As we approach 2026, cybersecurity threats continue to escalate in complexity and frequency. With organizations increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, the human element remains the most vulnerable entry point for cyberattacks. Studies show that 95% of data breaches stem from human errors, which can be employees clicking on malicious links, using weak passwords, or mishandling sensitive data.
The financial and reputational consequences have never been more severe, with breaches costing millions in remediation, legal penalties, and permanent brand damage. As regulatory requirements tighten and AI-powered attacks grow more sophisticated, cybersecurity awareness training has evolved from an IT concern into a fundamental business priority that requires active participation from every employee across all departments.
What is Cybersecurity Awareness?
Cybersecurity awareness is the ongoing process of educating individuals and employees about digital threats that exist in cyberspace and teaching them how to act responsibly to protect themselves and their organizations from cyberattacks. Unlike technical security measures that rely on software and infrastructure, cybersecurity awareness focuses on the human element, i.e., building knowledge, skills, and behavioral habits that prevent security incidents before they occur.
Key Components of Cyber Awareness
At its core, cybersecurity awareness involves understanding how to recognize common cybersecurity threats, such as phishing emails, social engineering attempts, malware, and ransomware, while knowing the appropriate response actions to take.
It encompasses practical knowledge about using strong passwords, identifying suspicious communications, handling sensitive data properly, keeping software up to date, and reporting potential security incidents promptly. This awareness extends beyond simply knowing threats exist; it requires individuals to integrate security-conscious behaviors into their daily digital activities.
Building a Human Firewall
Effective cybersecurity awareness shifts security from an isolated IT department responsibility into an organization-wide culture where every employee understands their critical role in protecting company assets. When employees possess strong cybersecurity awareness, they become proactive defenders who can identify and prevent attacks that bypass technical security controls.
In return, creating a "human firewall" that complements technical measures and significantly reduces organizational risk exposure. In 2026, this also involves understanding emerging threats powered by artificial intelligence and sophisticated social engineering tactics.
Why Cybersecurity Awareness Matters?
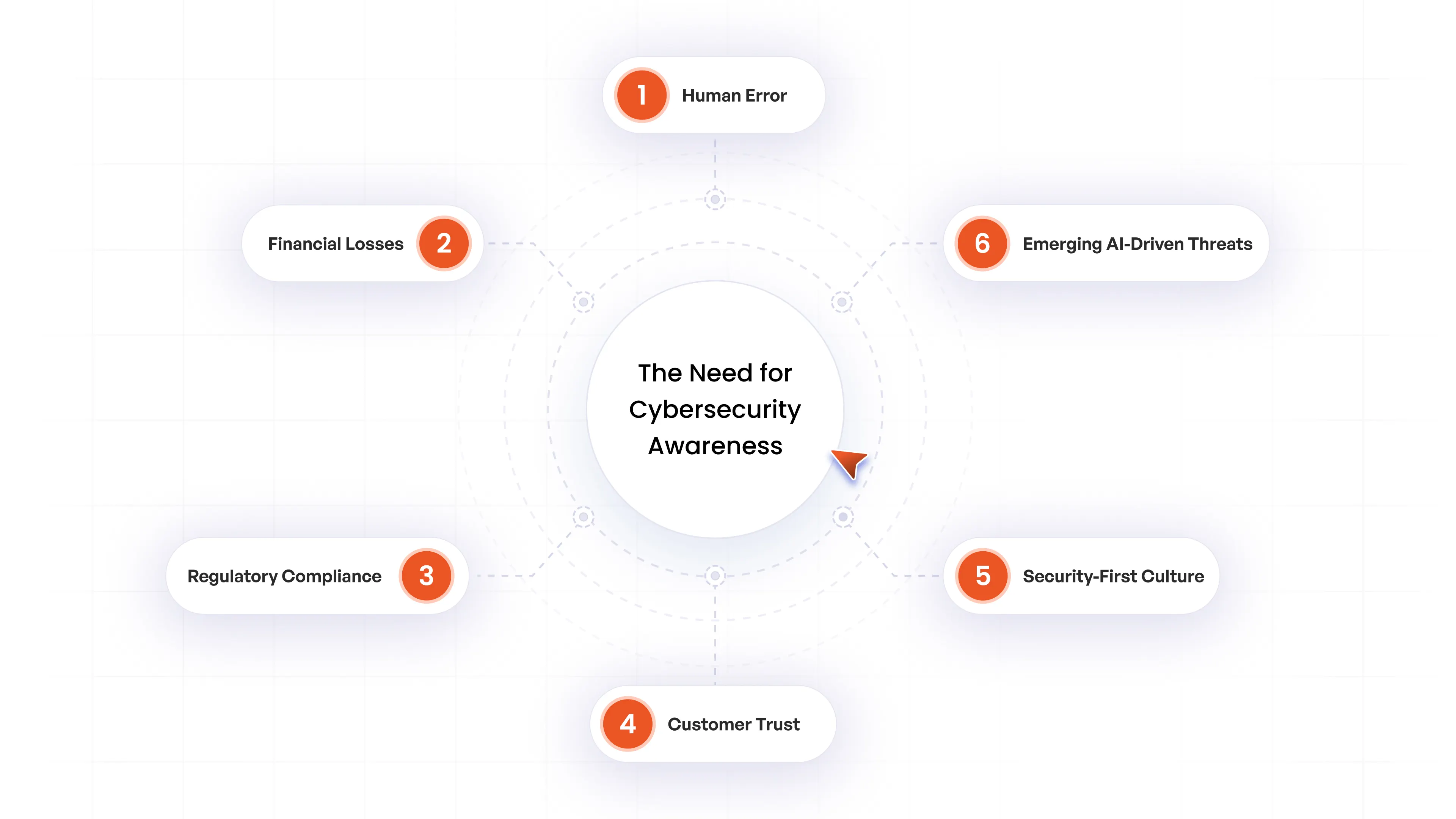
Reduces Human Error and Security Incidents
Human error accounts for 68% of successful cyberattacks, making employees both the greatest vulnerability and strongest defense. Cybersecurity awareness training transforms employees from potential weak links into vigilant defenders who recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and suspicious activities before they cause breaches. Educated staff become the first line of defense against evolving threats.
