Air-gapped networks have long represented the gold standard in isolating critical systems from external or internal cybersecurity threats.
Yet, as cyber entities grow more cunning, physical isolation alone leaves dangerous blind spots. From the infamous Stuxnet attack to modern ransomware agents, history shows that network air gaps are not impenetrable.
This blog brings clarity to a security measure, highlighting why Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is now a necessary asset for air-gapped systems, and not just a nice-to-have, but a necessity for critical industry environments, private clouds, and legacy systems.
What is an Air-Gapped Network?

Air-gapped networks are physically and logically isolated from any external connectivity, including the public internet and internal enterprise Local Area Network (LANs).
They exist as standalone “islands”, sometimes in separate rooms or buildings, where strict controls prevent any wired or wireless bridging.
This design reduces the attack surface by making remote attacks nearly impossible. Yet, their very separation can lead to management headaches and operational risks, especially when authentication is not taken seriously.
What are the Challenges of Managing Air-Gapped Networks?
- Complex Management Overhead: Routine tasks like patching, updates, or troubleshooting must happen manually, without remote access and network convenience.
- Higher Operational Cost: Organizations must duplicate key systems (e.g., AD, servers), multiplying effort and expense with each isolated segment.
- Human-Centered Risk: Even in isolated environments, legitimate users access and manage systems, often using vulnerable passwords.
- Data Exchange Pitfalls: Removable media (USBs, drives) used for updates or transfers can introduce sophisticated malware.
- Insider Threats: Rogue employees with privileged access remain one of the largest attack vectors.
Who Uses Air-Gapped Networks and Why?
