In 2024, Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities accounted for 40% of all reportable Microsoft security vulnerabilities, as per a recent report, a total of over 550. But that is more than a number; that is a strong signal of where threat actors are focused on gaining unauthorized access: EoP. Bad actors can circumvent controls, exfiltrate sensitive data, and disrupt your business operations through EoP exploitations, all while staying hidden from alarm triggers. In today's high-risk world, a single unnoticed vulnerability can provide access to your entire organization.
This article explores seven effective ways to prevent privilege escalation attacks and protect your business from the risks of unauthorized elevated access. We’ll explain the EoP attack types (vertical, horizontal, and hybrid), how these variations on this type of breach happen, and industry best practices on how to monitor and respond to them. We will also review how enterprise Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions such as miniOrange help you safeguard your premises in real time. Finally, we will present our recommended roadmap for securing your privileged access to deter potential threats.
What are Privilege Escalation Attacks in Cybersecurity?
Privilege escalation attacks result when attackers gain more privileged access than normal system access and gain admin (or root) access. When attackers get higher-level access than they are authorized for, they can disable security controls, steal sensitive data, or take full control of the systems.
There are two primary types of privilege escalation attacks: vertical and horizontal. A vertical escalation attack occurs when an attacker changes from a normal user account to an administrative account. A horizontal escalation attack occurs when an attacker exploits vulnerabilities in other user’s accounts or resources at the same privilege level, without increasing their own privileges. Both types of escalation attacks are extremely harmful because they can largely go unnoticed until there has been a limited, yet significant, impact on the company.
Poor access controls, unpatched vulnerabilities, password hygiene problems, and misconfigured privileges make up the most common vulnerabilities. When the attackers gain access to the network, they will continue to use their escalated privileges to grow their foothold, conduct several lateral attacks, and persist in the area of the network perimeter.
Types of Privilege Escalation Attacks
Privilege escalation attacks employ various techniques, but their common goal is to gain a higher level of control and access. These three types help recognize signs and stop these attacks:
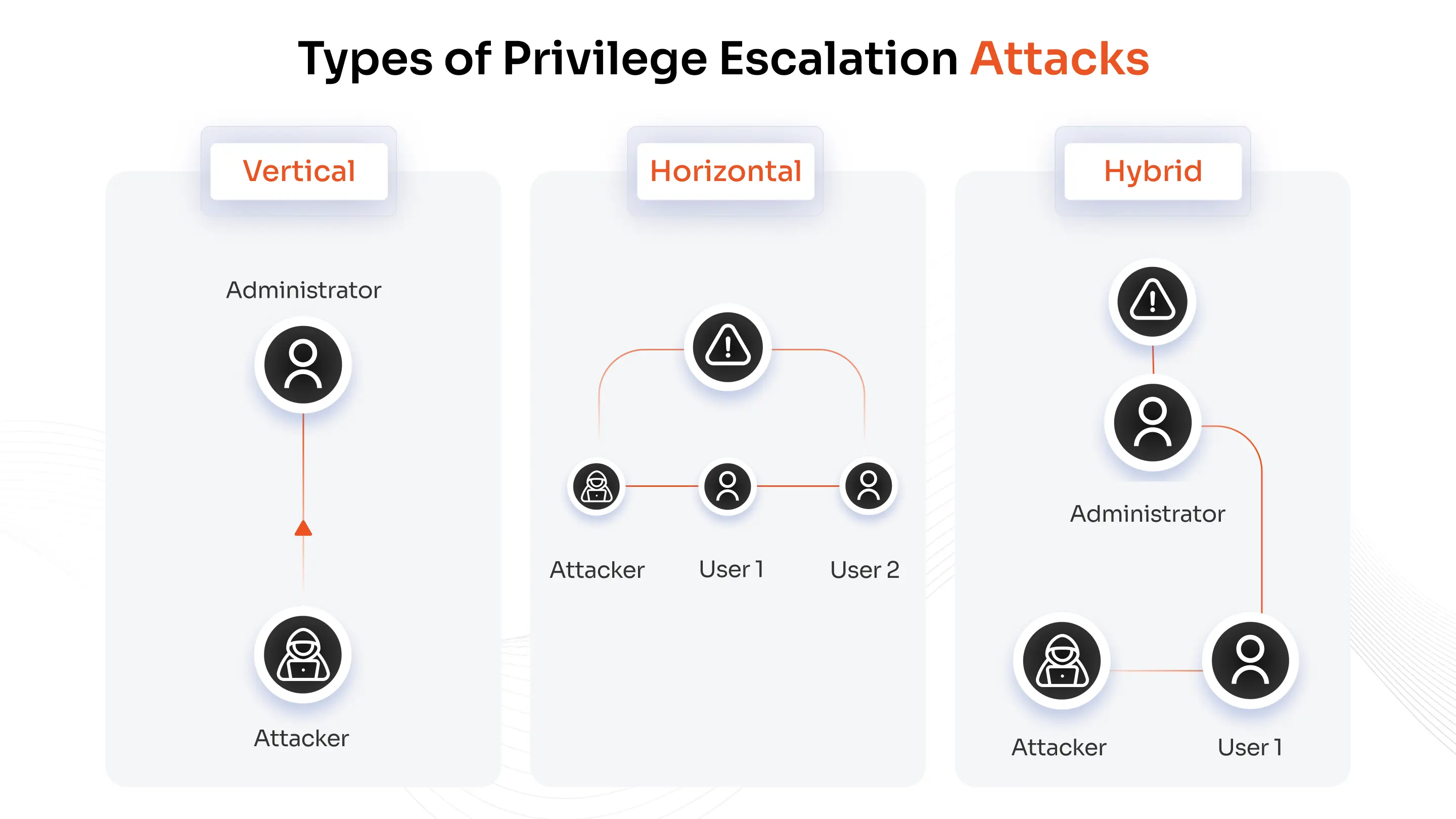
1. Vertical Privilege Escalation:
Vertical escalation occurs when an attacker escalates a low-privilege account to an admin or root account, which helps the attacker to bypass security controls much faster to have control over my critical systems. Attackers can do this by taking advantage of OS and kernel vulnerabilities that allow them to take superadmin privileges to run malicious code. Unpatched software vulnerabilities would be exploited to escalate privilege levels.
