What is Privileged Entitlements Management?
Privileged Entitlements Management (PEM) is a specialized cybersecurity practice that focuses on securely managing high-risk entitlements, also known as permissions, access rights, or privileges, which grant access to sensitive data, critical resources, and essential services across an organization's IT infrastructure.
PEM management continuously discovers, governs, and controls all privileged entitlements assigned to users, applications, and systems, particularly within cloud environments like AWS, Azure, and GCP, where any IAM user, group, or role can be assigned permissions to perform critical actions such as modifying configurations, accessing sensitive data, or managing entitlements for other users.
This discipline extends beyond traditional access management by implementing dynamic oversight mechanisms that prevent privilege creep, enforce least privilege principles, and ensure that high-risk entitlements remain tightly controlled and monitored throughout their lifecycle.
Core Functions of PEM
Discovery and Visibility
PEM solutions enable continuous oversight and governance of privileged access by automatically discovering all privileged entitlements across cloud and hybrid environments. This core function identifies every instance of elevated permissions from admin roles and root access to read-only roles that can access sensitive data, creating a comprehensive inventory of high-risk entitlements that could be exploited by attackers.
Access Governance and Policy Enforcement
Robust access governance ensures that privileged entitlements align strictly with the principle of least privilege through continuous access review processes and automated policy enforcement mechanisms.
Enterprises can implement strict controls over who can access critical entitlements, enforce Zero Standing Privileges with just-in-time access provisioning, and carefully restrict the time, entitlements, and approval (TEA) settings governing privileged sessions.
Session Monitoring and Audit
Comprehensive session monitoring and privileged session audit capabilities track all activities performed with elevated permissions, creating detailed audit trails essential for security forensics, regulatory compliance, and detecting potential misuse of high-risk entitlements.
PEM systems monitor privileged sessions in real-time to identify suspicious behavior and enable immediate response to prevent breaches, while recorded sessions provide searchable documentation that demonstrates compliance with industry standards and regulations.
PAM vs PEM: Understanding the Differences
This graphic below provides a quick understanding of how PAM and PEM differ in scope and approach.
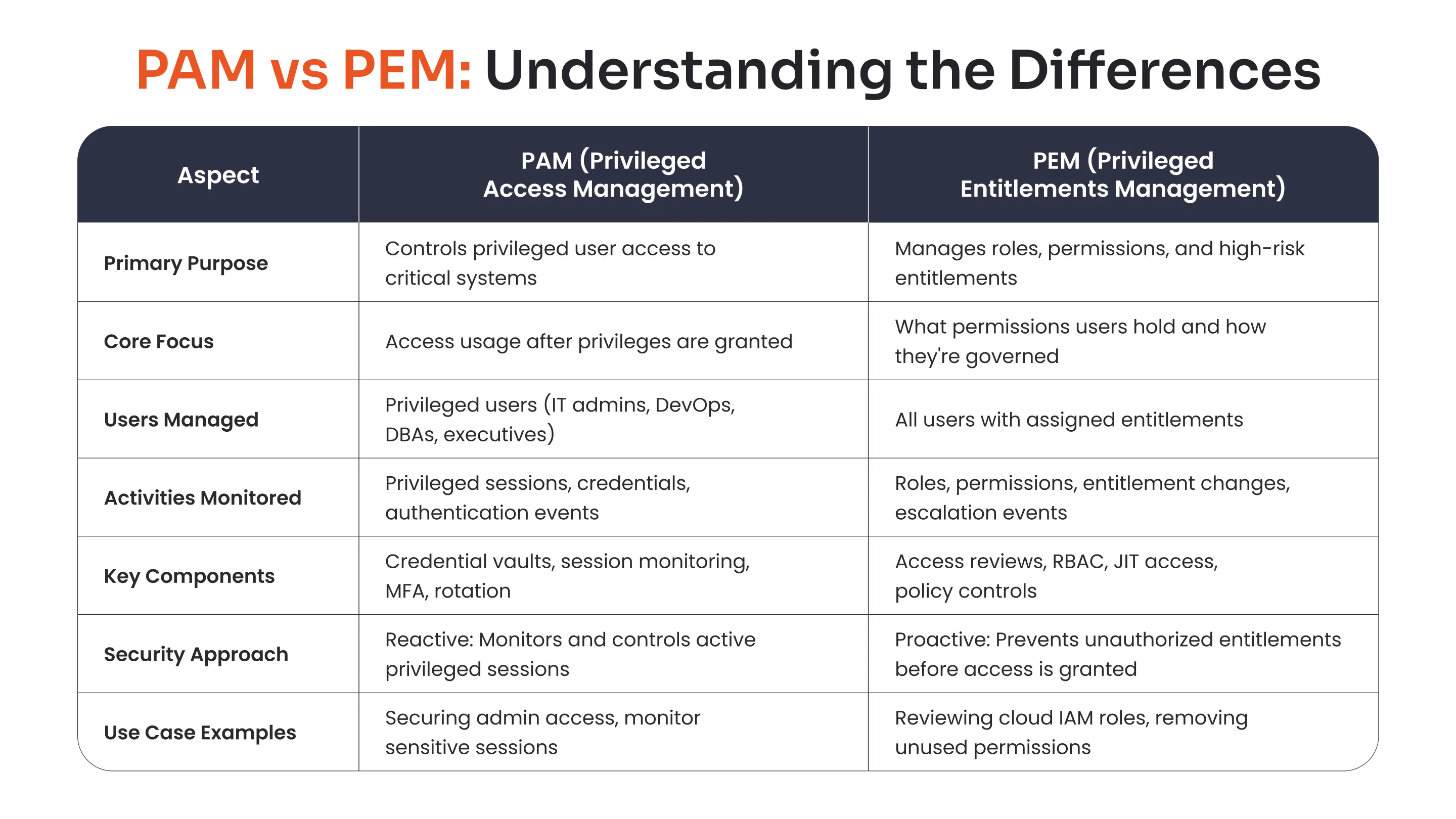
For a detailed comparison, see the table below:
| Aspect | PAM (Privileged Access Management) | PEM (Privileged Entitlements Management) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Controlling access to sensitive systems and data for privileged users | Managing roles, permissions, and high-risk entitlements across privileged users and applications |
