In the face of rising unauthorized logins and data breaches, having a single-layer defense strategy is not enough for businesses, and this is where types of multi-factor authentication come into the picture. As an organization grows more competitive and handles more data, it needs more security layers with the help of different multi-factor authentication types. Microsoft at the RSA Conference 2020 mentioned that 99.9% of compromised accounts do not use MFA. Large enterprises with over 10,000 employees now implement MFA as their primary defense against sophisticated attacks at a rate of 87%, as per JumpCloud.
Even if an attacker cracks the first layer, it is nearly impossible to take down the second layer of authentication in MFA. Some of the most powerful MFA types by miniOrange include FIDO2 security keys, biometrics like face and touch IDs, authenticator apps, time-based one-time passwords (OTPs), and SMS and email OTPs.
The blog provides information about MFA, together with its essential value, before explaining its operational process and presenting MFA types, including knowledge-based and possession-based methods. The article provides readers with a selection guide for MFA methods while demonstrating why miniOrange stands as a trusted MFA partner through an FAQ section.
What is Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) protects your account by asking for more than just a password. It uses extra steps like a code sent to your device or a fingerprint to make sure it’s really you. This makes it much harder for hackers to get in, even if they know your password.
An organization's digital security receives substantial enhancement through the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA). The system functions as a vital security measure because it demands multiple identity verification methods, including passwords, device codes and biometric scans, which substantially reduces unauthorized system access. The additional security measure protects sensitive data while simultaneously building customer trust and ensuring compliance with industry safety standards.
Read More: 2FA vs MFA: What’s the Difference?
Why Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
MFA security transforms through its requirement of multiple identity verification steps before access authorization. The combination of password security with one-time codes or biometric verification creates an instant barrier to unauthorized access when any single credential becomes compromised. The additional security measures protect sensitive information while creating unshakeable customer trust and establishing a strong reputation for security excellence for organizations. MFA functions as a strategic business differentiator in the current cyber threat environment. Savvy organizations are aware of the importance of MFA and utilize it as an extra security measure in every login.
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) functions by requiring users to prove their identity through multiple separate verification methods before access is granted. The user begins by entering their primary authentication credential, which usually takes the form of a password. The system then requires an additional verification step, which typically involves receiving a one-time code on a trusted device or one of the types of biometric authentication by performing a biometric scan with a fingerprint.
The individual identity verification process occurs independently for each step, ensuring security even if one authentication method is compromised. By implementing a robust authentication solution like MFA from miniOrange, organizations can build a strong defense against cyberattacks while enhancing user trust and reinforcing their security reputation in the face of evolving threats.
5 Types of Multi-Factor Authentication
The selection of the types of MFA depends on your organizational needs. No network? OTP fails; use biometrics, PINs, or hardware tokens. Having a global remote workforce? Go for a device-based or location-based login. Here are the MFA types that help you log in securely anytime, anywhere:
1. Knowledge-Based Factors (Something You Know)
The knowledge-based factors leverage what a user memorizes—information that only they should know. It is a traditional method, however, essential to an MFA strategy.
- Passwords: Traditional alphanumeric codes that are combinations of strong and unique strings of characters.
- PINs: 4-6-digit numeric sequences that provide quick access when entered correctly.
- Security Questions: Challenges users with personalized questions whose answers only the real user is likely to know. Generally, they are used during account lockout situations.
While familiar and direct, knowledge-based methods are best used alongside other techniques to improve the overall security posture.
2. Possession-Based Factors (Something You Have)
The possession-based factors work on something tangible—a device or physical token—to prove user identity. It makes sure that only the user with the physical hardware token or security key can complete the login process. Some of the possession-based MFA methods by miniOrange include:
- OTP over SMS: Sends a one-time, 6-8 digit code directly to the user’s mobile phone. This is one of the most common types of MFA.
- OTP over EMAIL: Delivers a one-time code through email, offering a reliable alternative when mobile access is not available.
- Out-of-Band SMS: Uses SMS messages that include a secure link to either approve or deny a login attempt, segregating the verification process from the main channel.
- Out-of-Band EMAIL: Works in the same way as out-of-band SMS, by sending an email with a secure link for confirmation.
- Phone Verification: Places an automated voice call that reads out a numeric code, adding an auditory layer of verification.
- Hardware Token: Provides a dedicated physical device that generates a unique code at each use.
- Push Notification: Delivers an instant alert to the user’s mobile app for one-tap approval or denial of a login request.
