As our day begins, we engage in countless digital interactions, be it logging into work systems, accessing cloud applications, or ordering food online. Each login is powered by identity management technology, but have you ever considered how different platforms secure user access? Are corporate systems and customer-facing applications authenticated in the same way, or do they rely on distinct security solutions?
This is where Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) come into play. In this article, we will explore their definitions, key differences, and help you determine the right identity solution for your business.
What is IAM?
Identity and Access Management or IAM, is a framework of policies, technologies, and processes that ensure only authorized individuals have access to specific systems, applications, and data. It plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by regulating user permissions and authentication mechanisms.
IAM solutions often include role-based access control (RBAC), privileged access management (PAM), and adaptive authentication to balance security with convenience. The miniOrange IAM is your unified solution for all security challenges, from SSO to user lifecycle management; you receive everything in a single platform.
Why Do You Need IAM?
IAM is essential for organizations to:
Enhance Security
Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and mitigate cyber threats like identity theft and data breaches.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Helps companies meet security standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
Improve Efficiency
Reduces administrative overhead by automating user authentication and role-based access control.
Optimize User Experience
Enables seamless access through features like Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
IAM Implementations
Enterprise Workforce Security
Organizations use IAM to manage employee access to internal systems, ensuring Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for secure authentication.
Banking & Financial Services
Financial institutions implement IAM to enforce role-based access control (RBAC), allowing only authorized personnel to access critical systems while maintaining compliance.
Healthcare Compliance
Hospitals and medical institutions use IAM to protect patient records, ensuring secure identity verification for healthcare professionals.
Cloud Security & DevOps
IAM solutions help developers manage permissions for cloud resources, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring least privilege access.
Learn the Key Differences Between 2FA and MFA
What is CIAM?
Customer Identity and Access Management or CIAM, is a specialized branch of IAM designed for managing external user identities (such as customers, partners, and vendors). Unlike traditional IAM, which primarily focuses on employees, CIAM integrates security with user experience in digital platforms. CIAM solutions often integrate with social logins, passwordless authentication solutions, biometric verification, and progressive profiling to improve accessibility while maintaining security.
Why Do You Need CIAM?
CIAM is vital for businesses that provide online services, e-commerce, or customer-facing applications because it:
Secure Customer Access
Protects user accounts from credential theft, fraud, and unauthorized access.
Personalization and Engagement
Uses identity data to tailor experiences, such as personalized recommendations.
Privacy and Compliance Requirements
Aligns with global regulations like GDPR and CCPA, ensuring safe handling of customer credentials.
Scalability and Performance
Manages millions of users while maintaining security and frictionless login experiences.
CIAM Implementations
E-Commerce & Retail
Online platforms use CIAM to provide social login options, allowing customers to sign in using existing credentials from other services.
Streaming Services
Digital entertainment platforms use CIAM to manage millions of user identities, ensuring secure authentication while offering personalized recommendations.
Banking & Fintech
CIAM solutions help financial institutions provide secure customer onboarding, fraud detection, and seamless login experiences across mobile apps and websites.
Gaming & Social Media
Online gaming and social platforms implement CIAM for passwordless authentication, biometric login, and risk-based authentication to enhance security and user experience.
