, roles, and groups.
- Evaluation: The Access control system receives an authorization request and evaluates whether the user can access the requested resource or not. Usually, policies are verified in this case.
- Decision: Based on the policies, the system either grants or denies the user’s request.
- Logging User Activities: The system records everything, including logins, session time, access time, the user’s identity, and more.
- Revoking Access Permissions: User access permissions can be revoked at any time, either automatically (based on access policy rules) or manually via an admin.
Passwordless Authentication Workflow
Another authentication method is the passwordless way, where users are validated without a password, and it works as follows:
What are the Common Types of Authentication Methods?
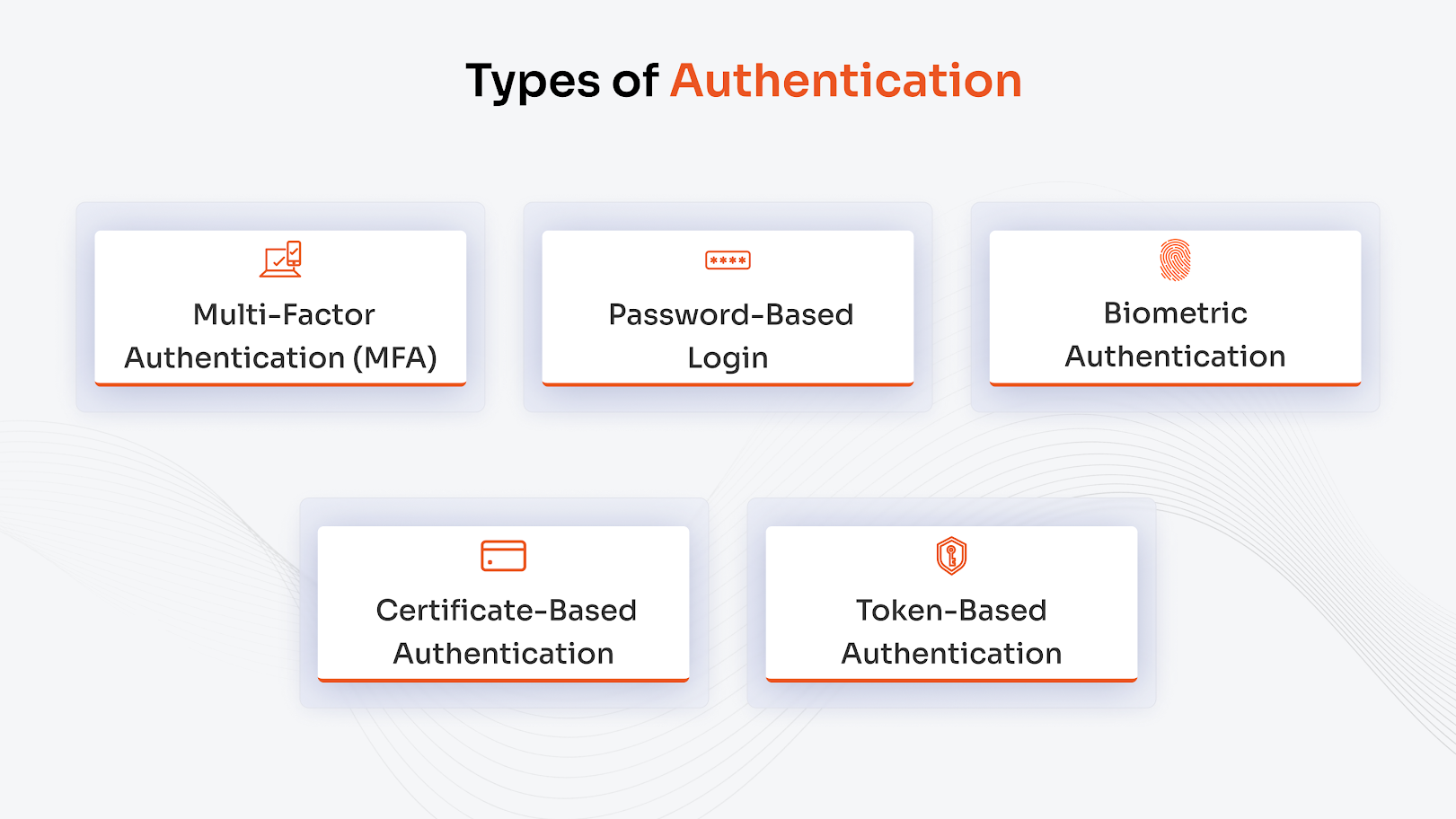
Businesses can secure their data and systems with user authentication, which is carried out using multiple authentication methods as explained below:
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an authentication method offering an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity with more than just a password.
