The biometric market will reach $60.32 billion by 2025 as businesses move beyond passwords, embracing IAM-driven secure authentication methods. In the United States, 72% of consumers prefer facial recognition over traditional login systems, accelerating the demand for advanced IAM solutions. The financial sector leads this shift, with 28% of institutions already implementing biometric authentication to strengthen security and user experience. The $2.5 trillion digital payments market will be protected by biometric authentication through IAM frameworks like miniOrange as remote transactions grow, which will establish its position as the standard for identity verification. Organizations that delay biometric adoption risk falling behind, as 86% of users favor biometrics over passwords in a security landscape where seamless and secure IAM protection is no longer optional.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication uses distinct physical and behavioral characteristics to perform precise identity verification, including fingerprints, iris patterns, and facial features. The adoption of inherent markers as authentication methods eliminates traditional passwords, which reduces fraud risks and strengthens security throughout digital and physical spaces.
The system uses sophisticated sensors together with algorithms to rapidly process and evaluate biometric information, which enables immediate and trustworthy access control. Organizations use biometric authentication to protect sensitive information and optimize operations while establishing trust through an effortless password-free user experience.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication employs individual characteristics such as fingerprints, iris patterns, and facial features to remove password weaknesses and decrease fraud possibilities. It enables passwordless authentication. The system provides strict compliance together with exact access control functions that work across digital and physical spaces.
The technology enables fast user verification, which reduces IT costs and speeds up secure access. Biometric authentication systems create trust with users while simplifying their experience, which leads organizations to gain market advantage in current fast-moving business conditions.
11 Types of Biometrics Authentication
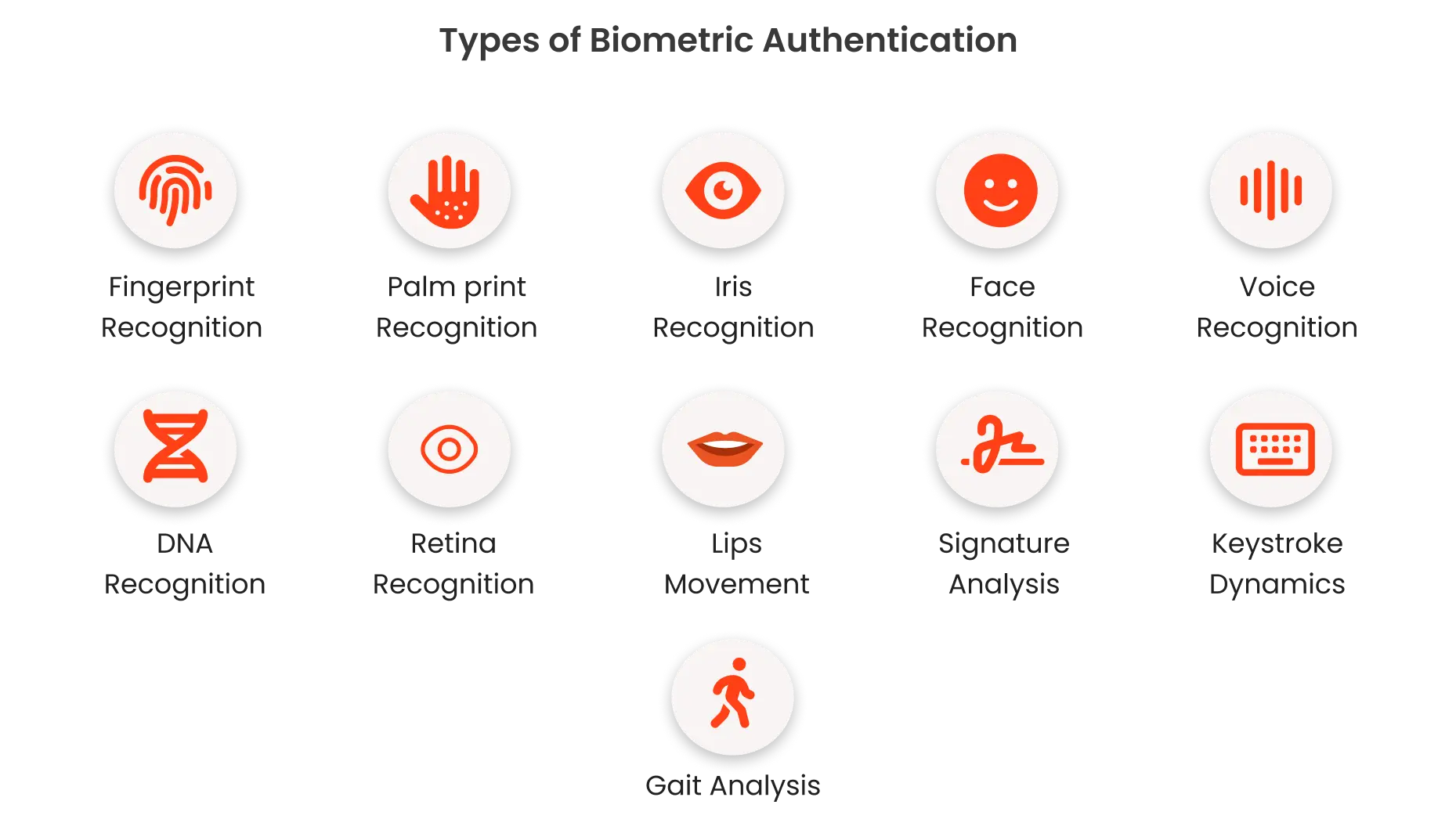
Companies in the competitive market use biometrics for securing their facilities, digital systems, and sensitive data. We implement physiological and behavioral biometric technologies because each type brings its own value to our authentication solution.
Physiological Biometrics
Physiological biometric authentication relies on distinct physical characteristics, such as:
1. Fingerprints Scanning
