5 Reasons to Deploy Context-Based Authentication for Your Organization
We are living in an age of rapid technological evolution and progression which none of our ancestors witnessed before. It took centuries for mankind to build a computer but mobile devices and microchips were built within a decade. The world wide web has brought the world together as a global village but these high technological capabilities in the wrong hands can do a lot of malice, especially to budding organizations and businesses.
Organizations are at greater risk from cyber attacks today. According to the research report by Risked Based Security, “Compared to the midyear of 2018, the number of reported breaches was up 54% and the number of exposed records was up 52%. Over 7 billion records were stolen in the third quarter of 2019.” The year 2019 is considered to be the “worst year on record” for breach activity.
“Are you doing enough to secure your business?”
In today’s digital landscape, securing sensitive data has become more crucial than ever. With the rise of cyber threats and data breaches, traditional password-based authentication systems are no longer sufficient to protect valuable information and data. As a result, many organizations are implementing context-based authentication as a more effective means of verifying the user or customer identity.
What is Context-Based Authentication?
Context-based authentication is a type of authentication that uses additional contextual factors beyond just a username and password to determine if a user is authorized to access a system or application. These additional factors can include location, time of day, the device used, and other context-based information. By incorporating these factors, context-based authentication can provide organizations and their employees with more protection from security breaches, password leaks, privacy breaches, personal data breaches, etc.
For example, if a user is trying to access an application from a new location, the system may prompt them to provide additional authentication factors such as a one-time password or a security question. This helps ensure that the user is who they claim to be, even if their login credentials have been compromised.
Context-based authentication can also take into account other factors such as the user’s behavior and past activity. By analyzing patterns and trends in user behavior, context-based authentication can detect and prevent fraudulent activity in real time, providing an added layer of security.
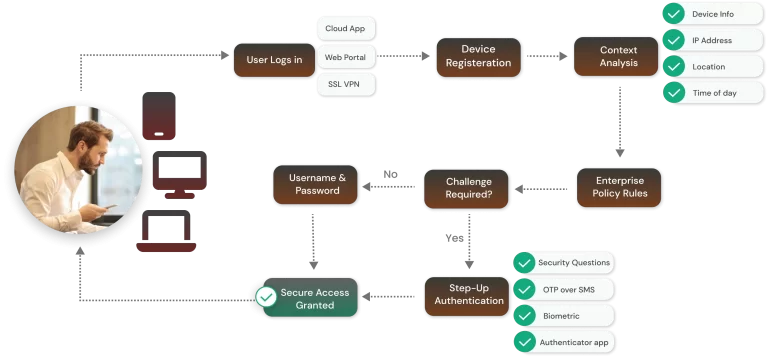
What are the Different Types of Context-Based Authentication?
There are many types of context-based authentication that organizations can deploy depending on their specific needs and security requirements. The most popular types of context-based or adaptive authentication are Location-based, Time-based, Device-based, Behavioral-based, and Risk-based authentication. These various types of context-based authentication will safeguard workforce identity for organizations and also customer identity in certain cases.
Location-Based Authentication
Location-based authentication method uses the user’s physical location to determine if they are authorized to access a system or application. For example, if the employee of an organization usually logs in from a specific geographic location, but suddenly attempts to log in from a different location, the system may prompt them to provide additional authentication factors under multi-factor authentication. This is very useful in the case of work from home employees who would usually log in from their home location.
Time-Based Authentication
The time factor used by this type of Adaptive Authentication method determines if a user is authorized to access a system or application. For example, if the employee of an organization typically logs in during business hours set by that particular organization (eg. 9 am to 6 pm), but if login is attempted by some hacker at late night (eg. 1 am), the system may prompt them to provide additional authentication factors. Because that additional 2FA factor will be sent directly to the employee, and the attempt by the hacker will be rendered unsuccessful.
Device-Based Authentication
This type of adaptive authentication records information about the user’s device and uses that data to determine whether the user is authorized to access a system or application. For example, if an employee typically logs in from a specific device like their office laptop, but suddenly the login is attempted from a different device outside the organization, the system may prompt them to provide additional authentication factors to verify the workforce identity of the employee.