Typically, users enter their username and password, then confirm their identities with various MFA methods, such as a one-time code via SMS/email, push notifications, hardware token, or mobile authenticators (like Google, Microsoft, Authy, etc.).
The miniOrange MFA product exemplifies this approach by enhancing the traditional password-based login with an additional layer of protection that can be tailored to your organization’s specific security needs.
Read about the Importance of the MFA product for your business
2. Password-Based Login
The combination of username (or mobile number) and password serves as the standard login method. Users who manage multiple online services tend to reuse passwords or forget them, which creates vulnerabilities to phishing attacks and data breaches.
Advanced multi-factor authentication solutions have become necessary because traditional password-based methods no longer provide adequate security.
3. Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication relies on storing physical characteristics like fingerprints, retina/iris patterns, facial features, and voice to verify user identity during each access attempt. Biometric authentication is gaining popularity due to its myriad benefits, including passwordless logins, quick user authentication, and increased security, as characteristics cannot be replicated.
On the other hand, false positives and false negatives of a biometric system can be considered as a major disadvantage. Further, the biometrics method finds its preferred use in corporate offices and airports because it provides strong security while maintaining an easy user experience.
1. Fingerprint
Fingerprint scanning is a biometric authentication method that verifies a user’s identity using their unique fingerprint patterns.
So, basically, the user places a finger on the scanner, which captures an image of the fingerprint using optical, capacitive, ultrasonic, or thermal sensors. The system analyzes the scan to detect unique fingerprint features such as ridge endings, bifurcations, and patterns.
From these features, a mathematical template, not the raw fingerprint image, is generated and securely stored (typically encrypted) on the device or in a database. When the user attempts authentication again, a new scan is captured and converted into a template. The system compares it to the stored one; if it matches, access is granted; if not, access is denied.
2. Retina and Iris
A strong light from a scanner shines into the eye to detect particular patterns in the eye's colourful ring surrounding the pupil in this biometric.
The scanned pattern undergoes comparison with database information. The accuracy of eye-based authentication gets disrupted when people use contact lenses or spectacles.
3. Facial Recognition
The process of facial authentication requires multiple facial aspects to be scanned from individuals attempting access to specific resources.
The results of face recognition become inconsistent when comparing faces from different perspectives or when dealing with similar-looking individuals, such as family members.
4. Voice Recognition
Voice tone information gets stored along with a standard secret code through the same procedure as above. The system performs a check because users need to speak each time they want access.
Get an in-depth insight into the top 11 types of biometric authentication
4. Certificate-Based Authentication
Digital certificates operate like driver's licenses to establish identities through certificate-based authentication, which combines public keys with trusted digital signatures.
The system authenticates users and devices through secure cryptographic methods by validating the certificate and verifying possession of the matching private key during server access.
5. Token-Based Authentication
Token-based authentication requires you to enter your credentials once to receive an encrypted token that proves your access, so you don't need to re-enter credentials for subsequent logins. This method is commonly used because it works with RESTful APIs for multiple frameworks and clients.
What is Authorization (AuthZ)?
After authentication, the authorization process determines and grants permissions to users' systems and applications. Authorization controls access to resources and actions by allowing entities only the permissions they have been explicitly granted while following security principles, including least privilege access restrictions and role-based access control (RBAC) with predefined roles for permission assignment.
The authorization system in modern frameworks uses attribute-based access control (ABAC) to make decisions based on user attributes. Authorization defines permissions and access levels to safeguard sensitive data and systems while reducing security risks and meeting legal and organizational standards.
