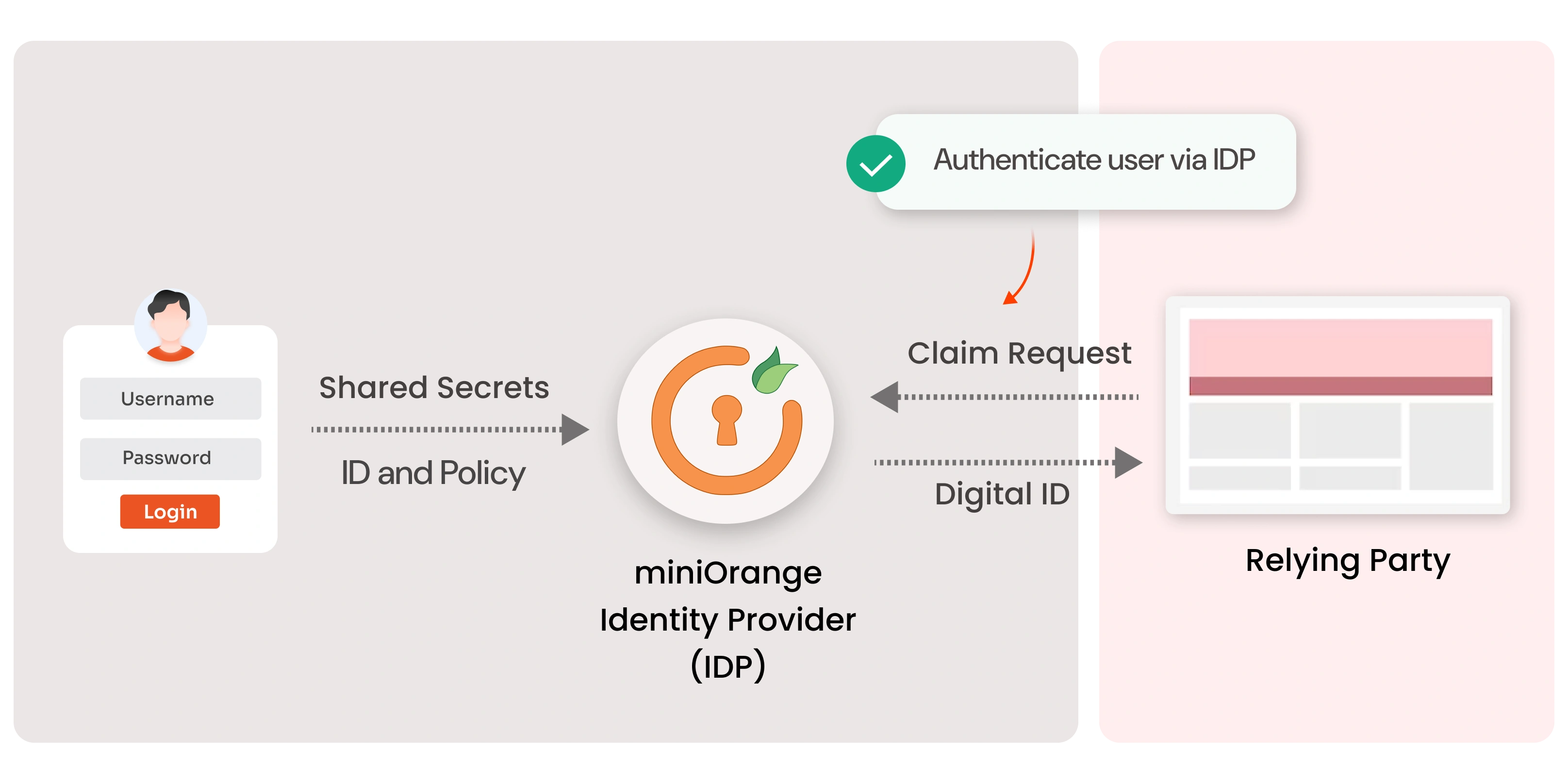
An Identity Provider (IDP) is a digital service that creates and manages a user’s digital identity and the identity-related attributes associated with it. IDPs authenticate users to third-party service providers (like websites, web applications, etc) using these identities.
miniOrange IDP allows users to bring their own identities to their workspace and enables them to sign up/ log into a web service or application using an existing set of credentials in place of creating new ones for the service or application.
Google is also a popular Identity Provider, the “Sign-up using Google/Login using Google” option, denotes we are using Google’s services to sign in to or log in to another service. By doing this, users can access the resources of the service using their Google Credentials.

User identity refers to the unique information and characteristics that will define an individual or entity in a digital system or platform. It can include various attributes, such as a user’s name, email address, phone number, username, password, biometric data (such as fingerprints or facial recognition), and other personal or demographic information.
In the context of Authentication & Identity Providers, user identity can be the user’s credentials or biometric data which might be stored in a directory. In order to authenticate the user, the identity provider will fetch the user identity from the directory to authenticate them and which will allow the user to access their accounts and interact with the particular platform.