- Mobile Authentication: Involves scanning a QR code via the miniOrange mobile app to quickly and securely authenticate. It uses the FIDO 2 authentication protocol and is the base of passwordless authentication, one of the best types of MFA.
This set of methods leverages tangible proof of identity, ensuring that possession of a trusted device is key to access—even if other elements are compromised.
3. Inherence-Based Factors (Something You Are)
Biometric solutions anchor this category by verifying identity through unique physical or behavioral traits inherent to the user. This approach leverages characteristics that are nearly impossible to replicate, providing a robust barrier against unauthorized access.
- Fingerprint Recognition: Uses the unique patterns of a user’s fingerprint to unlock devices and authenticate logins quickly and securely.
- Face ID (Facial Recognition): Analyzes distinct facial features to confirm identity, offering a seamless and reliable method of access validation.
- Voice Authentication: Utilizes the unique qualities of a user’s voice to ensure that the speaker is indeed the authorized individual.
By combining these biometric techniques, miniOrange MFA delivers a highly secure and personalized authentication process that reinforces trust and minimizes the risk of fraudulent access.
4. Location-Based Factors (Somewhere You Are)
Location-based factors verify where a user is when attempting to log in. This method adds an extra layer of security by verifying users’ geographic data during login attempts; the miniOrange MFA suite includes a dedicated location-based method.
Organizations seeking to incorporate geographical context into their security can consider miniOrange MFA for additional location-based solutions such as location-based restriction for a wide range of apps supporting different authentication protocols such as SAML, OAuth, LDAP, JWT and more. miniOrange provides context-based authentication with location as a factor enabled.
5. Time-Based Factors (Time You Use)
Time-based methods rely on codes that are valid only for a brief period, ensuring that even if intercepted, they quickly lose their value. This dynamic approach minimizes the window for potential attacks and adds a critical element to a layered security strategy.
- Soft Token (miniOrange Authenticator): Leverages the miniOrange mobile app to generate dynamic 6-digit codes that expire within moments, ensuring every authentication session is fresh and secure.
- Google Authenticator: Integrates with the Google Authenticator app to produce time-based one-time passwords (TOTP), adding an extra layer of protection through continually refreshed codes.
- Microsoft Authenticator: Connects with the Microsoft Authenticator app to generate time-sensitive codes, offering another trusted solution that fits seamlessly into a modern, multi-platform security framework.
These techniques, with their transient and frequently changing codes, significantly drop the risk of unauthorized access. It ensures that any given passcode is useful only for a very short window.