| Core Focus | Access-centric: How users utilize privileged access after it's granted | Entitlement-centric: What permissions users have and governance of those entitlements |
| Users Managed | Privileged users (IT admins, DevOps, DBAs, executives) | All users with assigned entitlements, including both privileged and non-privileged users |
| Activities Monitored | User sessions, credentials used by privileged users, and authentication events | Roles, permissions, entitlements granted to users, and privilege escalation events |
| Key Components | Credential vaults, session monitoring and recording, MFA, password rotation | Access reviews, role-based access controls, just-in-time access, policy enforcement |
| Primary Capabilities | Session management, credential protection, privileged session audit, and real-time monitoring | Entitlement discovery, access governance, privilege creep prevention, and continuous compliance |
| Security Approach | Reactive: Monitors and controls active privileged sessions | Proactive: Prevents unauthorized entitlements before access is granted |
| Use Case Examples | Securing admin access to databases, monitoring DevOps sessions, and rotating service account passwords | Reviewing cloud IAM roles, removing unused permissions, and enforcing least privilege across applications |
How PEM Works: Key Functions Explained
Step 1: Identifying High-Risk Accounts
The foundation of PEM management begins with privileged identity discovery, where organizations conduct comprehensive audits to identify all privileged accounts across their IT environment, including admins, executives, service accounts, and machine identities.
This critical step involves mapping the high-risk entitlements associated with each account to ensure complete visibility into who has access to what resources and sensitive data. Automated discovery tools continuously scan cloud platforms, on-premises systems, and hybrid infrastructures to detect shadow accounts and extended privileges.
Step 2: Enforcing Least Privilege
PEM then enforces the principle of least privilege by assigning granular, role-based access controls that follow the just-enough-access principle. This means removing unnecessary privileges wherever possible and ensuring users and systems have only the minimum entitlements necessary to perform their job functions.
Organizations implement strict policy enforcement mechanisms with predefined roles and privileges, so when someone is hired or changes roles, it's clear exactly what entitlements they should be assigned.
Step 3: Continuous Monitoring & Session Auditing
PEM solutions continuously track entitlement usage, monitor privilege escalation events, and conduct privileged session audit activities to detect suspicious behavior in real-time. This includes comprehensive session monitoring that logs all actions performed with elevated permissions, records privileged sessions for forensic analysis, and reviews entitlement changes at defined intervals.