How Does User Authorization Work?
Authorization depends on the user’s permissions, and this is how it works:
What are the Common Types of Authorization Methods?
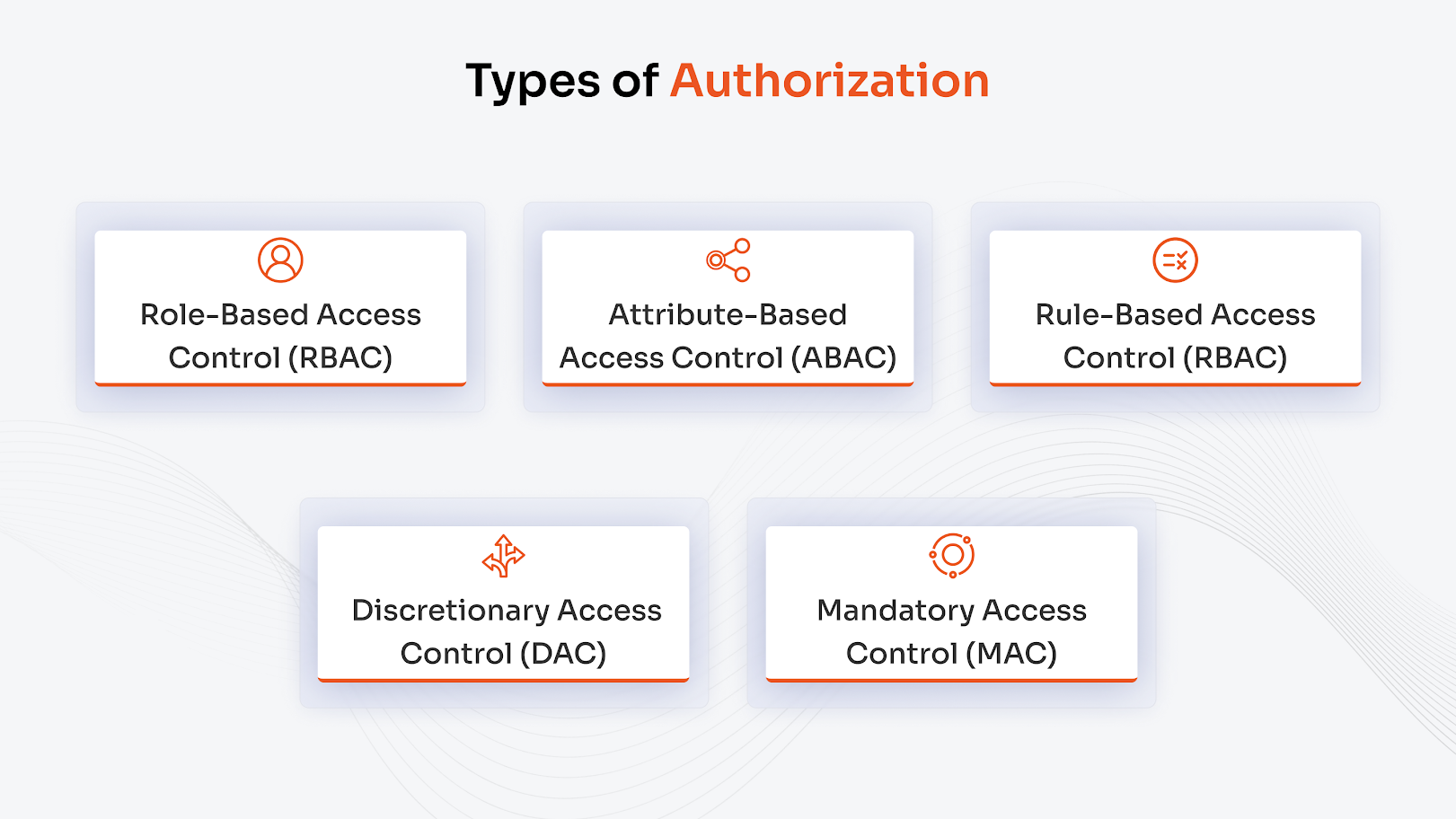
Following authentication, authorization determines access permissions, which are based on organizational policies, and what data users can read and what actions they can perform or delete. Common authZ methods are as follows:
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
The RBAC is an authorization technique where end-users are granted access to applications, systems, and data based on the user’s predefined roles/permissions. For example, the system grants regular employees access only to their HR information, which includes salary data, leave reports, and benefit details, but HR managers can handle every employee record with full access to additions and updates, and deletions.