Additionally, weak access controls/settings and excessive user privileges can also be topics that are fast-tracked to escalate privilege levels. After privilege escalation occurs, attackers can change settings, turn off protection and view very sensitive information, which increases its almost permanent impact on the system.
2. Horizontal Privilege Escalation:
Horizontal escalation is when attackers move laterally to target a user with the same privileges, which supports covert assumption of user identity. Attackers read email and other users' protected files and mask actions as peers' accounts to not draw attention. Attackers collect credentials through compromised identities, then reconnoiter the attack surface, and prepare for further escalation without raising alarms.
3. Hybrid Privilege Escalation:
Hybrid escalation is presently the most observable form of lateral and vertical experiential attack, particularly in multi-tenant or hybrid cloud environments where it is difficult to detect and respond to. When an attacker laterally traverses several accounts, it is usually through gradually escalating privileges at different points of the kill chain.
Attackers aim to exploit system trust for pivoting, masking logs, reenacting high-privilege views, and exfiltrating over several environments. Hybrid escalation is the most dangerous course of action, as it is distinctly lower in the attack surface to attack multiple systems and multi-layer attacks simultaneously.
Altogether, this can make detection and response much more difficult.
How Do Privilege Escalation Attacks Occur?
Privilege escalation is not a single step but an entire process the attacker carries out. Once you know the flow and how it works, you can detect it early and stop it from happening.
Entry Point
Privilege escalation involves several steps during which attackers exploit a minor access point in an environment to ultimately gain full control. Entry point lifecycle helps you identify and mitigate threats before they grow into critical targets.
Reconnaissance
Initial access is gained via weak passwords, phishing to deceive an employee into divulging credentials, stolen passwords, compromised API keys, exploitation of publicly known software vulnerabilities, or poorly configured accounts; access has been granted, a foothold exists, and the attacker moves forward.
Exploitation methods
Attackers exploit OS or application vulnerabilities, misuse insecure-by-default preconfigured defenses or brittle behavior throughout the application lifecycle, use pass-the-hash or token-reuse techniques, take advantage of user relationships to authorize themselves, or exploit chained attacks to bypass or defeat low-level access controls.
Privilege Escalation
Attackers escalate privileges vertically to gain access to the admin or root user, laterally by impersonating peer users, and across hybrid, multi-cloud environments to gain and consolidate privileged access, thus overcoming implemented protections.