Behavioral-Based Authentication
The information about the user’s behavior is used to authenticate contextual access for users to systems or applications they need. For example, if an employee displays a certain behavioral pattern according to which they typically access an organizational application from a specific location, at a specific time, and using a specific device, then any deviation from this pattern could trigger additional authentication measures. This method is the most secure adaptive authentication method which is popularly used with multi-factor authentication. Behavioral data is also used in Biometric authentication, which can be used to authenticate both workforce identity and customer identity.
Risk-Based Authentication
A risk-based approach is used in this type of context-based authentication, which is also known as risk-based authentication. Using this risk-based approach, it is determined which level of user authentication is required based on the perceived risk of the login attempt. For eg., if a user (which can be an employee or customer of a business) is attempting to log in from a high-risk location, the system may require additional authentication factors to be provided otherwise If your customer is trying to log in from a safe location, from their usual device, then additional authentication factors are not needed because the risk is very low. This form of authentication can also remove login hassles and security threats for your customers. This way the customer identity is safe in different risk scenarios.
5 Reasons: Why Deploy Context-Based Authentication?
It is evident that Context-based authentication is a highly advanced security mechanism because it evaluates various contextual factors to determine whether or not to grant access to a system or application. Here are five reasons why organizations should deploy context-based authentication to secure both workforce identity and customer identity:
1. Enhanced Security: Contextual access provides an additional layer of security beyond traditional authentication methods such as passwords, pins, or tokens. It evaluates contextual factors such as user location, the time factor, device type, and network connectivity to determine whether or not access should be granted. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches. Even if the user credentials are compromised, a hacker cannot access the user’s account because the deviation in context will trigger multi-factor authentication like OTP sent to the user’s mobile.
2. Improved User Experience: The user experience of both the employees and customers of an organization or business can be significantly improved by reducing the need for users to remember multiple passwords or credentials. Users can simply log in from their devices and access the system or application based on their contextual factors. Contextual access can help to reduce frustration and increase productivity. Also, a more secure environment helps to build a strong trust factor and reputation among the customers, employees, and stakeholders. This is extremely crucial for the success of any organization.
3. Compliance: Many regulatory compliance frameworks require companies to implement advanced security measures to protect sensitive data. Many of these compliances are enforced by the local governing bodies and for any business which may be locally based or multi-national, following these compliances are very crucial in order to function in that particular region or country. For multi-national companies, thing gets more complication as they have to follow multiple compliances set by governments of different countries. Context-based authentication can help organizations to meet these compliance requirements by providing an additional layer of security beyond traditional authentication methods.
4. Cost-Effective: Every organization should focus on cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. Being cost-effective doesn’t mean spending less, it means every penny you invest is for the righteous cause which brings positive results for the betterment of your business. Cost-effective solutions can help in scalability and bring growth to your organization. When it comes to secure authentication, Context-based authentication can be a cost-effective security measure because it reduces the need for expensive hardware or software-based authentication methods. It can also reduce the unnecessary costs associated with password resets and help desk support.
5. Scalability: When any organization decides to spend on security then it is very important to focus on the scalability factor. The security solution must be able to meet the growing demand of the organization. If 100 people organization when grows to 1000+, then the security solution also must simultaneously scale in order to cater to the increasing headcount. Similarly, this might be the case with a growing customer base. Context-based authentication can be easily scaled to meet the needs of a growing organization.
