As remote and hybrid workforces continue to expand, every organization is looking to protect their employees online using VPN. For enterprise-grade security, VPNs with just a username and password are not enough, which calls for a need for another layer, such as 2FA or two-factor authentication, to effectively safeguard your VPN.
A VPN is a high-value target and a secure tunnel into your network. An attacker can breach the perimeter and gain access to sensitive systems, files, and sets of active credentials. If your VPN credentials are compromised, it acts like a single entry point, and a hacker can fake a real user to move in your network and go undetected. Thus, organizations are enhancing their security by adding an additional 2FA layer to their traditional VPN credentials.
In this article, discuss the need for VPN protection, how to implement 2FA for popular VPNs like Fortinet, and various methods of using 2FA to secure your VPN. Also, it covers how miniOrange 2FA can protect your VPN with its strong security features.
Why Do Organizations Rely on VPNs?
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) set up a secure connection and safely encrypt information and access to a company’s system. Most organizations would not be able to implement remote work without VPN functionality; organizations commonly rely on VPNs for:
- Locking up sensitive information when staff work remotely
- Enabling access to enterprise applications from anywhere
- Providing an extra level of security to limit information being read by adversaries eavesdropping or acting on cyber threats from outside the organization.
As hybrid work is how many workplaces function, VPN access from anywhere is highly recommended for enterprise security, but relying solely on VPNs can create risk. In fact, over 80% of breaches in 2024 were associated with having password(s) that are stolen or weak, and VPN access is an excellent target. Organizations depend on strong controls like 2FA to close the gap.
Are VPNs Really Secure on Their Own?
VPNs encrypt traffic but cannot verify user identity on their own. They represent an important component in protecting against attacks, but they leave important gaps that are not only well-known but are also commonly exploited by attackers. Common risks are:
- Password theft and reuse: Phished, weak or reused passwords are the preferred method of entry by a hacker
- Stolen VPN keys or certificates: Once stolen, they offer a solution to bypass every different encryption control in that key or certificate
- Misconfigured VPN policies: Setup issues offers a way in to an organizational network
- Credential stuffing: Automated bot phenomenon is always attempting to use password lists against any VPNs logins
Typically, hackers make compromised credentials their first entry point and later infiltrate the entire channel to conduct sophisticated man-in-the-middle attacks. VPNs protect communication in transit, but any attempt to protect identity only succeeds with many more layers of protection, including, but not limited to, 2FA.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Help Increase Your VPN Security?
2FA provides a much-needed second layer of verification beyond username and password. Users will authenticate their identity after they have provided their credentials by validating who they are through something they have (smartphone, OTP, hardware token) or something they are (biometric) and that increases VPN security.
Here are three ways 2FA for VPN can provide:
1. Improved User Verification:
2FA identifies not only who logged in but also how they can prove who they are to log in:
- The first factor is a password, which is something the user knows.
- The second factor is either something the user has (smartphone app, OTP code, or hardware token) or is (biometric fingerprint or facial recognition).
This prevents someone from being able to access the VPN just because they have a said username and password because now they require physical or biometric authentication as well.
2. Protection Against Advanced Attack Methods:
Most cyberattacks targeting the VPN exploit weak passwords, reused passwords, or phished passwords. With 2FA, stopping hacking attempts becomes easy if you:
Require an OTP or confirmation through a push notification app; this feature essentially makes automated "credential stuffing" (i.e., trying as many username and password combinations until finding one that works) and brute force attacks difficult if not useless.
It stops an adversary even if they acquire the credentials because they now lack the second factor, which can block their login attempt based on time (i.e. when the code is issued from the authenticator app), by the device (i.e., the code is only generated from the authorized device), or by biometrics (i.e. fingerprints or facial).
2FA mitigates threats from phishing, keyloggers, or man-in-the-middle attacks, with 2FA codes being valid for very limited times (i.e., usually 30 seconds to 1 minute), so the reuse of those codes quickly diminishes in likelihood.
3. Flexibility for Different Environments
2FA is flexible and configurable depending on the enterprise context.
For remote work scenarios, staff can now authenticate their identity safely from anywhere while not exposing the organization to identity theft through weak password habits.
2FA can also be delivered through SMS, apps, email, hardware keys, or biometrics, meaning there is a delivery mechanism for nearly every type of user group and device type, and it always improves security without necessarily eroding usability.
Benefits of 2FA for VPN

In the past two years, almost half of organizations (48%) made headlines in the context of a VPN-related breach, with hackers taking advantage of stolen credentials and VPN weaknesses to bypass VPN security and gain unauthorized access. While there is no way to stop every breach, the above data shows how critical 2FA is to improving your VPN security.
As we mentioned, 2FA is a second layer of defense that will improve your VPN access communicatively, making it more secure and stronger. We have outlined major 2FA advantages that help you add security to your VPN's first line of defense:
1. Blocks unverified login attempts and access even when password is exposed to hackers
2FA provides a second verification step for authentication, which means stolen passwords alone won’t give hackers access. Because of the additional verification, hackers can’t just log into your VPN simply using the username and password.
2. Minimizes Insider access threats by providing stronger identity checks
Because 2FA requires multi-factor authentication verification, it reduces the chance of unauthorized insiders using their authorization, either intentionally or through company negligence. Therefore, 2FA improves internal controls for security.