Protects Against Devastating Financial Losses
Cyberattacks cost organizations millions in remediation, legal fees, regulatory fines, and operational downtime. With global cybercrime projected to exceed $10.5 trillion annually by 2026, investing in awareness programs significantly reduces financial exposure by preventing incidents before they occur. Research shows training reduces breach costs by an average of $232,867 per incident.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance Across Industries
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and ISO 27001 mandate employee cybersecurity training and documented security practices. Organizations must prove ongoing education and compliance readiness during audits. Awareness programs ensure staff understand their responsibilities in protecting sensitive data, helping businesses avoid costly penalties, legal liabilities, and operational restrictions.
Builds Customer Trust and Competitive Advantage
Customers and partners prioritize doing business with organizations that demonstrate strong data protection practices. A single breach can erode years of trust and damage brand reputation permanently. Companies with trained employees signal commitment to security, building stakeholder confidence and setting themselves apart in competitive markets where cybersecurity awareness provides a measurable business advantage.
Creates a Security-First Organizational Culture
Ongoing awareness training builds an organizational culture where security becomes everyone's responsibility, not just the IT department's concern. When employees feel empowered rather than blamed, they actively report suspicious activities and participate in defending company assets. This collective vigilance creates a proactive, security-conscious workplace that adapts to emerging threats.
Prepares Organizations for AI-Driven Emerging Threats
Cyber threats continue evolving with AI-driven attacks, deepfakes, and sophisticated social engineering becoming more prevalent in 2026. Regular awareness training keeps employees updated on emerging attack vectors, ensuring they can recognize and respond to new tactics that bypass traditional security controls. Prepared teams reduce organizational vulnerability and improve overall resilience.
Importance of Cybersecurity Awareness Training for Employees
Empowers Employees as Active Security Defenders
Training empowers employees to become proactive participants in organizational security rather than passive users who unknowingly enable attacks. Through comprehensive education on threat identification, employees develop skills to detect phishing emails, verify suspicious requests, and question unusual activities. This empowerment creates confident staff who understand their vital role in protecting company assets.
