What is Privileged Account Management?
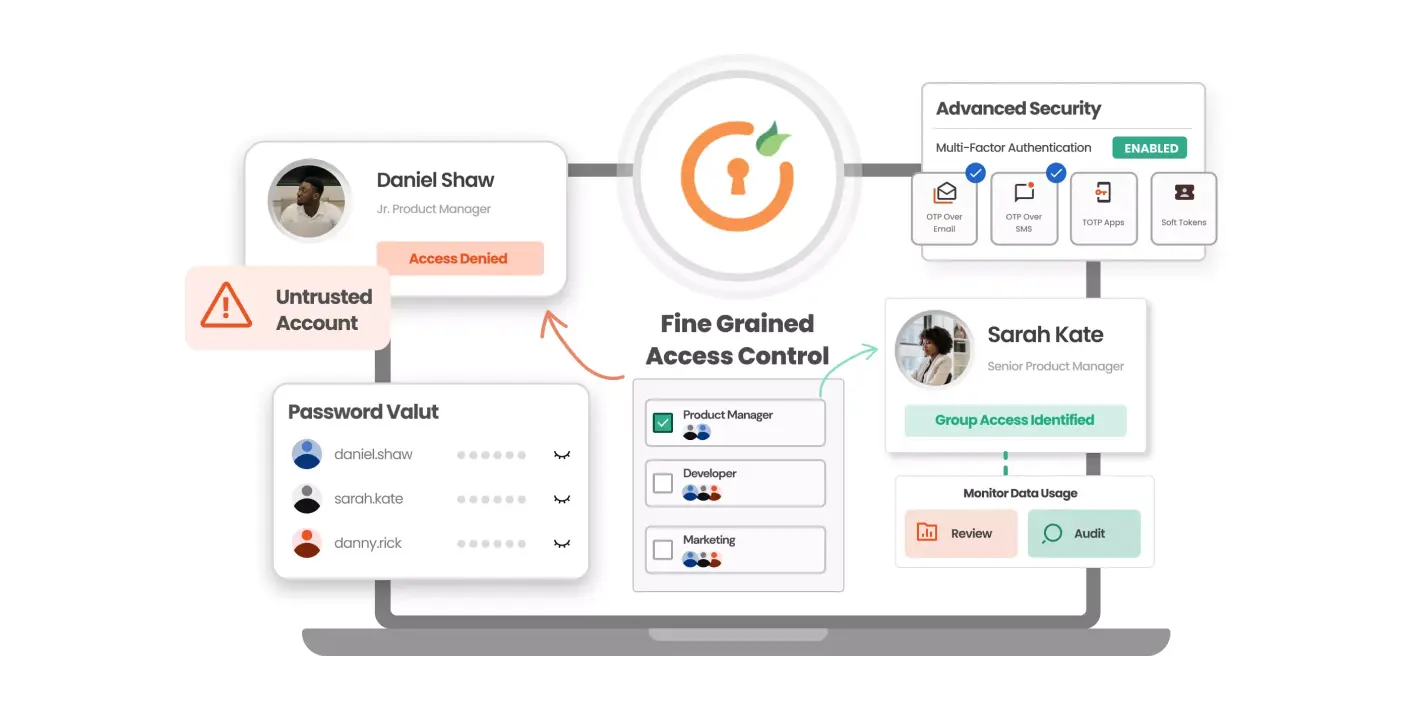
Privileged Account Management (PAM) is a process that focuses on managing and securing privileged accounts that get access to sensitive servers within an organization's IT environment. It consists of various roles such as granting permissions, making modifications to sensitive data, in simple words who can unlock a system, get access to the system and also take a look at what is inside the IT ecosystem.
Privileged accounts are accounts that have elevated access rights, allowing users to perform critical and sensitive tasks, such as system administration, configuration changes, and access to sensitive data. The privileged account management solution aims to control, monitor, and audit these privileged accounts to ensure that access is granted only to authorized users and for approved activities. Through Privileged Account Management, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, insider threats, and potential data breaches, while also meeting compliance requirements and enhancing overall cybersecurity.
Privileged Account Management is essential for organizations to protect against cyberattacks that target privileged accounts. If these accounts are compromised, attackers can freely move within the network, conducting harmful actions like downloading malicious files, taking control of servers, and causing financial loss and damage to the organization's reputation. PAM helps prevent such risks and ensures the security of the privileged account.
