The security protocols of industries underwent a transformation through biometric authentication, which uses distinctive physical and behavioral traits. Organizations currently adopt biometric solutions to protect sensitive information and block unauthorized access because cyber threats continue to advance in complexity. The security transformation leads through miniOrange because their authentication solutions merge perfectly with current infrastructure systems.
Our digital environment demands authentic methods of verification like never before. The miniOrange Authentication Solutions unite advanced biometric technology with secure frameworks that defend organizations from modern threats while keeping users convenient and meeting regulatory requirements.
What are Biometrics?
Biometrics describes specific measurable biological characteristics together with behavioral patterns that serve to distinguish individual people. The identification system uses both physical characteristics, including fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns and voice recognition, and behavioral characteristics, including typing rhythm, gait analysis and signature dynamics. The unique characteristics serve as perfect security identifiers because they are both quantifiable and resistant to duplication.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication verifies identity through biological or behavioral characteristics, which replace traditional passwords and PINs. Learn how to enhance security by using Biometric Authentication, as biometric traits provide superior protection against unauthorized access because they remain unique to each person and cannot be shared, stolen, or forgotten. Learn how to enhance security through biometric authentication, which offers strong protection for systems and sensitive data.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work?
The three-step procedure of biometric authentication operates as follows. The first step of enrollment uses sensors to collect biometric information from users, which gets stored as encrypted digital templates in a secure database. The system requires a new biometric data capture from users during authentication procedures. The verification process compares the newly collected sample to the stored template through advanced algorithms that examine essential points and patterns. The system grants access when the match confidence reaches above the established threshold. The entire process runs in seconds to provide both security features and convenient access.
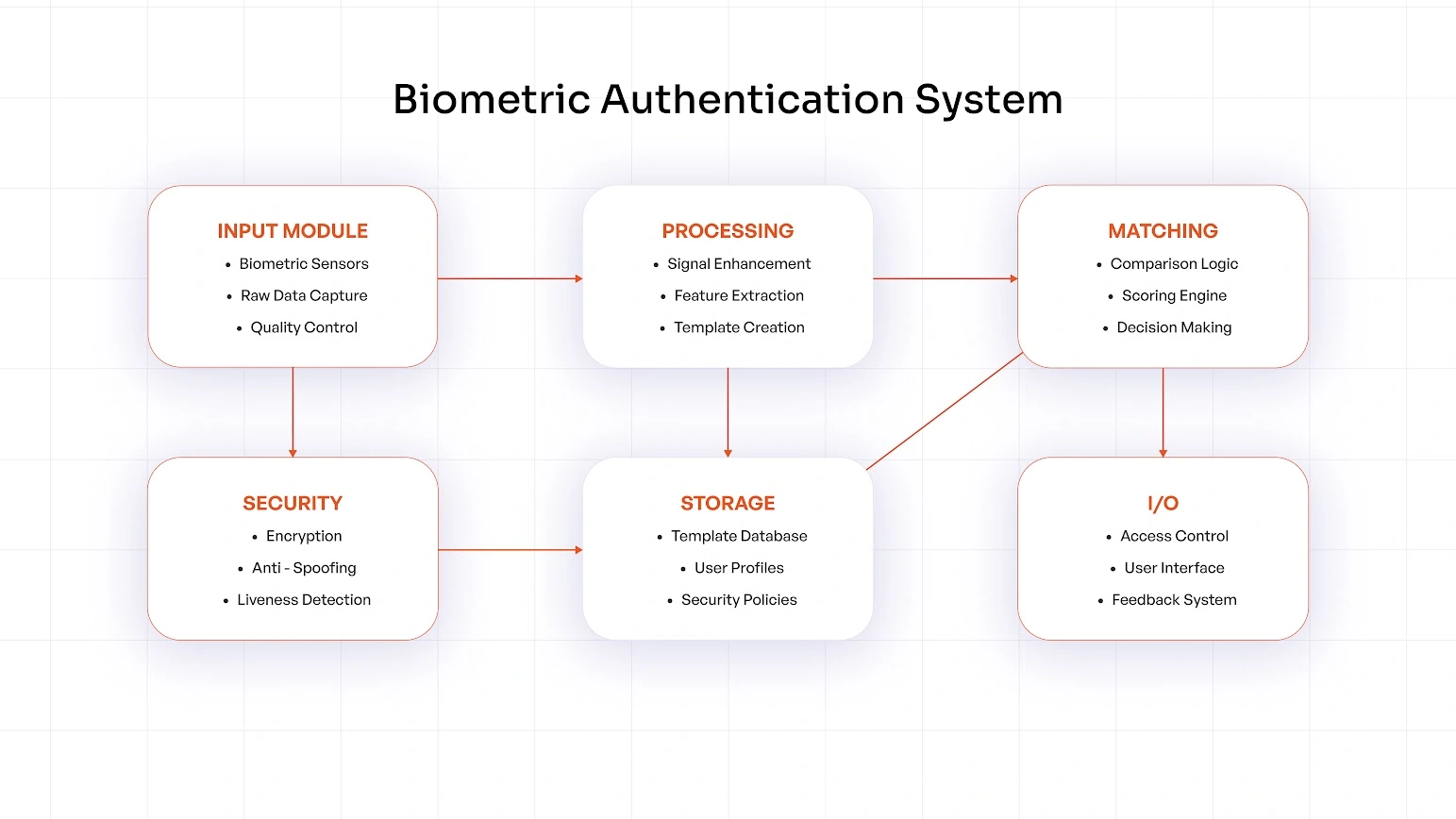
Advantages of Biometric Authentication
Learning about the advantages and disadvantages of biometric authentication improves informed decision-making for different business cases. Here are some of the key benefits of biometric authentication:
1. High Security and Assurance
Biometric authentication establishes high security because it uses distinct personal characteristics, which make impersonation virtually impossible. It is one of the biggest biometric authentication advantages that the security risks from unauthorized access decrease substantially because biometric traits remain with each person and cannot be lost or distributed to others.
2. Convenience for Users
Users no longer need to remember multiple complex passwords or carry physical tokens. The inherent characteristics of users enable authentication without needing additional effort because these traits remain present during verification, thus simplifying the login process.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Biometric verification processes take only seconds to complete, making them much faster than typing passwords or retrieving physical credentials. This major advantage of biometric authentication, the high efficiency of the system, enables better throughput at access points while reducing user friction in busy environments.
4. Reduced Fraud Risks