Provides Practical Skills for Daily Security Decisions
Employees face security decisions constantly, from choosing passwords to sharing files and accessing networks. Training provides practical competencies such as recognizing social engineering, implementing multi-factor authentication, using VPNs securely, practicing safe browsing, and understanding data classification. These essential skills enable informed decision-making that protects both personal and organizational information across all work scenarios.
Improves Incident Detection and Response Speed
Half of trained employees report real security threats within six months of beginning training programs, demonstrating heightened threat awareness. When employees know how to recognize and report incidents quickly, IT teams can contain breaches before they spread. Training on escalation procedures, communication channels, and immediate response steps minimizes damage and enables faster recovery.
Develops Long-Term Security Mindset and Habits
Effective training creates lasting behavioral changes rather than temporary awareness. Through ongoing education, simulated attacks, and regular reinforcement, employees develop security-conscious habits that extend beyond the workplace into their personal digital lives. Organizations with regular training programs achieve 96% improvement in phishing susceptibility compared to infrequently trained groups.
Fosters Security Culture Through Shared Responsibility
Training breaks down the perception that security is solely IT's responsibility, creating shared accountability across all departments. When employees understand how their actions impact overall security posture, they become advocates who encourage peers, question risky behaviors, and contribute to continuous improvement. This cultural shift transforms security from a compliance burden into a collective organizational value.
Core Cybersecurity Training Topics

Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing attacks remain the primary attack vector targeting employees through emails, texts, and phone calls. Training teaches staff to scrutinize sender addresses, verify URLs before clicking, recognize urgency tactics, and question unexpected credential requests. Understanding social engineering psychology helps employees verify identities before responding.
Password Management and Authentication
Weak passwords enable over 80% of breaches. Employees learn to create strong, unique passwords, implement password managers, and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all accounts for effective password authentication. Training emphasizes that MFA blocks 99.9% of account compromises, making it essential.
Secure Internet Browsing
Unsafe browsing exposes organizations to malware and data theft. Training covers verifying HTTPS connections, avoiding untrusted downloads, recognizing risky websites, understanding public Wi-Fi dangers, and using VPNs when working remotely.
Device and Mobile Security
Mobile devices present major vulnerabilities requiring dedicated protection. Training addresses keeping software updated, securing devices with authentication, avoiding unauthorized apps, protecting against physical theft, and following BYOD policies.
Data Protection and Privacy
Proper data handling prevents breaches and ensures compliance. Employees learn to classify information by sensitivity, encrypt sensitive data, understand privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, and follow secure file-sharing protocols. Zero trust principles reinforce continuous verification.
Reporting Incidents and Response Steps
Fast incident reporting minimizes breach damage. Your workforce gets clear escalation procedures, teaches recognition of security incidents, emphasizes reporting without blame, outlines immediate response steps, and establishes timeline expectations.
Ransomware and Malware Awareness
Ransomware attacks have surged 150% since 2024. Training covers how ransomware encrypts files, common infection vectors, prevention through backups and updates, recognizing early warning signs, and understanding organizational response plans. Cyber risk management requires constant vigilance.
Common Training Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Security Fatigue
Security fatigue occurs when constant exposure to alerts, authentication prompts, and training requirements leads to desensitization and weariness among employees. This exhaustion causes staff to ignore warnings, reuse passwords, skip procedures, and take shortcuts that compromise security.
Solutions: Simplify the user experience through single sign-on (SSO) and password managers to reduce authentication friction. Implement risk-based authentication that only prompts for MFA when unusual activity is detected, rather than constantly interrupting workflows. Automate repetitive tasks like patch management and security updates to remove the burden from employees.
Engaging Remote and Hybrid Workforces
Remote employees face unique security challenges, including unsecured home networks, personal device usage, and isolation from organizational security culture. The shift to hybrid work has introduced multiple authentication points and confusing access layers that increase cognitive load and create engagement barriers.
Solutions: Develop remote-specific training modules that address home network security, VPN usage, and securing personal devices. Use virtual learning platforms with interactive scenarios tailored to remote work situations. Implement multi-channel delivery through videos, microlearning modules, and mobile-accessible content that accommodates flexible schedules.
Keeping Training Content Relevant and Updated
Cyber threats evolve constantly, with new attack vectors emerging regularly through AI-driven tactics, deepfakes, and sophisticated social engineering. Annual training sessions quickly become outdated and irrelevant, fostering disengagement rather than building a security culture.