What is a Privileged Account?
A Privileged Account, also known as an elevated account, is a powerful and essential type of account in an IT environment. It serves as the foundation for managing organizational resources, including hardware and software. Privileged accounts encompass various types, such as Linux/Unix root accounts, Windows Administrator, Database Administrator (DBA), and various application accounts. These accounts hold significant permissions, allowing IT teams to perform critical tasks like setting up architecture, running essential applications and services, installing software, and overseeing software maintenance tasks. Essentially, privileged accounts act as master keys, providing access to critical IT assets and sensitive information within an organization.
Due to their elevated privileges, privileged accounts are high-value targets for cyber attackers, emphasizing the importance of robust security and management practices, such as granular access control and zero trust, to protect the organization's IT environment.
Types of Privileged Accounts
- Linux/Unix Root Accounts: These pam accounts have the highest level of access in Unix-like systems.
- Windows Administrator Accounts: These accounts have complete control over the Windows environment.
- Database Administrator (DBA) Accounts: These privileged accounts manage and maintain database systems.
- Application Accounts: These accounts are used by applications to access databases and other services.
The management of these privileged accounts is crucial to ensuring the security and integrity of the IT infrastructure. PAM account solutions play an important role in controlling and monitoring access, ensuring that only authorized personnel can perform critical operations.
How to manage Privileged Accounts?
Usually, organizations use various password management software to help employees maintain their credentials for their applications. This approach requires a bit of attention while employees choose and manage their passwords effectively. In today’s times, companies are moving forward with their password management and security practices. To accomplish this, robust privileged account and access management solutions must be deployed efficiently. Therefore, privileged account management tools enable your company to improve password protection and strengthen privileged account security overall.
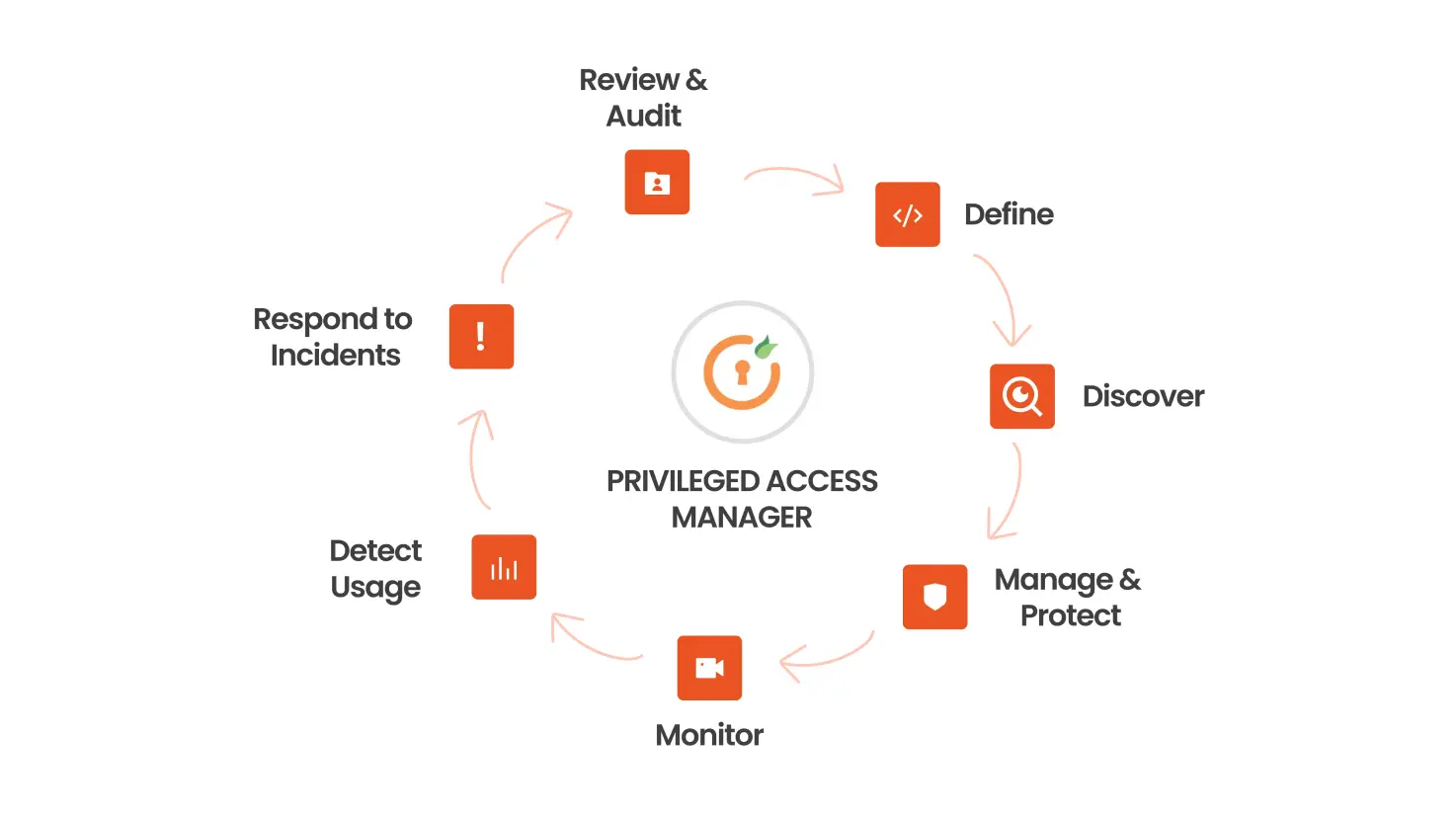
To effectively manage privileged accounts, follow these steps for the PAM Lifecycle:
- Define and Classify Privileged Accounts: Begin by defining and classifying privileged accounts. Your business functions rely on data, systems, and access, and dependence on these entities varies from one organization to another. Consult your disaster recovery plan, which typically classifies your critical systems, and align your privileged accounts to your business risk and operations. Develop IT security policies that explicitly cover privileged accounts, detailing acceptable use and responsibilities.