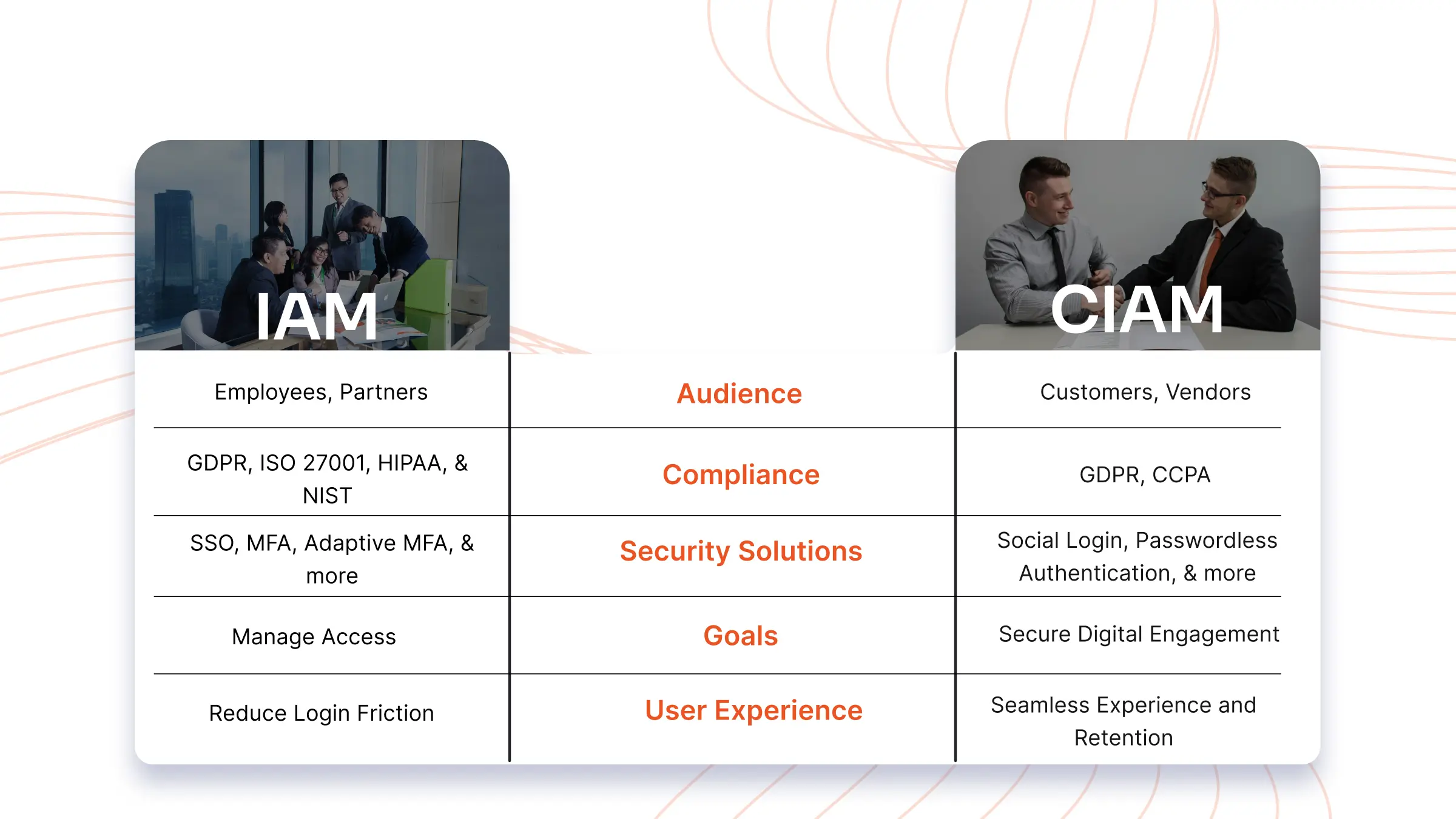
Key Differences Between IAM and CIAM
| Aspect | IAM (Identity & Access Management) | CIAM (Customer Identity & Access Management) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Purpose & Audience | IAM is designed for managing access to corporate resources for internal users (employees, contractors, partners). It ensures secure access to enterprise systems and protects sensitive business data. | CIAM focuses on managing customer identities and access for external users (customers, vendors, partners). It enhances digital engagement while ensuring security and compliance with privacy regulations. |
| 2. Security & Compliance | Implements role-based access control (RBAC), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Single Sign-On (SSO) to protect internal systems. Ensures compliance with industry regulations like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and NIST. | Uses adaptive authentication, passwordless login, and fraud detection to secure customer interactions. Ensures compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other data privacy laws to protect customer information. |
| 3. User Experience (UX) | Prioritizes efficiency for employees with streamlined authentication. UX enhancements focus on reducing login friction while maintaining security. Employees are trained to use IAM systems, making usability less critical. | UX is customer-centric, enabling social logins, biometric authentication, and personalized access to improve engagement and retention. A seamless experience is crucial for customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. |
| 4. Scalability | Generally built to support thousands of enterprise users within an organization. Scaling requires structured identity provisioning and management, often involving directory services and federated identity solutions. | Designed for millions of customers across various platforms. Must accommodate high traffic, global access, and real-time personalization without performance issues. CIAM solutions are optimized for large-scale deployments. |
| 5. Deployment Complexity | Requires integration within corporate IT infrastructure, including on-premise or hybrid environments. Deployment involves identity federation, directory services, and security policies tailored to enterprise needs. | Integrates with digital platforms like mobile apps, e-commerce sites, and SaaS applications. Cloud-native CIAM solutions simplify deployment while ensuring high security and seamless user experiences. |
| 6. Data Privacy & Consent Management | Focuses on internal data protection, ensuring employees access only authorized resources. Data privacy is enforced through access control policies and audit logs to track user activity. | Manages customer data privacy, ensuring compliance with consent management regulations. Customers must explicitly grant permission for data usage, and CIAM solutions provide self-service privacy controls. |
| 7. Analytics & Personalization | Tracks login attempts, access patterns, and security incidents to improve enterprise security posture. Analytics focus on risk assessment and compliance monitoring. | Monitors customer behavior, preferences, and engagement to enhance user experience. CIAM solutions leverage data-driven insights for personalized recommendations and targeted marketing strategies. |
Explore the Top Cybersecurity Threats You Should Know
How to Choose Between IAM and CIAM?
Business Objective