- Government and Defence Sectors: Enforces regulatory standards (e.g., FIPS-140-2), operates mission-critical and classified systems.
- Critical Infrastructure: Power, manufacturing, air traffic, and transit rely on air gaps to keep industrial control networks resilient and segmented.
- Banking, FinTech, and Finance: Protects sensitive transactions, supports disaster recovery, isolates legacy environments in regulatory compliance landscapes.
- Healthcare: Makes sure about isolated operations for life-supporting medical devices and sensitive patient systems.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated, physically disconnected cloud systems such as Google Distributed Cloud Hosted.
Are Air-gapped Networks as Secure as They Seem?
The security illusion is real, an air gap is not an armor-plated shield. High-profile breaches, including the Stuxnet incident, illustrate that isolated networks are vulnerable to “bridging” attacks. These include:
- Malware infection via USB or external drives
- Electromagnetic and side-channel attacks
- Insider abuse through credential theft or deliberate sabotage
- Light, thermal, or radio-based data exfiltration
Physical isolation only delays the inevitable, once access is needed, the human element reintroduces risk.
Modern day attackers exploit social engineering or physical compromise to gain entry. If authentication relies on a single password, defenders are left exposed.
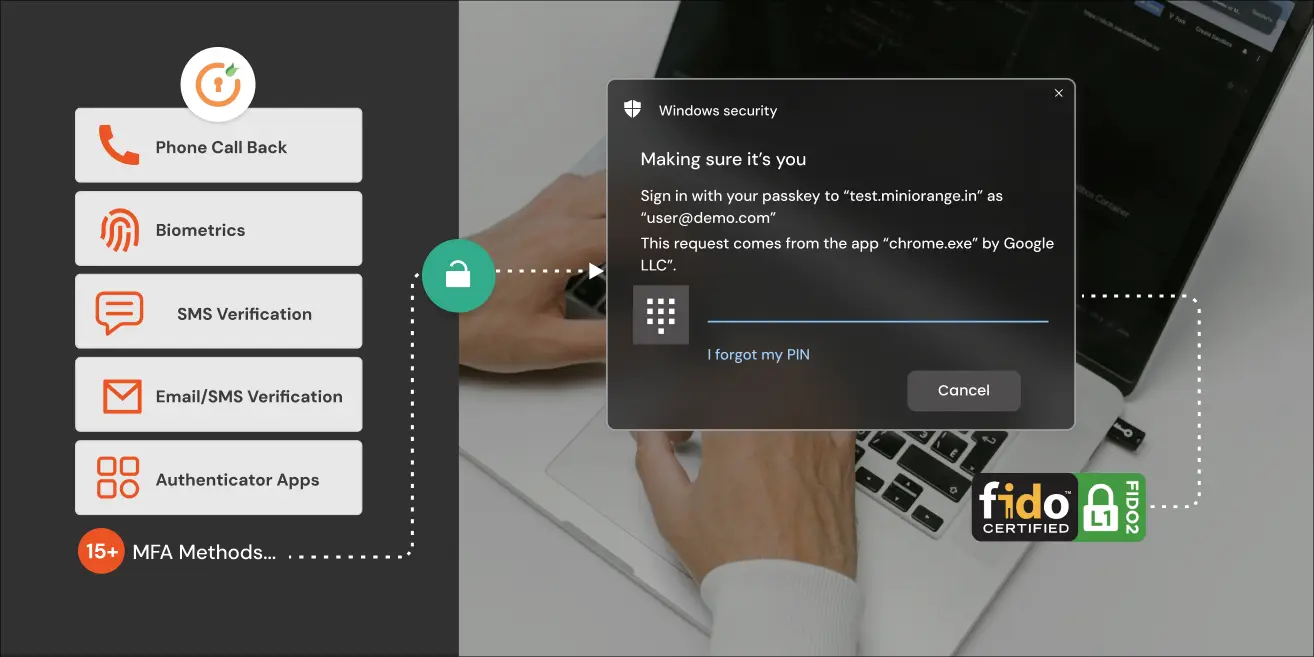
Role of MFA in Air-Gapped Networks
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) helps to bolster security for air-gapped networks. By layering access controls, combining something users know, have, and are, MFA transforms vulnerable spots into a formidable defence.
1. Overcoming the Built-in Security Restraints
- Traditional MFA methods require constant connectivity, leaving air-gapped zones out in the cold.
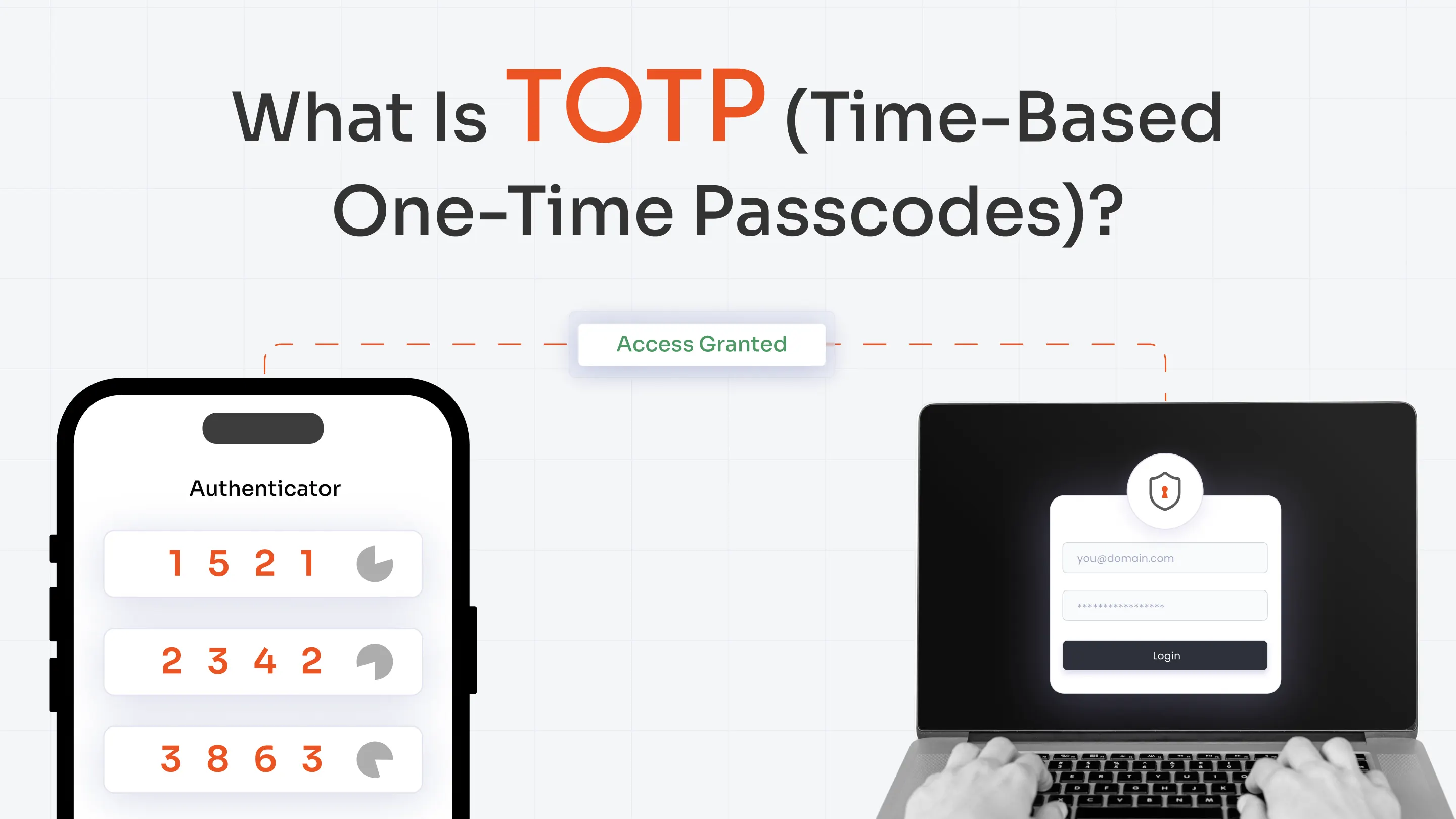
- Offline MFA solutions (TOTP/HOTP tokens, FIDO2 keys) offer critical protections without internet dependency.
