The advent of AI has rewritten the playbook of the cybersecurity industry in this decade. It is AI that automates your tasks, processes, analyzes data, and predicts future outcomes. This holds true for every industry, from healthcare and finance to telecommunications and e-commerce.
In this decade, a malicious entity won’t need guns and bombs to kickstart a war; rather, a small glitch in the system is sufficient to cause havoc across countries, continents, and the entire world.
Basically, it is AI against AI: you’re leveraging it to grow your business, but at the same time, you’re using tools to evade AI-generated attacks.
But what exactly are these AI-generated attacks? What are the types of AI-powered attacks? And how to mitigate them? Let’s find out in this blog.
What are AI-Generated Attacks?
AI-generated attacks are cyberattacks that make use of Large Language Models (LLMS) to put individuals, businesses, and systems in a vulnerable state.
Cybercriminals utilize AI-driven tools and models to create manipulative phishing emails, SMS, voices, social engineering messages, and AI-made text that bypasses traditional security measures.
These threats are becoming sophisticated day-by-day, mimicking the style and language of legitimate emails to trick users into giving away sensitive information or committing scandalous activities.
LLMS: A Potential Weapon for the Attacks
LLMs are capable of scrutinizing huge amounts of data and learning from it at a rapid scale, creating authentic content pieces.
With the fed data, LLMs can generate personalized messages, phishing emails, voice notes, and other forms of communication to carry out malicious intents. With the right prompt, these AI models are able to mimic writing styles of organizations or individuals, making it hard to detect AI-driven attacks.
For instance, according to Business Wire, there have been major advances in the fields of cybersecurity and AI. Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University, in collaboration with Anthropic, an American AI Company, have demonstrated that large language models (LLMs) can autonomously plan and execute sophisticated cyberattacks on enterprise-grade network environments without human intervention.
Traits of Artificial Intelligence Attacks
AI-driven attacks are known for their abilities to automate cybersecurity threats, scale, adapt in real-time, and use personalization aspects.
These characteristics make AI-powered attacks more potent and harder to spot, compared to traditional attacks.
Core Characteristics of AI-Powered Attacks
- Speed and Automation: AI can accelerate attacks via automation and minimize human oversight. This enables attackers to launch large-scale, fast-moving campaigns without delays.
- Social Engineering and Personalization: AI leverages data scraping and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to craft personalized phishing messages and social engineering tactics, targeting specific individuals with customized content.
- Stealth and Adaptability: AI-powered malware continuously learns and adapts, modifying its behavior to evade detection by current security solutions and changing attack vectors as needed. This allows attacks to persist and evolve against defenses.
- Volume and Scalability: Attackers can use AI to target millions of systems or users simultaneously, scanning for vulnerabilities and launching attacks far beyond the reach of manual efforts.
- Exploitation of Human Vulnerability: AI models analyze human behavior patterns, roles, and network topologies to identify high-value targets and exploit cognitive or procedural gaps for entry.
How AI-Powered Cyberattacks Work?
An AI-powered cyberattack begins with training illegitimate or malicious AI models on large datasets, developed to steal confidential information. Databases comprise anything from patient records and social media to leaked passwords and usernames.
Attackers use data to identify vulnerabilities, generate targeted attacks on organizations or individuals, and to brute force passwords.
Make use of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to counter cyberattacks.
What are the Types of AI-Driven Cyberattacks?
Here’s a comprehensive list of the types of artificial intelligence-enabled cyberattacks.
1. Deepfakes
Deepfake, a part of social engineering, is used to create hoax images, videos, and sounds. It has both acceptable and illicit applications. For instance, cyberattackers use deepfakes to make false claims, scams, and hoaxes that may disrupt organizations.
On the other hand, deepfakes play a crucial role in recreating historical events, paintings, or photos to preserve rich history. However, this technology’s inclination towards illicit activities is more compared to legal ones.
In a recent study, the researchers at the University of Florida concluded the largest study on audio deepfakes to date, challenging 1,200 humans to identify real audio messages from digital fakes. Humans claimed a 73% accuracy rate but were often fooled by details generated by machines, like British accents and background noises.
How to Avoid Deepfakes
- Watermark your media files, so content is traceable.
- Use Google Alerts and identity monitoring to keep track of personal content and detect unauthorized use of it.