How to Choose the Most Appropriate MFA Methods
Wrong MFA choices cause implementation delays that increase 40% and result in security vulnerabilities. Companies that conduct thorough evaluations focus on these essential elements first.
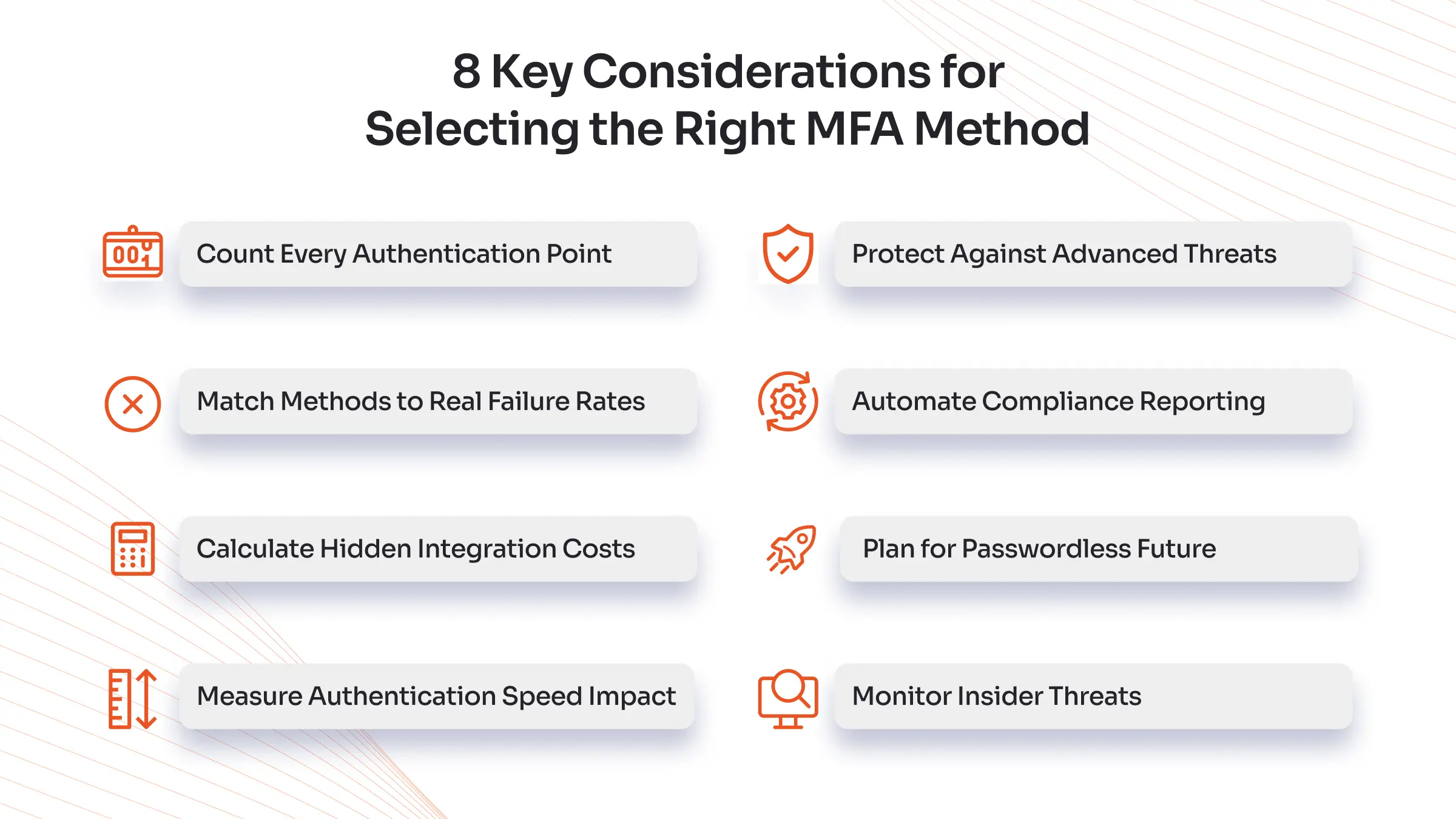
Count Every Authentication Point
Most businesses discover three times more login points than they originally anticipated when they analyze applications, APIs, admin panels, and legacy systems. Organizations should create a system map for identifying NTLM legacy protocol elements that require reverse proxy MFA solutions.
Match Methods to Real Failure Rates
The SMS authentication method experiences international failure rates of 12 percent. Authenticator apps achieve 94% success rates. Hardware tokens operate at 99.7% reliability, while their annual price per user ranges from $50 to $200. Users aged 60 and above experience a failure rate of 8% when using biometric authentication methods.
The selection of solutions that automatically switch to backup authentication methods should be a priority.
Calculate Hidden Integration Costs
Pre-built connectors help organizations avoid spending between $15,000 and $50,000 on developing customized applications. The testing process should include both just-in-time provisioning and conditional access policies together with API authentication for service accounts.
Measure Authentication Speed Impact
The implementation of MFA adds delay periods ranging from 3 to 8 seconds to the authentication process. Organizations with more than 1,000 daily logins experience weekly delays that amount to 2-4 hours. Modern authentication systems utilize predictive authentication technology to reduce delays by 60 percent.
Protect Against Advanced Threats
The standard implementation of MFA does not protect against SIM swapping, push notification fatigue, session hijacking, and machine-in-the-middle attacks. A secure solution must incorporate behavioral analytics with device fingerprinting and session binding capabilities.
Automate Compliance Reporting
Manual compliance consumes 40+ hours monthly. Advanced solutions auto-generate SOC 2, NIST 800-63B, and PCI-DSS reports with immutable audit logs.
Plan for Passwordless Future
The adoption of passwordless technology leads to annual savings of $1.2 million, although 73% of deployment efforts result in failure. Select solutions that support WebAuthn, FIDO2, and passkeys for current deployment.
Monitor Insider Threats
The modern authentication system tracks employee activities following authorization to identify irregular data access patterns along with abnormal working hours and privilege promotion activities. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) helps detect any threat that can bypass authentication.
The right MFA solution prepares you to deal with every threat that can arise over the years and secure your organization effectively.