- Discover Privileged Accounts: Use an automated privileged account discovery tool to identify and locate all these accounts in your IT environment. This will give you a comprehensive understanding of how many such accounts you have and where they are located. Continuous discovery helps curb privileged account sprawl, identify potential insider abuse, and reveal external threats. This step is crucial in the PAM Lifecycle.
- Manage and Protect Privileged Accounts: Protect your pam account passwords by proactively managing, monitoring, and controlling its access with password protection software. Ensure your password management solution can automatically discover and store credentials; schedule password rotation; audit, analyze, and manage individual privileged account session activity; and monitor password accounts to detect and respond to malicious activity proactively. Develop a least privilege policy to limit IT admin access to systems, granting privileges only when required and approved. Effective PAM implementation includes robust management and protection strategies.
- Monitor and Record Privileged Account Activity: Your Privileged Access Management solution should monitor and record privileged account activity. This helps enforce proper behavior and avoid user mistakes because users know their activities are being monitored. Monitoring also aids digital forensics in identifying the root cause of breaches and critical controls that can be improved to reduce future cybersecurity threats. Monitoring is a key component of the PAM Lifecycle.
- Detect Abnormal Usage: Track and alert on user behavior. Up to 80% of breaches involve a compromised user or privileged account. Gain insights into privileged account access and user behavior in real-time to catch suspected account compromises and potential user abuse. Behavioral analytics establish individual user baselines, including user activity, password access, similar user behavior, and time of access, to identify and alert on suspicious activity.
- Respond to Incidents: Prepare an incident response plan in case a pam account is compromised. Simply changing privileged account passwords or disabling them is not adequate when a privileged account is breached. Assume that if a domain administrator account is compromised, your entire Active Directory is also compromised. Follow a comprehensive incident response plan to address such breaches effectively. Incident response is a critical stage in the PAM Lifecycle.
- Review and Audit Privileged Account Activity: Continuously monitor privileged account usage via audits and reports to identify unusual behaviors, which may indicate a breach or misuse. Automated reports help track the cause of security incidents and demonstrate compliance with policies and regulations. Privileged account audits provide essential cybersecurity metrics and vital information for executive decision-making. Regular reviews and audits are integral to successful PAM implementation.
By following these steps and embracing the PAM Lifecycle approach, you can strengthen the security of your privileged accounts and ensure effective management of these critical assets.