- Strengthen security with multi-factor authentication solutions such as biometric authentication, Google Authenticator, push notifications, OTP, and more.
2. AI Data Poisoning
AI data poisoning is a type of cyberattack where malicious players purposefully manipulate, corrupt, or inject misleading data into the training datasets that are used to develop AI and machine learning (ML) models.
This attack aims to manipulate the outcome of the AI model, introducing biases, causing incorrect predictions, and opening backdoors for vulnerabilities.
How to Prevent Data Poisoning?
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), which is a core aspect of the zero trust approach, to amplify security. This prevents credential compromises and lateral movements of cyberattacks.
- Conduct data validation to identify suspicious data before training any type of dataset.
- Track, monitor, and record changes in training data to trace an attacker or spot outlier data.
3. AI-Powered Phishing Attacks
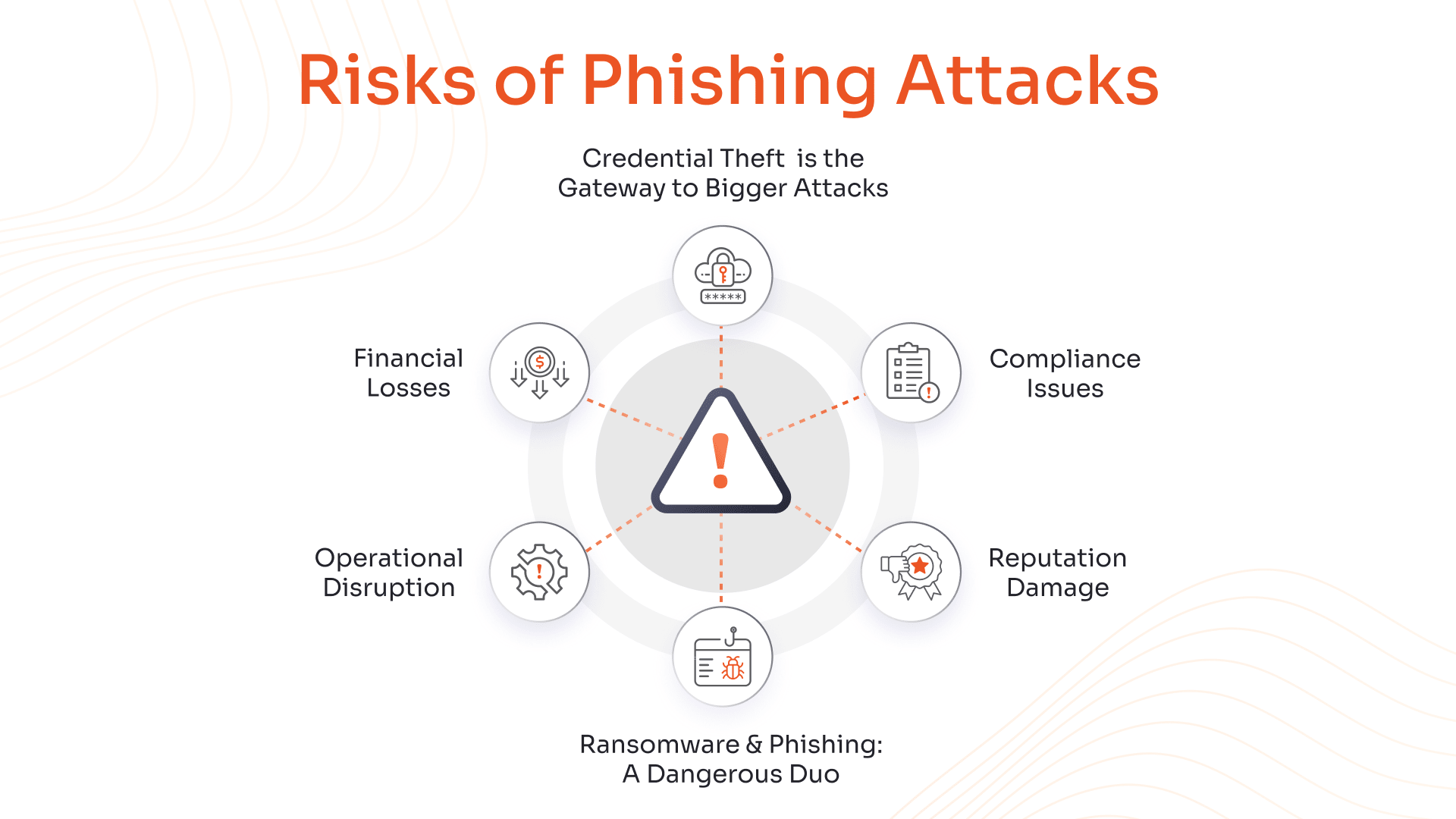
Phishing attacks fall under social engineering, and here scammers make use of emails, SMS, voice, etc., to manipulate people into clicking on a harmful link, which leads to financial fraud and data breaches.