IAM is designed for securing internal systems, ensuring employees and partners have controlled access to enterprise resources. CIAM, on the other hand, is built for customer-facing applications, prioritizing seamless authentication and personalized user experiences for millions of external users.
Authentication Methods
CIAM integrates User registration and management, social login, and passwordless access to balance security with user convenience while preventing fraud. IAM enforces strict access control through different types of authentication, including Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), role-based permissions, and privileged access management to protect sensitive corporate data.
User Lifecycle Management
Identity management handles user identity throughout an employee’s lifecycle, from onboarding to role changes and eventual offboarding, ensuring continuous security and access control. CIAM, on the other hand, manages customer identity creation, authentication, profile updates, and account recovery, prioritizing frictionless user engagement while maintaining security.
miniOrange for IAM & CIAM
miniOrange offers a comprehensive IAM and CIAM solution designed to enhance security, streamline access management, and improve user experience. For IAM, you get miniOrange SSO products, MFA with 15+ authentication methods, adaptive authentication, and seamless integration with 6000+ applications, ensuring secure workforce identity management.
In CIAM, it excels with user management, passwordless authentication, social login, progressive profiling, and consent management, enabling businesses to deliver personalized and secure customer experiences. With scalable and cost-effective features, miniOrange is a strong choice for organizations looking to balance security with usability across both internal and external identity management.
FAQs
Can IAM and CIAM be used together?
Yes, IAM and CIAM can complement each other within an organization. IAM secures internal access for employees, while CIAM manages customer identities and authentication. Businesses often integrate both to ensure consistent security policies across the workforce and customer-facing applications, while maintaining compliance and a positive user experience.
Is CIAM more secure than IAM?
CIAM and IAM serve different security needs. IAM focuses on internal security, enforcing strict access controls for employees, while CIAM prioritizes customer data protection with threat detection, adaptive authentication, and consent management. CIAM must handle higher scalability and privacy regulations, making it robust against external threats; however, IAM is equally critical for securing enterprise systems.
What are the top CIAM security features?
CIAM solutions offer multi-layered security, including Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), passwordless authentication, adaptive risk-based authentication, consent management, and fraud detection. Other key features include self-service account management, progressive profiling, and Single Sign-On (SSO) to enhance security while improving user experience.
Which is better for compliance: IAM or CIAM?
IAM ensures compliance with enterprise security standards like ISO 27001 and HIPAA, focusing on internal data protection and audit trails. CIAM aligns with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, offering consent management and secure identity handling for customer data. The choice depends on whether the organization prioritizes workforce security or customer data privacy.




Leave a Comment