RBAC enables efficient task performance by users while protecting sensitive information because it links access privileges to specific roles.
2. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
Attribute-based Access Control (ABAC) differs from RBAC because it bases permission grants on specific attributes instead of user roles. The system uses attributes to determine permissions, which can be derived from user characteristics (role, department, clearance level), environmental factors (location, time, organizational risk status), and resource characteristics (data classification and ownership).
The systematic structure provides dual protection for essential assets as well as efficient operational performance through customized access rights that adapt to different organizational requirements.
3. Rule-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Rule-Based Access Control (RBAC) allows user access to systems based on pre-defined rules. The admin determines the conditions that the users must meet before granting them access to the requested resources.
Rule-based systems compare user credentials to the rules database, and if the users satisfy the conditions explained in the database, they’re granted access; otherwise, they’re denied entry.
4. Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) is an authorization method where the owner of the data or resource decides who can access it and what actions users can undertake with it, such as write, edit, or read.
DAC has a decentralized model; it is flexible in nature and user-centric. It can be found in applications like Google Docs or file systems.
5. Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is a type of security approach in which access decisions are made by a central authority, which is based on system-wide policies, and not by individual users.
MAC is usually applied to that information, which, if compromised, can harm an entire organization. Types of files protected with MAC are trade secrets, Protected Health Information (PHI), financial data, or blueprints. Governments and defense sectors often use MAC to safeguard their information.
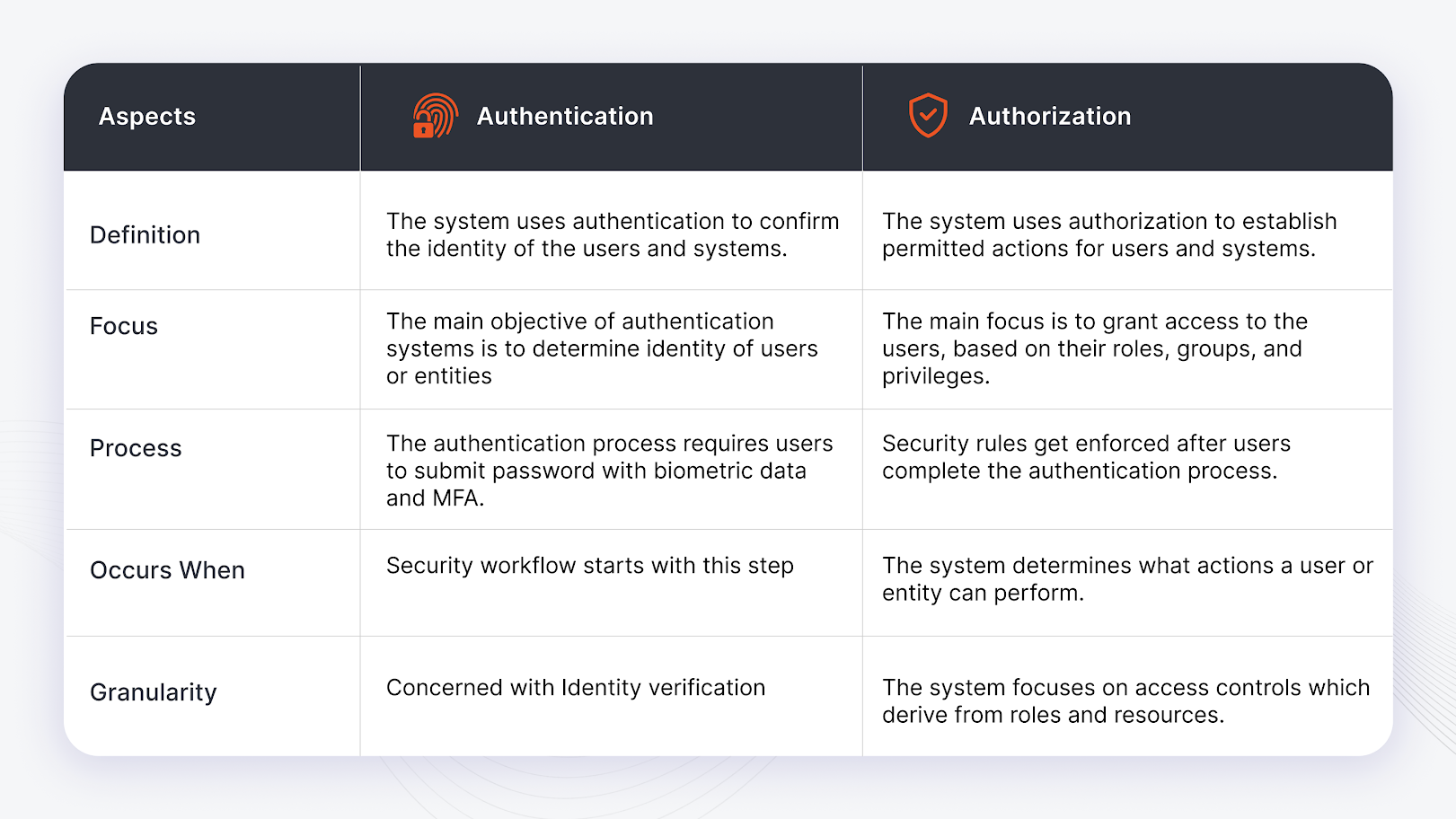
What is the Difference Between Authentication and Authorization?
The following table signifies the key differences between authentication and authorization.
Authentication and Authorization in Cloud Computing
Cloud security depends heavily on authentication and authorization processes. The authentication process confirms user identity through password verification, OTPs, and biometric scanning to authorize legitimate access to cloud services.
The system uses authorization approaches to establish user permissions after authentication by defining access levels according to user roles and responsibilities. The combination of these security processes protects customer data stored in shared infrastructure and enables secure scalability.