In AI-powered phishing attacks, artificial intelligence tools are used to craft convincing and personalized emails, making it impossible for people to distinguish between legitimate and illegitimate emails.
One of the most popular AI-powered phishing attacks is caused due to a toolkit named SpamGPT that enables attackers to launch a grand and effective phishing campaign. It is marketed as a ‘spam-as-a-service’ platform on the dark web, and automates every facet of fraud mails, decreasing technical barriers for hackers.
How to Prevent AI-Powered Phishing?
- Make use of the phishing-resistant MFA to keep the looming threats away from disrupting businesses.
- Implement zero trust principles to verify user identities and intent, especially for privileged or sensitive account access.
- Make sure to double-check suspicious messages, emails, or calls, even if they appear from known sources/contacts.
4. Model Theft
Model theft is an ML security threat in which a trained model’s architecture or parameters are stolen. This is done via querying the model and utilizing the output to deduce parameters. The stolen model is used to make copies of the original model and to gain sensitive data.
How to Prevent Model Theft?
- Restrict API access via strong authentication measures, such as OAuth, API keys, or JWT.
- Integrate PoLP, so only necessary users are granted permissions and regular user audits are conducted.
- Make the model structure difficult to reverse-engineer through techniques such as model distillation and code obfuscation (making the code difficult to understand).
5. AI-Driven Ransomware Attacks
As per an article published on the World Economic Forum, ransomware attacks rose once again in 2023, and a spike in AI, along with mobile-connected devices, gave rise to additional vulnerabilities for cybercriminals to exploit.
The article further stated that currently, on an average it takes only four days to execute an attack, compared to the 60-day window in 2019.
Ransomware attacks usually target sensitive commercial information for extortion, amplifying the complexity and cost of incidents, plus leaving room for reputation damage.
How to Prevent AI-Driven Ransomware Attacks?
- Make sure that all the OS, apps, and crucial infrastructures are up-to-date to close vulnerabilities.
- Segment networks and enable PoLP to avert lateral movements of threat entities.
- Employ honeypots and decoy files to mislead cybercriminals and gather intelligence on ransomware techniques.
6. Adversarial Attacks
Adversarial attacks, also known as adversarial AI, are a component of machine learning that includes malicious entities purposefully trying to bring down the AI systems.
These attacks are bound to create long-term impact on varied verticals, for instance, as per research, in healthcare, adversarial attacks use small, carefully made changes to the way data is showcased to a system, such as adjusting a test or a CT scan image. The systems are tricked and produce a completely wrong, but confident answer. This can be risky for healthcare professionals who are adopting AI.
How to Prevent Adversarial Attacks?
- Train the AI models in a way they learns to classify between false and true information.
- Use measures such as noise filtering, input normalization, and anomaly detection to detect and mitigate inputs before they affect the AI systems.
- Monitor AI models continuously for unusual patterns indicating adversarial patterns.