Privileged Account Management vs Privileged Access Management
The difference between Privileged Account Management (PAM) and Privileged Access Management (PAM) lies in their scope and focus:
1. Privileged Account Management (PAM):
Privileged Account Management specifically deals with the management and security of privileged accounts within an organization's IT environment. It focuses on managing and controlling the access rights and permissions of accounts that have elevated privileges, such as administrative accounts, root Linux/Unix accounts, and database administrator accounts. The main objective of it is to ensure that privileged accounts are properly protected, monitored, and audited to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of security breaches.
2. Privileged Access Management (PAM):
Privileged Access Management, on the other hand, encompasses a broader approach that goes beyond just managing privileged accounts. It involves managing and securing all aspects of privileged access within an organization, including not only privileged accounts but also privileged access to applications, systems, databases, and other critical resources. PAM focuses on implementing comprehensive strategies and technologies to control and monitor elevated access and permissions, minimizing the attack surface and enhancing overall security.
While Privileged Account Management (PAM) focuses specifically on managing privileged accounts, Privileged Access Management (PAM) takes a more comprehensive approach, addressing all aspects of privileged access within an organization's IT environment.
Why is Privileged Account Management important?
The Importance of Privileged Access Management:
Privileged Account Management (PAM) is essential for several reasons:
- Protection from cyberattacks : Privileged accounts are prime targets for hackers seeking to gain full access to sensitive data and systems. PAM helps secure these accounts and prevents unauthorized access.
- Mitigating insider threats : Internal users with elevated privileges can pose significant risks. PAM helps detect and prevent misuse of privileged accounts by insiders, reducing the potential for data breaches.
- Safeguarding against negligence : Careless employees may unknowingly expose critical credentials, creating security vulnerabilities. PAM ensures proper controls and minimizes the risk of accidental data exposure.
- Managing third-party access : Vendors and ex-employees with privileged access can also pose threats. PAM ensures proper oversight of third-party access to internal infrastructure.
- Enforcing least privilege : Many users have more privileges than necessary for their job roles. PAM enforces the principle of least privilege, granting only essential permissions for specific tasks.
- Proper privilege management : Over time, unused privileges may be forgotten, leading to security gaps. PAM helps track and revoke privileges when they are no longer needed, reducing the risk of unauthorized actions.
Overall, PAM plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring the overall integrity of an organization's IT environment.
FAQs
1. What is a privileged account management tool? A privileged account management tool is a software solution designed to manage and secure privileged accounts within an organization's IT environment. These tools help organizations ensure that individuals have only the necessary levels of access to perform their jobs, thereby minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Privileged account management tools offer several key features:
- Discovery and Inventory: Automatically discover and catalog all privileged accounts within the network.
- Access Control: Enforce policies to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive systems and data.
- Password Management: Securely manage and rotate passwords for privileged accounts to reduce the risk of compromise.
- Session Monitoring and Recording: Track and record user activities during privileged sessions to detect and respond to suspicious behaviors.
- Audit and Compliance: Provide detailed reports and audit trails to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies.
By implementing a privileged account management tool, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture, reduce the risk of insider threats, and ensure that access to critical IT resources is appropriately managed and monitored.
2. What is privileged account management software?
Privileged account management software is a specialized subset of Identity and Access Management (IAM) that enables organizations to control and monitor the activities of privileged users. These users have access levels above and beyond those of standard users, granting them the ability to perform critical tasks such as system administration, configuration changes, and access to sensitive data.
Privileged account management software offers several essential features:
- Access Control: Ensures that only authorized users can access and perform tasks with privileged accounts.
- Activity Monitoring: Continuously monitors and records the actions of privileged users once they are logged into the system, providing visibility into their activities.
- Password Management: Secures and manages passwords for privileged accounts, including automatic rotation and secure storage.
- Audit and Compliance: Generates detailed reports and audit trails to help organizations meet regulatory requirements and internal security policies.
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches by enforcing strict access controls and monitoring.
By using privileged account software, organizations can enhance their security posture by ensuring that privileged users have only the necessary access to perform their duties while closely monitoring their activities to detect and respond to any suspicious behavior. This helps safeguard critical IT resources and sensitive information from potential threats.
Author