What is Cloud Application Security?
Cloud Application Security refers to the set of tools, policies, and technologies that protect cloud-based applications and the sensitive data they handle. When we define cloud application security and its core components, it typically includes identity and access management, data security, API protection, threat detection, and compliance controls.
Modern cloud application security solutions also enable adaptive authentication, risk-based access control, and real-time visibility into cloud usage—ensuring employees can collaborate safely without exposing critical business data.
With the rise of SaaS adoption, remote work, and multi-cloud environments, businesses increasingly rely on dedicated tools for application security in cloud computing to balance productivity with protection.

Why is Cloud Application Security Important for Enterprises?
There are several reasons organizations need cloud application security, especially as they adopt SaaS platforms, collaboration tools, and cloud storage. As employees share and access business information across multiple devices and networks, protecting this data has become a top priority.
By implementing application-level security in cloud computing, IT teams can enforce enterprise-wide policies, prevent data leaks, and detect suspicious user behavior across apps. This layer of security ensures compliance, reduces risk, and keeps business-critical operations safe from evolving cyber threats.
Pros and Cons of Cloud App Security
Cloud application security comes with both its advantages and challenges that businesses need to check carefully.
Pros
Data Security & Visibility
Compliance Support & Policy Enforcement
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Zero Trust Protection
Secure Remote Work
Cons
Complex Deployment
Performance Overhead
Mobile Usability Challenges
User Resistance
Limited On-Premise Protection
Looking for Cloud Application Security that’s quick to deploy and easy to use?
Explore Cloud App SecurityChallenges of Cloud Application Security
Limited visibility across multiple cloud apps
Businesses often struggle to gain complete visibility into user activity, and data flows. Without centralized monitoring, blind spots emerge that attackers can exploit.
Complex configurations create security blind spots
Cloud applications involve intricate settings, permissions, and integrations that are difficult to manage. Misconfigured security controls often open doors to unauthorized access and data leaks.
Shadow IT apps bypassing security policies
Employees often use unsanctioned apps without IT approval, exposing sensitive business data to unmonitored risks. This lack of control increases the attack surface dramatically.
Rising compliance pressures across industries
Organizations face stricter compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Meeting these standards demands robust cloud application security to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Rapidly evolving threats targeting application
Cybercriminals continuously adapt their tactics, targeting vulnerabilities in cloud apps with sophisticated exploits. Security teams must constantly update defenses to keep pace with these evolving threats.
Weak identity and access controls
Poorly managed authentication, single-factor logins, or lack of role-based access leave apps vulnerable. Strengthening identity and access management (IAM) with MFA and SSO is crucial to prevent breaches.
Common Threats to Cloud Applications
-
Account Takeover (ATO)
Cybercriminals steal user credentials through phishing, brute force attacks, or credential stuffing. Once inside, they can impersonate users and access sensitive business data.
-
Data Breaches
Insecure APIs, weak encryption, or insider threats often cause massive data leaks. Data breaches not only compromise customer trust but also result in financial and regulatory consequences.
-
Misconfigurations
Overly permissive cloud settings or exposed databases are among the top causes of breaches. Attackers actively scan for these missteps to exploit unsecured environments.
-
API Vulnerabilities
Flaws like injection attacks, poor input validation, or lack of authentication expose apps to abuse. Since APIs connect critical services, securing them is essential to prevent large-scale compromises.
-
Malware & Ransomware
Malicious code spreads through cloud-hosted apps, endpoints, or shared files. Ransomware attacks can lock critical business data, disrupting operations and demanding high payouts.
-
Insider Threats
Negligent employees may mishandle data, while malicious insiders intentionally steal or expose sensitive information. These threats are harder to detect since they come from trusted users.
-
Supply Chain Attacks
Compromised third-party integrations or software updates allow attackers to infiltrate multiple organizations at once. This makes supply chain attacks one of the most damaging risks in cloud security.
What are the Key Best Practices for Securing Cloud Applications?
Protects Business Data
Protect customer, financial, and business data from breaches, leaks, and unauthorized access, ensuring data security and privacy. With strong user access controls, businesses can prevent exposure of confidential information and keep secure cloud applications running safely.
Regulatory Compliance
Helps businesses meet GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and other compliance requirements, avoiding fines and legal issues while maintaining industry trust. Cloud app security automates compliance checks and enforces security policies consistently, supporting common frameworks for cloud application security.
Lower Misconfiguration Risks
Monitors cloud setups to prevent insecure defaults, excessive permissions, or exposed data that could otherwise lead to breaches. Automated tools like CSPM continuously scan for risky configurations. This resolves one of the common challenges in implementing cloud application security: human error and mismanagement.
Secure Remote Work
Allows employees to safely access cloud apps from anywhere while maintaining control, visibility, and secure collaboration. Security policies adapt to diverse devices, locations, and networks. This is now one of the key best practices for securing cloud applications in hybrid work environments.
What are the Emerging Trends in Cloud Application Security?