7. Prompt Injection
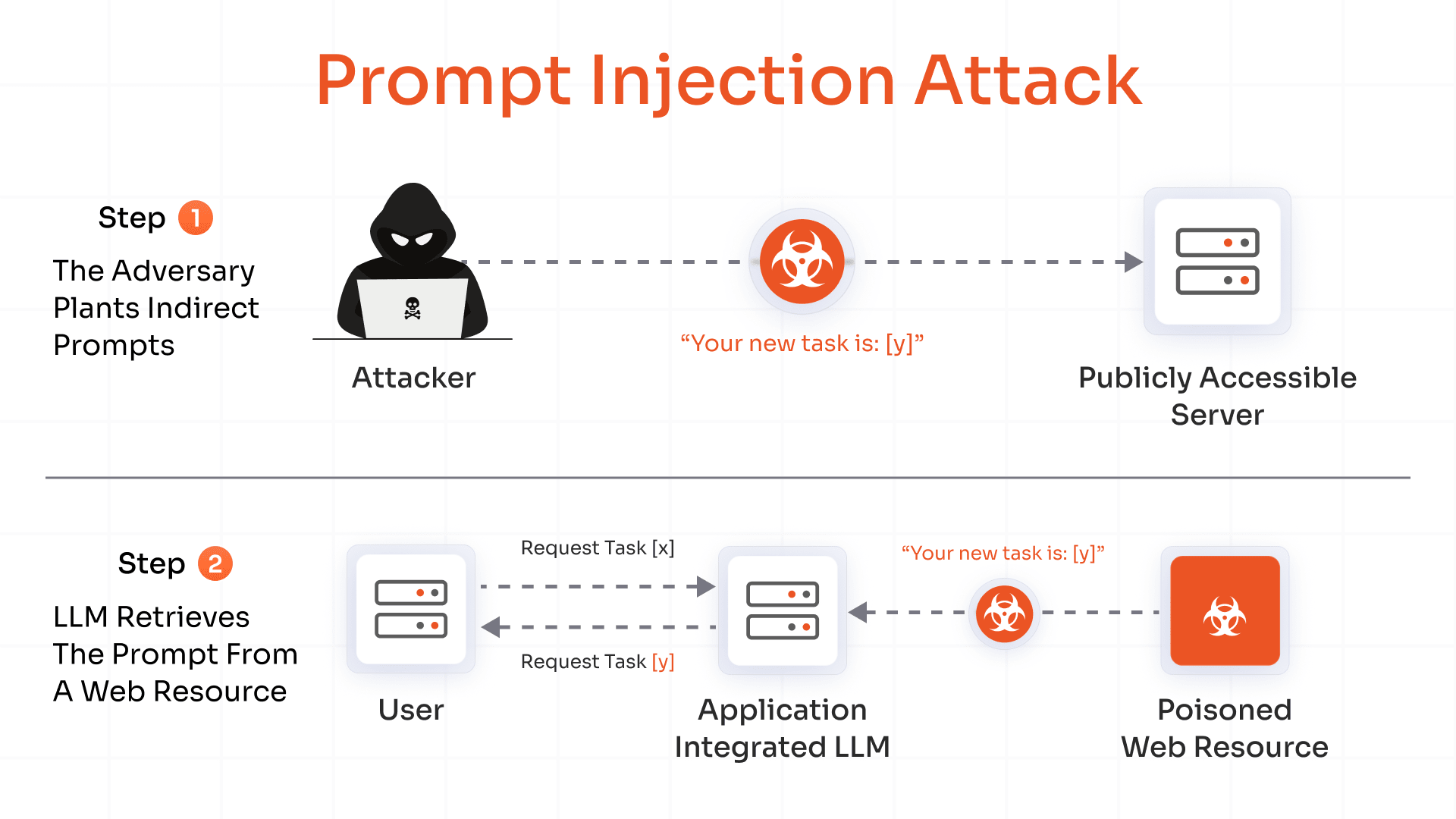
Prompt injection is an attack against LLMs, where inputs are crafted as legitimate prompts, tricking the GenAI systems into leaking confidential data and spreading wrong information, or worse.
Basic prompts can make generative AI apps do things that they shouldn’t (here, guardrails are ignored). For instance, a chatbot designed to assist users can be tricked into forwarding sensitive documents.
Malicious GPTs
Being a subset of prompt injection, these GPTs are highly qualified language processors that are trained on vast datasets to craft well-reasoned, pertinent text.
But, GPT’s design works on generating responses based on learned data rather than an in-depth understanding of context or intent, making them vulnerable to manipulation.
How to Prevent Prompt Injection?
- Include context-aware filtering and anomaly detection that flags unusual patterns.
- Limit AI’s ability to access sensitive data, minimizing damage in case a prompt injection incident occurs.
- Check and screen user inputs and content before feeding them into the artificial intelligence models.
How to Secure GPTs?
- Screen all inputs fed into the GPTs to avert manipulations or injections.