Solutions: Refresh training content quarterly based on emerging threats and real-world incidents affecting your industry. Deliver short, role-based, scenario-driven modules throughout the year instead of annual marathon sessions. Provide just-in-time education that delivers tips and feedback immediately after risky behaviors rather than months later.
Sustaining Employee Motivation and Participation
Security training often feels like a compliance burden rather than valuable skill development, leading to passive participation and minimal retention. Employees become disengaged when training feels punitive or disconnected from their daily responsibilities.
Solutions: Implement gamification elements like points, badges, leaderboards, and friendly competitions to make learning engaging. Recognize and reward secure behaviors like prompt incident reporting or perfect phishing simulation scores. Build a culture of support rather than blame, where leadership demonstrates secure behavior and openly discusses cyber hygiene.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Employees
Update Software Regularly
Keep all operating systems, browsers, and applications up to date with the latest patches. Automatic updates reduce vulnerabilities that attackers exploit and help maintain a strong security posture.
Use Secure Networks
Avoid public Wi-Fi whenever possible. If you must connect, use VPNs and always verify network legitimacy before transferring sensitive data. Secure home and office networks with strong passwords.
Explore Network Devices Security
Practice Strong Password Etiquette
Create unique, complex passwords for every account. Use password managers, enable multi-factor authentication, and avoid sharing login credentials. Change passwords regularly to prevent unauthorized access.
Report Suspicious Activity Immediately
If you notice unusual emails, device behavior, or suspect a breach, contact your IT or security team at once. Quick reporting helps contain threats and prevent wider compromise.
Follow Organizational Protocols
Familiarize yourself with company security policies, accepted use guidelines, and incident reporting procedures. Adhering to these protocols maintains unified defenses and reinforces collective employee vigilance.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Training
Track Phishing Click Rates
Monitor how many employees click on simulated phishing emails during training. Declining rates indicate improved learning retention and stronger threat recognition across staff.
Incident Reporting Frequency
Evaluate how often employees report suspicious activity or potential breaches. Increased reporting shows a more security-aware culture and effective training outcomes.
Quiz and Assessment Scores
Regular quizzes help gauge employee understanding of training concepts. Rising test scores signify successful program delivery and improved knowledge among participants.
Gather Surveys and Feedback
Collect employee feedback on training modules and workshops. Insights from surveys enable you to refine content, address gaps, and boost overall program effectiveness.
Review Performance Metrics
Analyze broader performance indicators like reduced actual breaches, improved remediation speed, and lowered downtime as a result of employee security awareness efforts.
In Summary
Employees represent both your greatest vulnerability and strongest defense against cyberattacks. Through comprehensive training covering phishing, password management, secure browsing, data protection, and incident response, organizations transform staff from potential weak links into proactive security defenders.
Leaders must recognize that investing in ongoing cybersecurity awareness training delivers lasting value that protects not just data and systems, but the organization's reputation, competitive position, and long-term viability. The time to act is now. Prioritize continuous security education and uplift your workforce to become your most effective cybersecurity defense.
FAQs
What is the difference between cybersecurity awareness and training?
Cybersecurity awareness creates a general understanding of threats and promotes a security-conscious culture across the organization. Training provides structured, hands-on instruction teaching specific skills like identifying phishing attacks, managing passwords, and responding to incidents through practical scenarios and simulations.
How often should cybersecurity awareness training be delivered?
Training should be continuous rather than annual. Implement quarterly content refreshes with monthly microlearning modules, regular phishing simulations, and just-in-time education delivered immediately after risky behaviors. Ongoing engagement maintains vigilance and keeps employees updated on emerging threats.
What best practices ensure effective employee security training?
Use interactive simulations and real-world scenarios that build procedural knowledge. Implement gamification, personalized learning paths, and multi-channel delivery. Provide immediate feedback, measure behavioral change rather than just test scores, and create a blame-free culture that encourages reporting and participation.
Why is employee commitment vital for cybersecurity solutions?
Technical cybersecurity solutions cannot function effectively without engaged employees who recognize threats and follow protocols. Human error causes the majority of breaches, making employee commitment essential for creating the "human firewall" that complements technical defenses and transforms security from IT responsibility into an organization-wide cultural priority.

Leave a Comment