We identify people through fingerprint scanning by their fingerprint ridge patterns. Our systems obtain detailed fingerprint images that they then use to quickly compare with stored templates for fast and reliable access. This technology is widely used in smartphones, secure facilities, and workforce management systems.
2. Palm Vein recognition
We employ palm vein recognition to extract vascular patterns from the hand of a user. This method uses near-infrared light to actively scan the vein structure and then analyze the unique vein configuration for identity verification. This method minimizes the chances of forgery and improves security for risky applications.
3. Iris recognition
The companies employ iris recognition to study the intricate patterns that can be found in human iris tissue. The high-resolution cameras of our system capture the iris, and then the system actively searches the database for matching iris features to confirm identity. This technology stands out for its accuracy and its ability to work under different environmental conditions.
4. Facial recognition
We utilize facial recognition systems to identify people by comparing their facial features. Our algorithms scan key attributes, including the distance between the eyes, the shape of the jawline, and the face contour, and compare them to stored records in real time. This real-time identification process finds application in security checkpoints, customer engagement, and time-tracking.
5. Voice Recognition
We have voice recognition to detect different vocal characteristics. Our systems capture tone, pitch, and cadence in real time and actively match these parameters against trusted voice profiles. The use of this technology is seen in call centers, secure banking transactions, and speaker verification to increase user security.
6. DNA Matching
Some organizations choose ultra-high security through DNA matching. Our authentication system uses active comparison of genetic markers to verify identities in controlled settings. DNA matching requires more time to process than other methods yet provides high accuracy for highly regulated industries.
7. Retina scanning
Our system uses retina scanning to document the intricate eye blood vessel patterns. Our devices take retinal images, which get compared to stored data to grant access only to verified users. The implementation of this technology occurs mainly in secure facilities, including data centers and research laboratories.
Behavioral biometrics
Behavioral biometrics verifies identity through interaction patterns like keystrokes, mouse movements, and gestures. Here are its main types:
8. Lips Movement
We utilize lip movement as a multifactor authentication process in our system. Our systems capture the subtle dynamics of a person’s lip movements during speech, adding an extra layer of verification that supplements voice recognition systems in secure communications.