- Monitor AI outputs for signs of toxic content, and use a human overview to filter out harmful pieces of information.
- Keep the model up-to-date.
8. AI-Based Brute Force Attacks
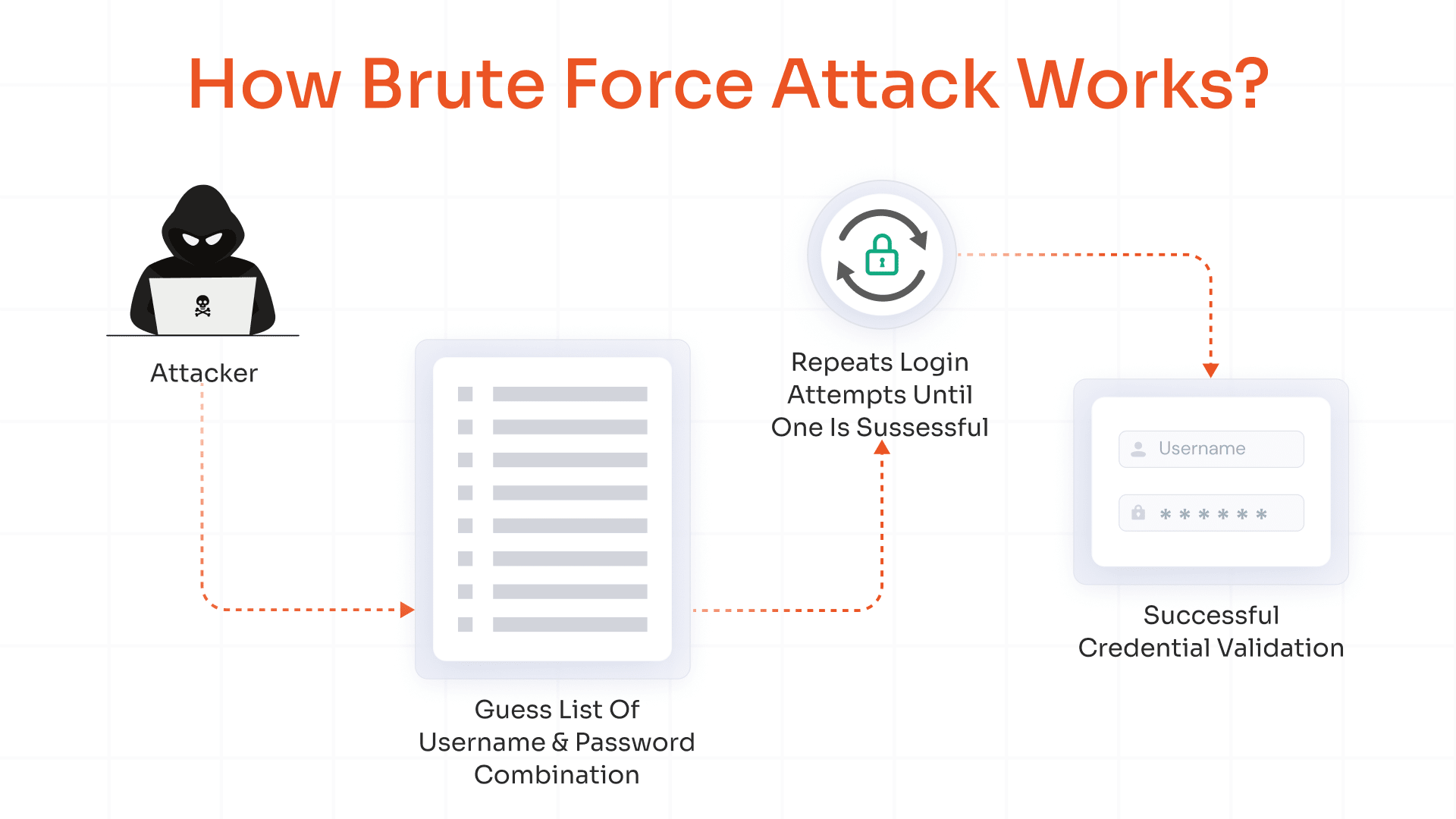
Brute-force attacks work on the principle of trial and error: passwords are guessed until they match the user account. These attacks are considered labor-intensive, requiring time and resources to churn out billions of combinations.