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions provide secure control over who can access what in cloud applications. With features like Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), IAM ensures only the right users get access to the right resources.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
SASE combines networking and security functions into a unified, cloud-native service. It provides secure access for remote users and branch offices, making it easier for businesses to secure cloud applications in distributed environments.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM solutions continuously monitor cloud environments to detect misconfigurations, enforce policies, and ensure compliance. They help businesses prevent data leaks caused by common cloud misconfigurations.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP tools monitor and control the movement of sensitive data across cloud apps, preventing unauthorized sharing or leaks. It protects intellectual property and customer data from accidental or malicious exposure.
API Security
APIs connect apps and services, but if left unprotected, they can be exploited by attackers. Strong authentication, input validation, and rate-limiting safeguard APIs from misuse and breaches at the application level security in cloud computing layer.
Cloud Application Security Framework
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
Acts as a security checkpoint between users and cloud applications, enforcing policies, controlling access, and monitoring for risky activities.
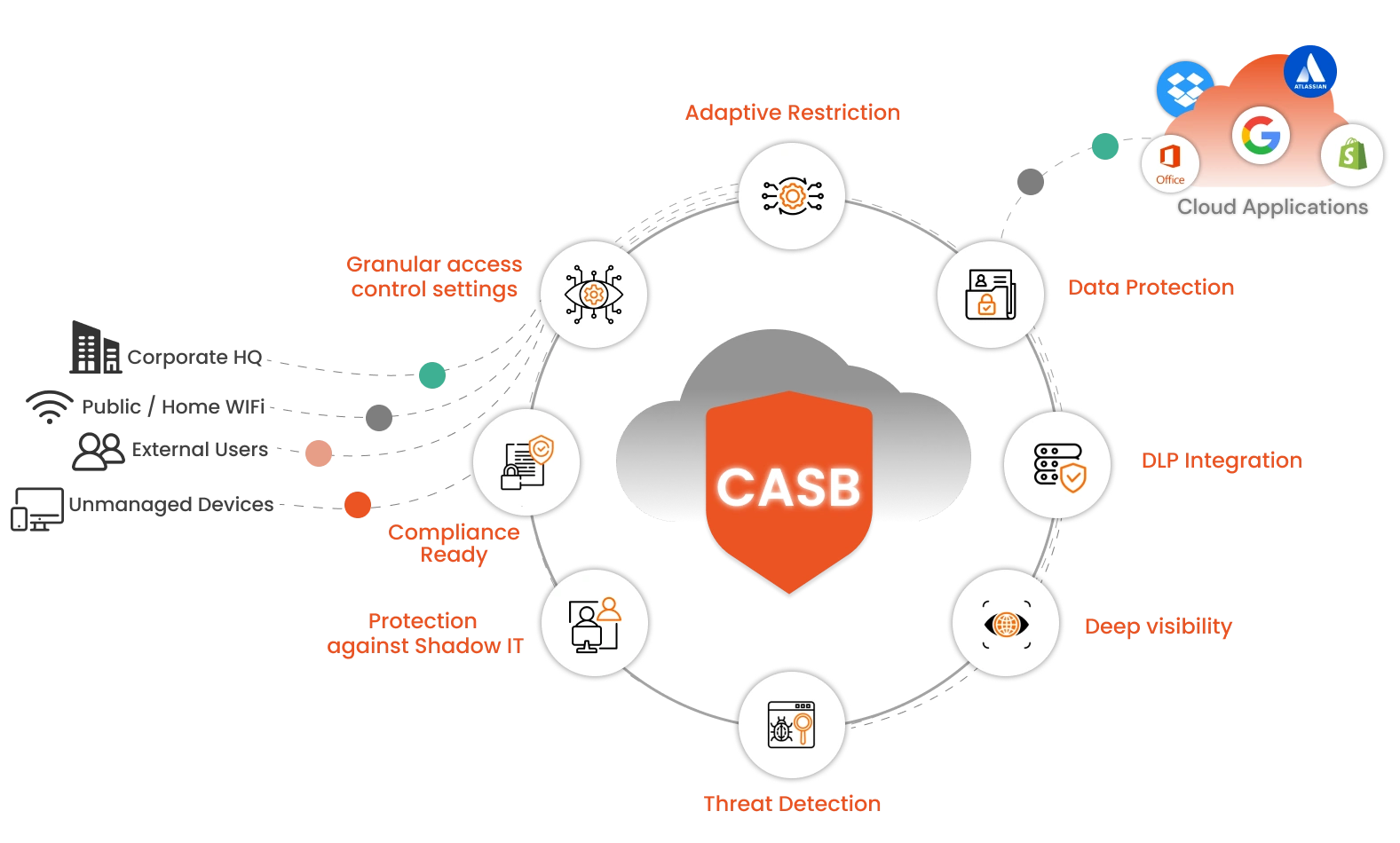

Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA ensures that no user or device is trusted by default, even if they are within the network perimeter. Access is continuously verified using context such as identity, device health, and location.