Why Choose miniOrange for MFA Solutions?
miniOrange protects 3 million global users through enterprise-grade MFA solutions that deliver optimal security alongside an excellent user interface. The importance of MFA cannot be overstated, as it is one of the building blocks of a great security posture.
miniOrange MFA delivers enterprise-grade security with 15+ authentication methods including SMS, email, push, biometrics, and hardware tokens and supports Google and Microsoft Authenticators to simplify user adoption. Its zero-trust engine performs intelligent risk assessments to block 99.9% of attacks while allowing auto-verification in high-risk scenarios. With 3,000+ pre-built integrations (Salesforce, Office 365, AWS, Google Workspace) and flexible deployment options, it scales seamlessly from 10 to 100,000+ users.
The system detects threats in real time while its built-in intelligence system blocks malicious IP addresses. With 24/7 expert support and response within two hours, it ensures fast issue resolution. Its transparent per user pricing includes all authentication methods and unlimited apps, reducing security costs by 40 to 60 percent. Trusted by Fortune 500s and startups, it is compliant with SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR with no extra setup required. Organizations see a 95 percent drop in security incidents and a 25 percent boost in productivity.
miniOrange MFA Features:
- 15+ MFA methods, zero-trust security to prevent 99.9% of attacks.
- 3,000+ integrations deploy in days (Salesforce, Office 365, AWS).
- Scale from 10 to 100,000+ users, flexible cloud, on-premises and hybrid deployment.
- Real-time threat detection, 24/7 support, sub-2-hour response.
- Pay-per-active-user pricing with 40-60% cost savings with miniOrange MFA product.
miniOrange delivers multi-factor user logins without compromising user experience or breaking your bank. Talk to our expert to find the right MFA for your use case. Take an MFA free trial today.
Getting Started with MFA for Your Secure Future
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is not just an upgrade; it’s the beginning of an era of secure logins everywhere. Each method, from push notifications and one-time passcodes to biometrics and hardware tokens and more, has been designed to drop the risk of breaches significantly. This helps not just with additional sign-in options but also gives your users the confidence that their data remains in safe hands. Advantages of biometrics are many, and it may have privacy concerns of individuals; however, it is regarded as a safe method to verify user identities.
By integrating these layers into multi-factor authentication, businesses don't just secure assets: they inspire confidence, trust, and reliability their employees and customers can build upon. And each secure login is a promise of security, engendering an environment where people truly feel safe and can navigate digital challenges with a sense of empowerment and ease.
For organizations poised to elevate their security posture, miniOrange MFA serves as a powerful, user-centric solution that elevates the standards of access management and fosters a sense of peace in every login. Choose from different types of biometric authentication within the miniOrange MFA methods. To choose miniOrange MFA is to choose a future where security is intuitive and humanity resides at the heart of every interaction.
FAQ's
What is the most common MFA?
The three main MFA methods used today include SMS codes, authenticator apps (such as Google Authenticator), and email tokens. SMS-based MFA remains widely used because of its ease of use, but authenticator apps gain popularity because they provide enhanced security features.
What are the main types of multi-factor authentication?
The four primary authentication factors used in multi-factor authentication consist of:
- Knowledge: Something you know (e.g., password, PIN, security question)
- Possession: Something you have (e.g., phone, hardware token, security key)
- Inherence: Something you are (e.g., fingerprint, facial recognition, biometrics)
- Location: Somewhere you are (e.g., geographic location, IP address)
Which MFA type is the most secure?
A hardware security key represents the most secure MFA type because it includes FIDO2 or WebAuthn devices. Research shows these keys resist phishing attempts and protect against almost all types of attacks which makes them one of the most invincible types of multi-factor authentication. Hardware security keys represent the most secure option for high-security needs, although biometric authentication provides strong protection.
Can MFA be hacked?
Yes, all MFA methods can be hacked, but some are much harder to bypass than others. The methods used to bypass MFA include social engineering, technical exploits (such as SIM swapping for SMS codes), physical attacks (such as stealing tokens or copying biometrics), and combinations of these methods. Security keys are much harder to crack than SMS or email codes.
How does miniOrange MFA improve security?
The miniOrange MFA system improves security through multiple authentication methods, which combine password verification with device authentication biometric verification, hardware token authentication and push notification verification.
The system integrates well in all kinds of deployments, including cloud, on-premises, VPN, and legacy systems, and controls access that keeps changing, usually based on location and login attempt risk factors. The system enables offline access and provides easy user enrollment for management.


Leave a Comment