The extreme difficulty of creating fake biometric identifiers leads to a significant reduction in identity theft and impersonation attacks. The implementation of biometric authentication establishes robust protection against fraudulent activities, especially when used in financial dealings and public services and healthcare systems.
5. Improved User Experience
The unbroken authentication process leads to better user satisfaction because it removes the need for users to manage their credentials. The combination of single-touch and passive authentication systems provides users with a seamless experience, which leads to better adoption rates and decreased support requirements.
6. Compliance with Modern Security Standards
Current regulatory standards either mandate or suggest the implementation of biometric authentication as part of multi-factor authentication systems. Organizations that implement these solutions fulfill GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS and other compliance standards while showing their dedication to security.
7. Near Spoof-Proof
Advanced biometric security system use liveness detection and anti-spoofing technologies to identify authentic biometric samples from forgeries. Security barriers become exceptionally robust when multiple biometric factors operate together in a single system.
8. Flexible and Scalable
Contemporary biometric systems work across different security settings, which range from individual devices to corporate networks. Cloud-based solutions provide uniform authentication across various locations and devices and support the growth of organizations.
Disadvantages of Biometric Authentication
While biometric authentication has many advantages and a few disadvantages, these are some of the factors to be considered before you go for biometric authentication:
1. Privacy Concerns
The permanent connection of biometric characteristics to individual identities creates major privacy problems because these characteristics remain associated with people even after data breaches. Organizations need to handle intricate regulations that govern the consent process and storage and processing methods for this highly sensitive data.
2. High Implementation Cost
The deployment of biometric systems demands significant financial resources for dedicated hardware acquisition and software integration and user registration processes. Organizations need to evaluate both initial capital expenditures and continuous operational costs against anticipated security advantages.
3. Risk of Biometric Data Breach
When biometric templates get compromised, users face severe consequences because their biological characteristics cannot be altered. Secure template storage requires encryption, but it increases system complexity and implementation costs.
4. False Positives or Negatives
Every biometric authentication system contains imperfections in its accuracy performance. Security vulnerabilities emerge from false acceptances, while legitimate users experience frustration due to false rejections. Most implementations struggle to determine the balance point between security measures and user convenience during authentication processes.
5. Limited Accessibility
Users with physical disabilities or medical conditions cannot provide specific biometric samples because of their physical limitations. Organizations need to provide additional authentication options to guarantee accessibility for all users while preventing discriminatory practices.
6. Dependence on Technology
Environmental elements such as lighting and noise, together with dirt contaminants, can disrupt biometric reading processes. Systems need periodic maintenance and updates to preserve accuracy, which generates possible authentication workflow failure points.
7. Software Malfunction
Biometric systems experience unpredictable authentication failures due to algorithmic errors or software bugs. Organizations need to establish strong backup systems that enable them to continue operating business as usual during system technical problems.