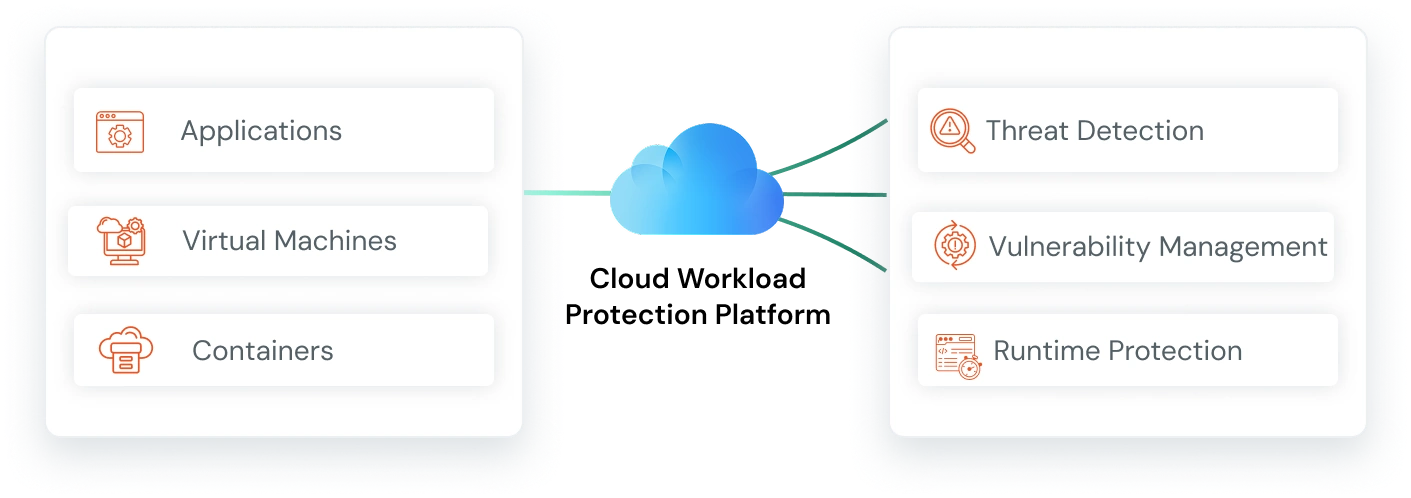
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
Secures applications, virtual machines, and containers running in the cloud by providing threat detection, vulnerability management, and runtime protection.
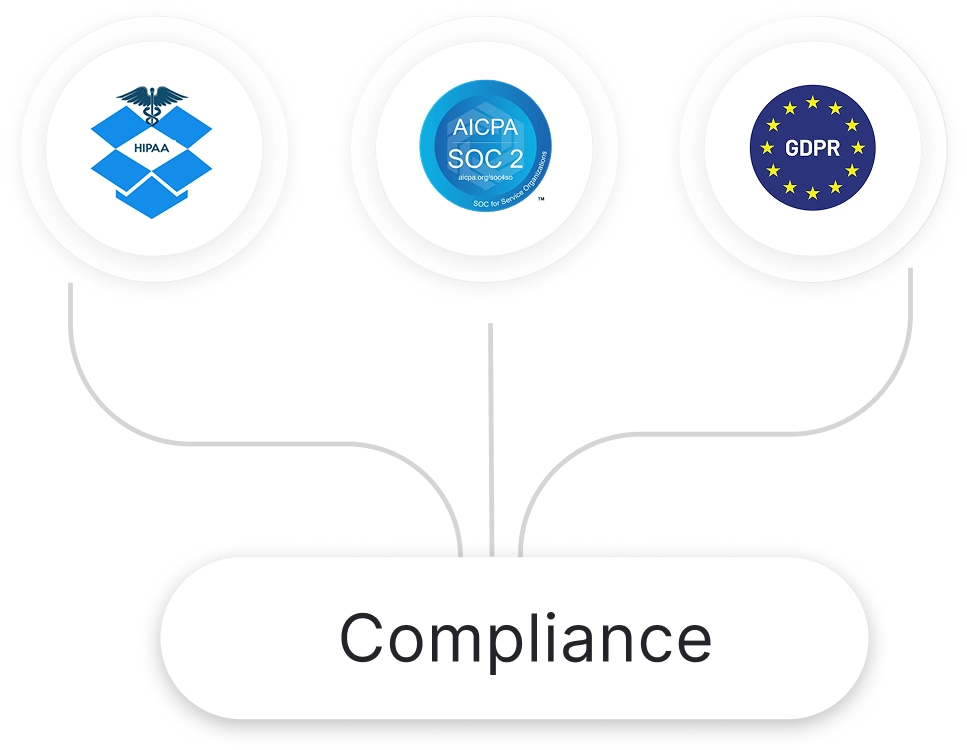
Compliance and Governance Controls
Enforces business-specific rules and policies to ensure your cloud applications and services meet the necessary industry and legal standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.