Businesses can quickly identify anomalous activity, respond immediately to potential threats, and demonstrate regulatory compliance through searchable documentation by maintaining detailed audit trails.
Step 4: Dynamic Access & Deprovisioning
Modern PEM implementations enable just-in-time access provisioning, granting privileged entitlements temporarily based on contextual signals and automatically revoking them when they are no longer required.
Now you will have minimized long-standing privileges and reduced the attack surface by ensuring access is time-bound with defined start and end dates, requiring approval to activate privileged roles, and enforcing MFA for additional security. Automated deprovisioning workflows handle the removal or alteration of access rights as roles change, eliminating unnecessary entitlements.
Benefits of a Strong PEM Strategy
Reduces Attack Surface
By enforcing least privilege and eliminating unnecessary high-risk entitlements, PEM significantly reduces your organization's attack surface. It prevents privilege creep, removes orphaned accounts, and ensures users have only the minimum permissions necessary, limiting pathways cybercriminals can exploit to access sensitive systems and data.
Increases Visibility and Control
PEM provides complete visibility into all privileged entitlements across cloud and hybrid environments through a centralized platform. Security teams gain real-time insights into who has access to what resources, track privilege escalation events, and maintain accountability by monitoring all privileged actions and entitlement changes.
Simplifies Audits and Compliance
PEM simplifies compliance with HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR by providing detailed audit trails, automated access reviews, and continuous certification of privileged entitlements. Organizations can easily demonstrate regulatory adherence through comprehensive logging that records all privileged actions and entitlement changes, avoiding costly penalties.
Improves Operational Efficiency
PEM automates entitlement lifecycle management through just-in-time access provisioning and policy-driven workflows, reducing manual burden on security teams. Streamlined access requests, timely deprovisioning, and centralized management improve productivity while maintaining strong security controls and minimizing the risk of costly data breaches.
Best Practices for Privileged Entitlements Management
Define Clear Roles for All Users
Establish clear, role-based access controls for all users and systems by granting only the minimum necessary access required for each job function. Regularly review and update these role assignments as roles evolve or organizational structures change, conducting periodic access reviews to prevent privilege creep and ensure entitlements remain appropriate.
Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication
For high-risk or privileged accounts, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an additional layer of security beyond passwords. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access from credential theft or phishing attacks, ensuring that compromised credentials alone cannot be exploited to access sensitive systems and high-risk entitlements.
Integrate PEM with Other IAM & PAM Systems
Seamlessly integrate PEM with broader Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Privileged Access Management (PAM) systems to create a unified access governance framework. This integration enables centralized visibility across all privileged entitlements, automated approval workflows, consistent policy enforcement, and instant access revocation upon employee termination through identity provider integration.
Conduct Regular Access Reviews
Schedule periodic access reviews and privileged session audits to validate that only necessary permissions are assigned to each user, identifying excessive privileges or unused accounts that violate least privilege. Maintain detailed audit trails and session recordings for all privileged activities, using real-time session monitoring to detect suspicious behavior and ensure continuous compliance with security policies.
Employee Training and Education
Continuously train all users about the latest security threats and best practices for managing privileged accounts, including strong passwords, MFA, and recognizing phishing and social engineering attacks. Security awareness programs should be ongoing since attack methods constantly evolve, creating a frontline defense and ensuring everyone understands their role in maintaining robust access governance.
FAQs
How does PEM differ from PAM?
PAM controls access to sensitive systems and monitors privileged user sessions, while PEM manages roles, permissions, and entitlements across all users and applications. PAM is access-centric, securing credential usage, whereas PEM is entitlement-centric, preventing privilege creep through proactive governance and just-in-time provisioning.
What are examples of entitlements in cybersecurity?
Entitlements include permissions granting resource access, such as admin roles in AWS IAM or Azure AD, root access on servers, and database read/write permissions. High-risk entitlements include the ability to create accounts, modify security configurations, access sensitive data, or manage encryption keys assigned to users or machine identities.
How does PEM support compliance?
PEM supports compliance by providing continuous audit trails, automated access reviews, and detailed reporting required by HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR. Organizations demonstrate adherence through certification processes that document who has access, when it is granted, and who approves it, while enforcing the principle of least privilege to avoid penalties.


Leave a Comment