How Can miniOrange Help You Implement Authentication and Authorization in Your Organization?
Top-notch organizations rely on miniOrange to simplify authentication and authorization processes. The platform provides Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) solutions, and advanced access management solutions, which allow users to access multiple applications and platforms seamlessly.
Our solutions optimize security while providing a smooth user experience to help you meet regulatory standards and protect sensitive data.
Start your organizational transformation today by contacting us to learn more or beginning a free trial to experience the benefits firsthand. The miniOrange IAM solution simplifies complex IAM operations so your business can maintain its forward momentum.
Conclusion
Authentication reveals identity, while authorization defines permissible actions. These two security elements create the fundamental structure that protects your important data and maintains user trust.
The combination of modern authentication methods, including context-based authentication and learning about MFA, protects your systems from current threats while providing future-ready security.
FAQs
What are the different types of authentication?
Authentication exists in three main categories, viz., knowledge-based, possession-based, and biometric-based authentication. Knowledge-based methods consist of something you know (passwords, PINs). Possession-based methods include something you have (security tokens, smart cards). Biometric-based methods include something you are (fingerprints, face recognition).
What is authentication in cybersecurity?
The authentication process verifies user or system identity to secure resource access for authorized entities who interact with sensitive data.
How does authorization work?
After authentication success, authorization decides if users or systems have permission to access resources or execute particular actions, based on access policies.
What are the common types of authorization?
Common types of authorization methods include Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), Mandatory Access Control (MAC), Discretionary Access Control (DAC), and Rule-Based Access Control (RBAC).
What are authentication and authorization in API?
APIs use authentication to confirm the identity of requesters through API keys and OAuth tokens, but authorization determines if the authenticated requester has permission to access or modify resources.
What is identity authentication?
Identity authentication verifies the identity of people, devices, and services to grant secure access to systems and resources. Organizations use identity authentication as a fundamental cybersecurity element to stop unauthorized access and defend their sensitive information.



Leave a Comment