Persistence
To facilitate long-standing persistence, attackers create stealth admin accounts and backdoors and modify authentication mechanisms to maintain access and privately grow privileges.
Impact
Full privileges create an even bigger impact that can involve exfiltration of sensitive data, ransomware deployment or other extortion, disruption of platforms and services, and hiding of malicious operations that gradually grant the attackers stealth access for weeks or months until discovered.
By the time you get to interrogations, it is ensured that consequential attacks were maybe weeks or months subsequent to the breach implementation.
How Unauthorized Privilege Escalation Can Hurt Your Business
When attackers get elevated access they shouldn’t have, it quickly damages systems, data, and operations. The harsh consequences for modern enterprises are enlisted here:
Data Theft and Intellectual Property Theft
Attackers can steal sensitive files, exfiltrate million-dollar secrets, and grab customer data directly from your systems. Attackers can figure out your business plans, retrieve financial records and trade secrets or product designs, and then exfiltrate customer’s PII (Personally Identifiable Information) to sell or abuse. Losing control of this data is damaging to competitive advantage, which may result in long, costly legal challenges.
Compliance Violation and Legal Liabilities
Privilege escalation can generate compromises of regulated data privacy laws (i.e., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) when combined with data access. Attackers can generate mishandled regulated data, create audit and reporting control failures, and generate fines or penalties. Regulatory risk can drain resources and lead to reduced access to critical markets.
Financial Fraud and Ill-Gotten Transactions
With admin privileges, attackers can initiate payments, manipulate accounting records to steal and cover their tracks with funds, and quickly reroute billable amounts to their advantage. These activities generate an immediate financial loss and residual mistrust from customers and business partners.
Service Interruption and Downtime
Privilege escalation allows attackers to intentionally or accidentally bring down critical systems. Attackers can deactivate critical applications or services, change the system configurations, and disrupt customer-facing systems. Downtime adds up to loss of revenue, reduced productivity, and damage to your customer’s relationship.
Deploying Ransomware and Extortion
Finding privilege escalation makes ransomware attacks exponentially worse, as it allows attackers to encrypt networks and backups and dictate disclosure for the recovery process. Attackers can even threaten the disclosure of stolen data to further apply pressure. The combined operational stop and reputation risk can be devastating.
Reputation Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
Incidents associated with privilege escalation drive negative press and customer churn from security issues. This can create a lasting stigma between the incident and the business, and it could take years to restore the trust or cost much more than the incident itself.
Long-Term Infiltration and Undetected Back Doors
Attackers with escalation privileges can stay hidden for months or years, creating unattributed admin accounts along with persistently installing malware or rootkits and altering authenticating configurations. This persistence allows for further collection of data, sabotage actions, and surveillance.
Privilege escalation is not only a technical issue but also a business risk, even a business-critical risk. Understanding these consequences allows for the implementation of prevention countermeasures that allow others to thrive for generations.
Best Practices to Prevent Privilege Escalation Attacks
Privilege escalation prevention means a layered, proactive approach. By implementing hardening and continuous monitoring, stop the attackers from gaining unauthorized access to critical systems.

1. Ensure Systems and Software are Up to Date
Attackers will target known vulnerabilities before anything else, so patching is your fastest form of mitigation.
- Ensure all systems are current with security patches when applicable
- Automate patches when possible to minimize human error
- Remove unsupported or legacy applications
Regular updates reduce your attack surface and prevent or reduce some of the commonplace escalation attacks.
2. Detecting Unusual User Activity and Network Traffic
Suspicious activity often signals the early stages of an escalation attempt.
- Leverage SIEM tools to log network activity such as login events, privilege changes, or data transfer
- Alert for suspicious log-on, privilege change, or data ‘transfer’ sequences
- Investigate as close to real-time as possible
Continuous monitoring turns potential breaches into manageable incidents.
3. Regular Vulnerability Scans & Pen Tests
Testing your security will help you find privilege escalation vulnerability before attackers do.
- Scan explicitly for privilege escalation risks
- Do internal and external penetration testing
- Fix flagged items quickly
Regular security assessment activities keep your security posture relevant and effective.
4. Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Restrict users to what information is required for their work, nothing else.
- Apply least privilege by default
- Review and revoke unused or outdated privileges regularly.
- Use tokenized access
The principle of least privilege (PoLP) will minimize the harm from someone obtaining account privileges.
5. Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Policy
Weak or stolen credentials are a common entry point for privilege escalation.
- Use secure, complex, and unique passwords
- Utilize a timed password rotation policy to ensure regular credentials updation
- Follow a multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an additional verification layer.
Strong authentication methods dissuade bad actors from impersonating privileged users.
6. Regular Training for Security Awareness
Your end users are the most effective security
- Train and test employees on phishing and social engineering
- Encourage them to verify authentication safeguards before entering credentials
- Conduct simulated phishing and social engineering exercises
Trained employees can stop unwanted activity before it escalates.
7. Use Privileged Access Management (PAM) Solution
Having centralized control over privileged accounts adds an essential layer of security and helps prevent unauthorized privilege escalation. Having a Privileged access management (PAM) solution Allows
- Privileges will only be applied when needed and for the required duration
- Privileged user activities will be continuously monitored and detect unusual behavior.
- Ensures secure storage of privileged passwords in an encrypted vault.
Centralized procedures will make it difficult for an attacker to escalate privileges, and you’ll catch it quickly.
By using normal processes within the methodology that a technology user uses, a privilege account mask of malware will create a safe environment for responsible control of privileges, as well as a reactive one.
How miniOrange PAM Detects and Prevents Privilege Escalation Attacks
Even the best organizations may have problems if privileged accounts aren’t managed. miniOrange Privileged Access Management (PAM) layers a strong protective barrier by detecting and stopping escalation attempts in real time, all while maintaining legitimate access smoothly and with controls.
Granular Access Management
By using Role based access control, Specify exactly who, what, and when, and how much privilege an account has.
- Limit permission to systems and time
- Implement role-based access for access consistency and security
- Remove all unused privileges to reduce potential attack vectors
Just-in-Time Privilege Elevation
Provide elevated access on a just-in-time basis and revoke it immediately afterward.
- Limit options for attackers
- Prevent standing admin rights from being exploited.
- Automatically expire privileged access within a tight timeframe.
Privileged session captures
Detect and record all privileged activity for compliance and/or forensics
- Obtain keystrokes, commands, and screen activity detection
- Detect suspicious activity in real time
- Maintain audit trails for investigations and reporting purposes
Credential Vaulting and Rotation
Securely store privileged credentials.
- Encrypt passwords and keys in a vault.
- Rotate credentials automatically so they cannot be reused.
- Avoid hard-coding privileged credentials into application scripts.
Integrate MFA for an added layer of security
Use a second factor or “something you have” to validate privileged logins.
- Ensure that the login process requires multi-factor authentication before granting privileged access.
- Deny access for unauthorized logins using derived credentials even if they were stolen.
- Strength in compliance with regulatory compliance requirements.
When combined together, miniOrange PAM closes the scope of privilege escalation attacks. miniOrange PAM also gives visibility, control, and confidence, and it doesn’t slow down legitimate work.
By taking action now, you can preserve the value of your systems and ensure the protection of other systems and applications. The total protection of your reputation, regulatory compliance, and customer service is now in your control. Any delays in implementing strong privileged access controls risk the time attackers will spend mapping your system.
Protect your access now with miniOrange. Submit form to get miniOrange PAM Demo today
FAQs
What are the consequences of privilege escalation?
Picture this as someone handing over their house keys to a burglar. The attackers receive the ability to access assets, steal sensitive data, install backdoors, or even shut down environments. The real kicker? In many cases, you may not be aware of the intrusion till the time it has caused irreversible damage.
What tools help detect privilege escalation attacks?
PAM, SIEM, EDR, and threat hunting tools act as CCTV cameras for the IT environment to identify and track suspicious privileged jumps by users. Even built-in utilities such as Linux auditd or Windows Event Logs can serve as tripwires to detect unusual access behavior.
Can PAM tools prevent privilege escalation?
Absolutely, PAM is like a bodyguard who only allows admins into the VIP section when they are truly on the guest list. PAM vaults credentials, rotates passwords, and enforces just-in-time access to aim to lock the entry points attackers try to exploit.
Why are privilege escalation attacks hard to detect manually?
Because privilege escalation is literally hiding in plain sight, it looks like any user is doing their job. If you really plan to read boring thousands of logs a day, you won't notice it, it'd be like noticing one pickpocket in a packed stadium.





Leave a Comment