9. Signature Recognition
We enforce signature recognition by comparing a user’s handwritten signature to a stored template. Our software actively measures stroke order, pressure, and rhythm to verify authenticity during critical transactions such as contract signings or financial approvals.
10. Keystroke Recognition
We use keystroke recognition to monitor an individual’s unique typing rhythm. Our applications actively record the timing, speed, and pressure of keystrokes to flag deviations from established patterns. Continuous authentication methods help detect unauthorized access and combat fraud in real time.
11. Gait Scanning
We adopt gait scanning to evaluate and monitor walking patterns unique to each individual. Our systems actively analyze step length, speed, and overall dynamics to identify users discreetly, even from a distance. This innovative approach enhances security in environments where traditional access controls might struggle.
We design and deploy these biometric authentication technologies with precision to meet our business needs. We integrate both physiological and behavioral biometrics to proactively secure our assets and continuously verify identities with accuracy. We are committed to investing in advanced biometric solutions to improve security and operational efficiency and tailor each tool to our specific risk profile and business environment.
miniOrange MFA Supports Biometric Authentication
miniOrange MFA provides enhanced biometric authentication through its integration of multi-factor security with identity verification to deliver a seamless and secure authentication process. The use of biometric verification methods as standalone authentication tools exposes users to risks from spoofing attacks and data breaches. The combination of biometric authentication with one-time passwords and hardware tokens through miniOrange MFA establishes a dual-layer security system that fulfills regulatory standards while effectively minimizing unauthorized entry attempts. The combination of multiple security elements provides comprehensive compliance solutions for all industries while removing password-related hassles to deliver a smooth, robust login experience through an integrated identity and access management system.
The biometric authentication system of miniOrange MFA works harmoniously with Windows, Linux, Mac, and cloud applications. miniOrange supports voice recognition, fingerprint and facial recognition with the help of native-device biometric sensors supporting the FIDO2 protocol. Organizations can boost security by linking biometric authentication to SAML, RADIUS, OpenID, and JWT protocols to create a solution that matches their specific operational requirements to complement the traditional MFA methods. The security system of miniOrange MFA adjusts its authentication needs automatically through real-time risk evaluations to protect against current cyber threats. Businesses can establish robust, secure biometric authentication through miniOrange MFA to achieve both user-friendly access and compliance. Contact us to discuss the possibilities for your security.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication transforms identity verification through fingerprint scanning, iris recognition, and facial analysis methods. Your investigation into modern security technologies will likely lead you to ask about WebAuthn, which serves as an open standard that uses biometric authentication for secure online access. The security measures become more effective through emerging authentication strategies that use environmental and behavioral cues for their implementation. Digital identity protection requires a complete understanding, which includes learning about MFA because it implements multiple authentication layers for robust security. Explore our free trial to see how miniOrange can help your business kickstart your biometric authentication journey.
FAQ’s
What is the most secure type of biometric authentication?
The most secure biometric authentication is iris recognition. It uses high-resolution imaging to capture intricate, stable iris patterns, even accounting for aging or cosmetic changes, and uses liveness detection and sub-millimeter precision to prevent spoofing.
Can biometric data be hacked?
Biometric data remains vulnerable to hacking attacks. The unique characteristics of fingerprints, iris patterns, and facial features become vulnerable through spoofing attacks, replay attacks, and storage vulnerabilities. The permanent nature of these identifiers makes it impossible to reset them, so organizations must implement additional security protocols, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, and liveness detection.
What industries benefit the most from biometrics?
Biometric authentication systems improve security and user experiences across banking, healthcare, hospitality, travel, retail, automotive, border control, law enforcement, education, and cybersecurity.
How is biometric authentication different from MFA?
Biometric authentication uses your unique physical traits (something you are) for identity verification, while MFA combines multiple authentication factors (something you know, something you have, and something you are) to enhance security.




Leave a Comment