Protecting user identity is an important aspect of digital security, as it helps prevent identity theft, fraud, and other types of cyber attacks. Methods like Single Sign-On and Multi-Factor Authentication ensure that User Identity is secure and prevents threats like unauthorized access & privacy breach.
Why do we need IDP? How do IDPs work with SSO Authentication?
An Identity Provider (IDP) plays a crucial role in Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication. SSO enables users to log into multiple applications with just a single set of credentials, hence increasing security and productivity simultaneously. To make this process happen, an IDP is required.
SSO involves a Service Provider (SP) & Identity Provider (IDP). A Service Provider is an application or service that requests authentication and authorization from an Identity Provider. It relies on the IDP to verify the identity of users and grant them access to protected resources. Once the user has been authenticated by the IDP, the SP can use the token provided by the IDP to grant the user access to its resources.
In SSO, when a user tries to access a protected resource, the SP requests authentication from the IDP. The IDP then authenticates the user and provides a token to the SP, which is used to grant the user access to the resource. One common protocol used by IDPs in SSO is the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML). SAML IDP, or SAML Identity Provider, is an IDP that uses SAML to provide SSO services. Other than SAML, IDPs like miniOrange also support other protocols like OAuth, JWT, OpenID, and special connectors for unique use cases.
Other forms of IDPs include Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) providers such as miniOrange, Okta, Ping Identity, etc., which offer cloud-based identity management services and integrations with various applications. Basically, they provide all the infrastructure required to manage the identities on behalf of your organization via a cloud setup. Identity-as-a-service in cloud computing can be a game changer by optimizing the costs, resources, and manpower of your organization.
Overall, IDPs play a critical role in enabling SSO and ensuring secure and streamlined access to applications and resources. With the growing adoption of cloud computing, IDPs and IDaaS providers are becoming increasingly important for managing identities and access in complex, distributed environments.
What steps are involved in the IDP Workflow?
Identity providers operate on a simple mechanism. Getting a digital ID requires you to provide unique information. It may be your username, password, security question, or captcha. With this unique information, you’ll receive a digital ID proving your identity. Users can gain access to all their required resources, including email and file management systems, by using an IDP.
IDP workflow includes three main steps:
- Authentication: The user is requested to enter some form of identification, such as a username and password or biometric data.
- Verification: The identity provider determines if a user has access to the system, and what they have access to.
- Authorization: Users are given access to specific resources based on their authorization.

Security Benefits of Using an Identity Provider
Typically, users logins into multiple platforms, and managing separate credentials for each platform or application can cause password fatigue. Credential re-used across multiple security platforms can present a considerable security risk to the system. Let us have a look at some of the benefits of using an Identity Provider to eliminate these risks:
- Identity providers offer robust authentication policies that provide users with secure login credentials for all configured services.
- Users can enhance security by enabling 2FA or Adaptive MFA.
- Access privileges can be allocated and managed for user groups, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to critical systems.
- Authorized users can access audit reports through IDP to review user authentication logs, resource access requests, and usage.
- IDP simplifies compliance management for enterprises by tracking all access requests and events in audits through Enterprise SSO.
- The enforcement of consistent security policies across all platforms and devices makes it easy to manage security measures efficiently.
Enforcement of the same security policies across all operating platforms and devices for the users allows the management of security measures quickly and easily.
In the event of a set of credentials getting compromised, it can lead to unauthorized access to user accounts on other platforms and may result in an information breach. An estimated 81% of data breaches are due to poor password security or stolen credentials.
Using an identity provider reduces the risk of a data breach caused due to password fatigue or compromised identity, adds additional security measures, and makes the task of user identity access management and privileges management easy.
5 Ways in Which Identity providers help users better manage their accounts?
1. Single Sign-On (SSO) : Users can access multiple applications and services with a single set of login credentials, saving time and reducing the hassle to remember multiple usernames and passwords.
2. Centralized Account Management : Users can update their profile information, reset passwords, and manage permissions for all applications and services from a single dashboard.
3. Enhanced Security : Identity providers offer advanced security measures such as two-factor authentication, encryption, and access control to protect users’ personal information from unauthorized access.
4. Seamless User Experience : Users can access all their applications and services from a single dashboard, making it easy to switch between them without having to log in again.
5. Reduced IT Overhead : Identity providers reduce the IT overhead of managing user accounts and permissions for multiple applications and services, enabling IT teams to easily add or remove users, manage permissions, and monitor user activity.
Overall, identity providers simplify the account management process, improve security, and enhance the user experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an Identity Provider (IDP) plays a crucial role in digital identity management, allowing users to bring their existing identities to access multiple web services and applications. IDPs operate on a simple mechanism of authentication, verification, and authorization, offering users a secure login experience and reducing the risk of compromised identities. Identity providers offer many security benefits, such as 2FA, access privileges management, and audit reports. IDPs also help users manage their accounts better with SSO, centralized account management, enhanced security, seamless user experience, and reduced IT overhead.
Further Reading
Author