2. Hardware Token Support
- FIDO2 and proprietary tokens can validate identities using local protocols, functioning in fully isolated settings.
- Authenticators like YubiKey and Token2 deliver passwordless access with phishing-resistant MFA, without adding complexity.
miniOrange Secure Authentication for Air-Gapped Networks
miniOrange stands out with a purpose-built, deployment-mode MFA framework designed for air-gapped functions.
1. A Dedicated Deployment Mode Agnostic to Internet Connectivity
Fully offline MFA capabilities, no relay to cloud or external servers. User authentication, auditing, and reporting are all contained within the local network.
2. Agentless Architecture with No Code Changes Required
Better integration with legacy applications, Active Directory, workstations, firewalls, and network switches. Eliminates the hassle and downtime of agent-based solutions or disruptive code changes.
3. FIDO2 Compliant Hardware Tokens
Hardware-based authentication (YubiKey, Token2, others) ensures credential privacy and resistance to phishing attacks.
Biometric verification and public key cryptography further boost protection without internet dependency.
4. Granular Access Controls
Role/time/device-based restrictions, session quotas, dynamic access controls by IP or risk signal.
Admins retain fine-grained control to limit exposure during maintenance windows or audits.
5. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Local monitoring tools provide instant notification of suspicious activity, no dependence on remote log review.
Custom policies for automatic response during anomaly detection.
6. Workstation Restrictions
Only approved users/devices can access sensitive machines, preventing lateral movement and privilege escalation.
7. Air-Gapped Network Auditing and Reporting
Rich event logs, session histories, and access event documentation enable compliance and forensic review. Satisfies regulatory requirements (GDPR, HIPAA, NIST) for the most sensitive sectors.
Secure Access to Your Air-Gapped Networks with MFA and Access Controls
Air-gapped networks demand layered defense. MFA closes the gaps by passwords and physical isolation, combining local controls with modern hardware tokens for strong identity verification.
Offline MFA solutions by miniOrange are positioned to defend against both digital and human-based attacks, maintain compliance, and automate security monitoring without sacrificing operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The last mile in defending air-gapped networks is a solid authentication mechanism. MFA, especially with FIDO2 hardware token support and granular on-premise controls, locks down the human factor, mitigates advanced threats, and ensures complex systems remain resilient.
Leaders and technologists must recognize that the future of air-gapped security is shaped not only by walls, wires, or protocols but by people, process, and authentication.
FAQs
Can air-gapped networks be attacked remotely?
While remote direct attacks are improbable, air-gapped systems can be breached using compromised USB drives, electromagnetic emissions, insider credentials, and physical methods. Layered MFA mitigates these risks.
Does MFA work without internet connectivity?
Yes, solutions like miniOrange offer full offline authentication, distinct from cloud or app-based methods.
What’s the best authentication method for air-gapped environments?
FIDO2-compliant hardware tokens and TOTP/HOTP-based authentication apps, with admin-enforced access controls.
Is MFA required for regulatory compliance?
Critical sectors (finance, healthcare, defense) increasingly mandate MFA for sensitive workforce and privileged accounts, even in physically isolated networks.

Leave a Comment