Use Cases of Context-Based Authentication
Context-based authentication is a kind of adaptive authentication mechanism that considers various contextual access factors, such as location, time, device type, and user behavior, to determine the level of access a user should have. Here are some common use cases of this kind of authentication method:
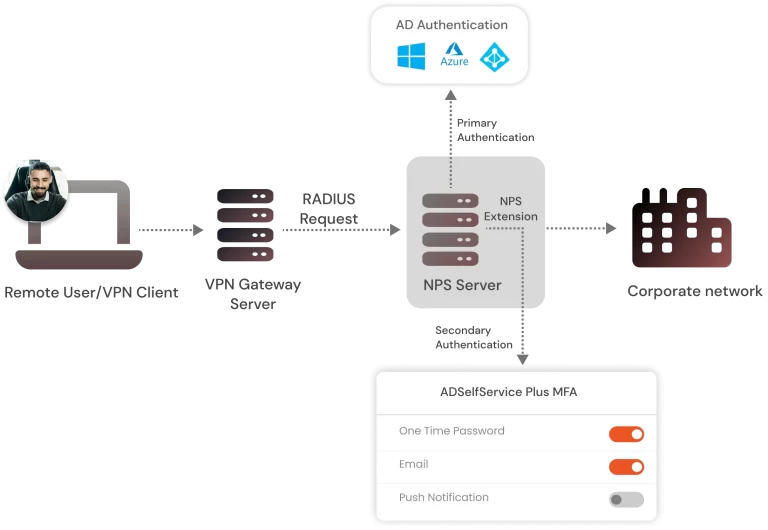
Case 1: Remote Access For Work From Home Employees Context-based authentication is particularly useful for remote access scenarios where a work from home or remote employee is accessing company resources from outside the corporate network. Let’s assume that the company has a team of remote employees who need to access the company’s internal network to work on projects and access sensitive data. Remote employees will require to access sensitive organizational information for their work. But there is this risk of sensitive information leak/theft if their system or network is hacked by cybercriminals.
To solve this problem, the company has implemented contextual access. Once the remote employee enters their login credentials, the system matches their credentials in the database, and if a match is found, then the user will be faced with a context-based authentication challenge. In this challenge, the user’s location and time of login will be analyzed and if any deviation is found then the challenge will require the remote employee to provide additional authentication factors to confirm their identity. Only upon successful completion of the challenge they will be granted access to the internal network.
Case 2: Contextual Access in eCommerce Websites
Context-based authentication can be a crucial security measure for eCommerce websites, particularly during the checkout process. Let’s assume that an eCommerce website is facing customer dropout in numerous instances. The troubleshooting team identified that most customers are opting out because the payment is not secure and there is a considerable risk that customers’ payment information may be leaked to cyber criminals. Fraudulent transactions have also been reported in many instances. Hence, the company needs to make the payment experience more secure to win back the trust of its customers.
To solve this problem, the eCommerce website has implemented Multi-Factor Authentication with contextual access beyond a customer’s username and password to verify their identity and protect their sensitive payment information. The website is using location-based factors such as the customer’s IP address, or device-based factors such as the device’s unique identifier. When the customer attempts to log in to make a payment while purchasing an item, contextual parameters like IP address and device used are checked. If a deviation is found then the website prompts additional factors like biometric verification. This way the eCommerce website ensures that the customer making the payment is the authorized user and prevents unauthorized access or fraudulent transactions.
Overall, implementing context-based authentication in the eCommerce checkout process can provide an added layer of security and help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive payment information. This will increase customer trust and confidence in the website and lead to increased successful transactions.
miniOrange as an IAM Provider, have a specialized security team responsible for implementing and maintaining the security protocols for context-based authentication for our clients. They will ensure that the authentication system is user-friendly, reliable, and efficient. Additionally, they will provide appropriate training and support to the client’s employees, stakeholders, and customers to ensure that they understand the authentication process and can use it effectively.
In Summary
Contextual access is no doubt the best passwordless security solution for modern businesses to secure their offline and online resources for their customers, employees, and stakeholders. In the future, this technology is going to become more personalized and secured with AI & ML.
The best time to invest in Context-Based Authentication is – TODAY!
With miniOrange IAM solutions, you get a whole suite of security services like Single-Sign On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Risked-Based or Context-Based Authentication (also known as Adaptive Authentication), and many more. You can access any one or combinations of them or all as per the security requirements of your organization. You get both On-Premise and Cloud solutions. We got you covered on all fronts, all you need is to choose a customized service for your business or we have specialists to help you with that also. You can request a demo and try out our service before investing in the full-scale solution.
Author