8. Fake Positives
Synthetic materials together with deepfakes represent emerging sophisticated spoofing methods that threaten biometric systems. Organizations need to dedicate ongoing funds to anti-spoofing technology development because security threats will continue to evolve.
Real-World Use Cases of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication influences every life daily in many ways, and here are some of the industrial applications of it:
Banking
Financial institutions use biometric authentication to protect mobile banking and ATM access and high-value transactions. The verification of customer identity occurs through voice recognition during call center interactions, and mobile banking apps use fingerprint and facial recognition for security purposes. The implementation of these measures has cut down on fraud while delivering better service to customers.
Government IDs
Biometric identification systems operate as standard practice in passport control and national ID programs and border security operations throughout the entire world. The system uses facial recognition together with fingerprints and iris scans to achieve strong verification of citizen identities. The immigration process becomes more efficient through this technology, while public service identity fraud prevention becomes possible.
Mobile devices
The smartphone industry made biometric authentication mainstream through fingerprint sensors and facial recognition. The security features protect personal information as they provide users with easy device access. The large-scale implementation of biometric technology has made consumers more comfortable with its use, which led to broader adoption across different applications.
Workplace access control
Organizations implement biometric systems to protect their physical facilities together with their digital resources. The combination of fingerprint scanners limits access to restricted areas, and behavioral biometrics tracks system access patterns to detect unusual behavior. The implementation of these systems cuts down credential sharing while generating audit trails for meeting compliance standards.
Healthcare
Medical facilities implement biometric authentication systems to protect patient records along with ensuring accurate medication distribution. The use of palm vein or iris scanning for patient identification prevents medical errors and identity theft. Biometric authentication systems help healthcare organizations protect controlled substances and secure sensitive areas.
Is Biometric Authentication Right for Your Organization?
Your organization needs to assess multiple factors to determine if biometric authentication is appropriate. Your organization needs to assess security needs along with user demographics and financial limitations and regulatory requirements. The organizations that deal with sensitive information or conduct high-value transactions derive the most advantage from implementing biometric systems. Assess security risks extensively to determine if the expected security enhancements outweigh the difficulties of implementation. The deployment should begin with pilot tests in essential areas before expansion, and organizations must offer alternative authentication methods for accessibility purposes.
miniOrange Biometric Authentication Solutions
The miniOrange platform provides complete biometric authentication solutions that work perfectly with current IT infrastructure. The platform accepts various biometric authentication methods, including fingerprint and facial recognition, as well as voice recognition and additional modalities to match organizational security requirements. The solutions from miniOrange adapt to different deployment models, such as cloud and on-premises and hybrid systems, to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes, from small to enterprise.
User experience should never be sacrificed for security, which is why miniOrange MFA Software combines biometric authentication with an extensive authentication framework. The solutions include customizable security policies, advanced threat detection and detailed audit logging capabilities. Contact Us will perform a personalized security assessment to show you how miniOrange strengthens authentication security while improving user satisfaction.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication systems provide enhanced security features that simultaneously improve user access and operational efficiency while resolving privacy and cost and accessibility issues. Organizations should combine biometric security systems with their existing traditional methods to enhance their defense capabilities. The implementation of multi-factor authentication reduces security risks to a minimum because users must complete three verification steps consisting of passwords, one-time codes and biometric scans. Try miniOrange multi-factor authentication with biometric authentication features for free for 30 days.
The passwordless MFA system removes password obligations through device verification, biometric authentication and one-time codes, which provides better security and user experience and decreased IT support costs. Organizations can develop strong security systems by understanding authentication principles. The authentication solutions from miniOrange provide organizations customized security solutions that adapt to different needs with the help of authentication methods.
FAQs
How secure is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication offers strong security through unique traits and convenience, but it’s not foolproof. Hackers can spoof fingerprints and facial recognition, and stolen biometric data cannot be reset. Experts recommend multi-factor authentication using biometrics plus a password or security token.
Can biometric data be hacked?
Biometric data is secure but can be hacked via breaches, spoofing, and system weaknesses; encryption and multi-factor authentication improve protection.
Is biometric authentication better than passwords?
Biometric authentication is more secure and convenient than passwords but works best when combined with strong passwords or multi-factor authentication.
How does biometric authentication work in mobile apps?
Mobile apps authenticate users through fingerprint or facial scan verification against stored data, which is secured. Users can access PIN or password login as a backup option when verification fails.
What are the main problems with biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is secure but vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and weak protection. Breaches are irreversible since biometrics can’t be reset.



Leave a Comment