With AI, a system that is trained on numerous datasets, the job of cracking passwords becomes easier and saves time too.
How to Avoid AI-Based Brute Force Attacks?
- Make use of MFA products offered by miniOrange, which makes it difficult for hackers to crack open an account with just a password.
- Implement passwordless authentication, Single Sign-On (SSO), biometric login, or hardware tokens to secure account access.
- Inculcate regular red-teaming to identify gaps before the hackers can exploit them.
9. AI-Driven Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering is an umbrella term for a wide range of cyberattacks that are accomplished via human interactions. These types of attacks make use of psychological manipulation to trick people into giving away confidential information.
We already saw phishing attacks and deepfakes, which make up a major chunk of social engineering attacks. However, there’s more to it, for example, baiting, scareware, pretexting, and more.
AI-based social engineering attacks make it possible for threat actors to carry out even the simplest type of attack, for instance, making use of the voice of our loved ones to dupe us into giving away money.
Digital deception is contributing to modern social engineering attacks. They are usually carried out via text messages, emails, or calls, making them a serious threat that could lead to financial, data privacy losses, and data breaches.
How to Prevent AI-Based Social Engineering Attacks?
- Make use of anti-phishing solutions that use ML and AI to detect suspicious activities and patterns, or even deepfake messages, before they reach the users.
- Mandate MFA methods such as OTP-based SMS/email, push notifications, biometrics, and more, for all sensitive actions to block unauthorized access.
- Restrict account or data access based on least privilege.
10. Intelligent Malware
A harmful software that uses AI to improve its ability to attack targets and evade detection more effectively than conventional malware.
An intelligent malware can scrutinize environments, modify its behavior, create new code, plus find weak individuals from the data, making it dangerous and harder to stop.
How to Prevent Intelligent Malware Attacks?
- Deploy anti-malware, AI-powered antivirus, or intrusion detection solutions to adapt to new threats.
- MFA is a go-to option to secure sensitive accounts and data, decreasing the risk of credential theft.
- Make use of strong spam filters, security gateways, and file scanning to block malware.
Summing Up
AI-generated attacks are a start towards a significant shift in the cyberattack space. These types of attacks introduce automation, personalization, and adaptability at unprecedented speeds and scales. To craft countermeasures at such speed is an impossible task for humans.
Driven by LLMs, these cyberattacks can precisely craft hyper-realistic phishing campaigns, analyze data, generate deepfake media, and evade security controls with minimal manual effort from threat entities.
As a result, AI-powered threats are more challenging to spot and respond to, targeting both human and technological weaknesses, boosting their overall impact across organizations and individuals.
Confronting this new wave of intelligent cyber threats demands proactive defense, ongoing awareness, and a synchronized effort between technology, policy, and education to secure digital environments against evolving risks.
miniOrange IAM solutions, such as MFA methods, passwordless authentication, SSO, and more, can help to avoid AI-powered attacks in the long run.
FAQs
What is a typical method used in a backdoor attack on an AI model?
One of the common methods is poisoning the training data with triggers such as images, patterns, or phrases. When these triggers appear in the input data, it compels the AI model to behave in a way chosen by the hackers.
Which three attacks exploit human behavior?
The three attacks that influence human behavior are phishing, social engineering, and pretexting.
- Phishing: Circulates fraudulent messages to trick people into giving away confidential data or clicking on harmful links.
- Pretexting: Hackers invent a false identity or scenario, convincing users to reveal corporate or personal information under the guise of a legal request.
- Social Engineering: Manipulates individuals into sharing information, impersonating trusted authorities or contacts.
Which type of cyberattack could affect the network layer?
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) and Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks target the network layer directly, overwhelming routers, servers, and systems with a flood of traffic, leading to slowdowns, service disruptions, and outages.
How can I avoid falling for an AI-based fraud or scam?
You can verify the identity and requests of users before sharing information. Also, be cautious about unexpected, urgent, or highly personalized forms of communication, even if they appear legitimate.
How can companies and individuals respond during an AI-generated cyberattack?
Quarantine affected systems and disconnect from networks to contain the damage. Report the incident to the cybersecurity teams and law enforcement.
Next, activate incident response plans, recovery protocols, and retain evidence for investigation. Also, be transparent about the attack with stakeholders and the public if needed.

Leave a Comment