3. Helps your organization be compliant at all times to compliance standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, NIST and ISO 27001
Many compliance requirements require strong authentication. By providing 2FA for VPN access, organizations can easily comply with these cybersecurity controls listed by bodies.
4. Reduces phishing and brute-force threats
If shortcuts are taken either by phishing or by brute force, attackers cannot complete the login if they do not have the second form of authentication.
5. Provides visibility and control on who is Logging in remotely
A 2FA solution will often offer monitoring and logs and reports on who is accessing your VPN. With the strong reliance on VPN access, leveraging 2FA solutions gives a security team insight into all your organization’s VPN access activity and can alert a security team of suspicious or unauthorized access attempts.
2FA is more than a way to improve your security posture; it is an investment to keep your business running securely, build trust with employees and clients, and protect your most critical digital infrastructure from emerging cyber threats
How to Achieve Security of Your VPN with 2FA?
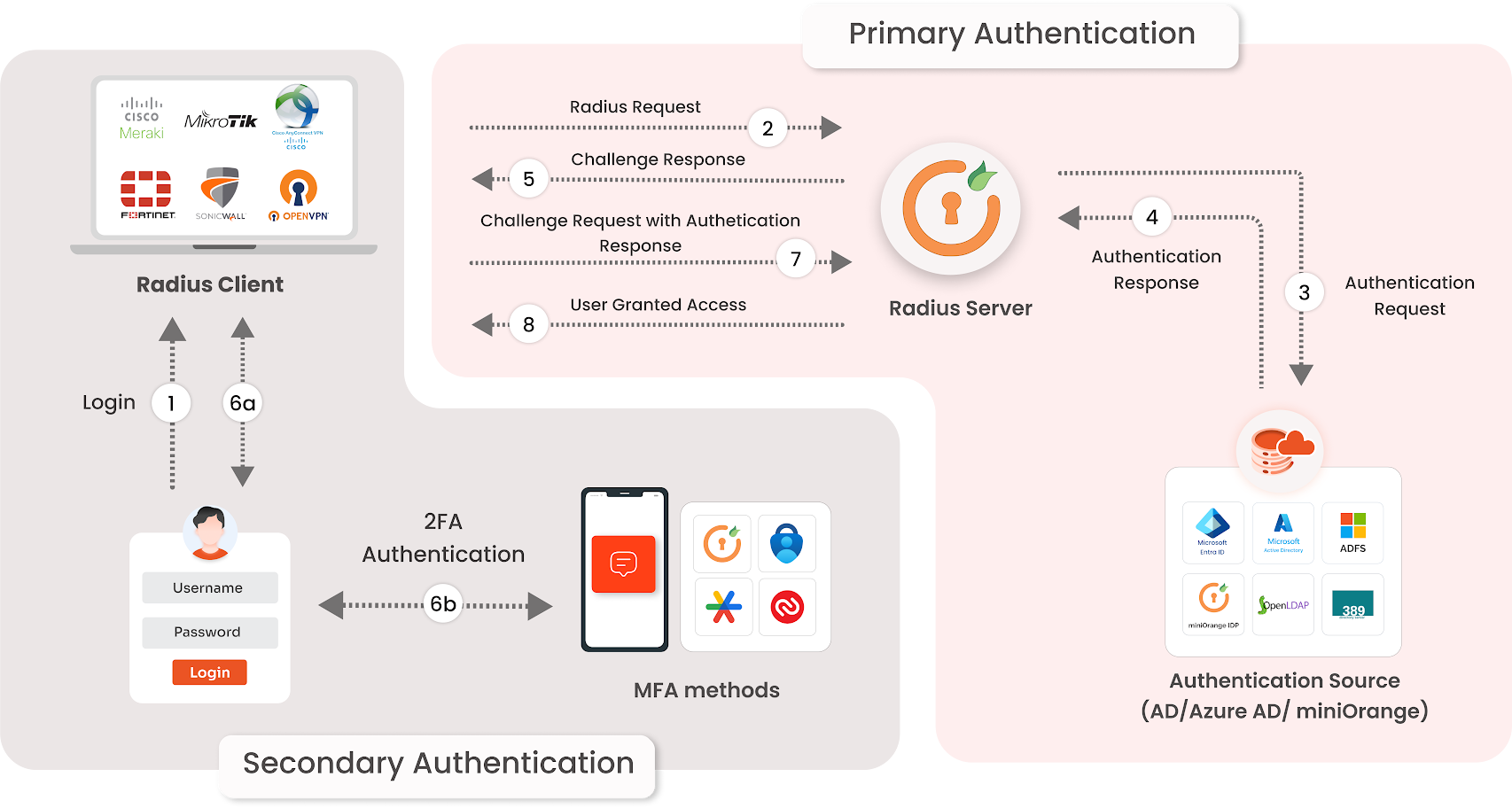
Here's how Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) really works to supplement your VPN security:
- First, the user authenticates to the VPN with a username and password
- The VPN server authenticates the user with an Identity Provider (IdP) or authentication provider like miniOrange
- Once authenticated, the user is challenged with a second factor verification, like a one-time password (OTP), push verification, hardware token, or biometrics
- Once the second factor verification is successful, the user is granted access to the VPN
Using this method means only authorized users can access VPN; even in case of compromise of their password, they still cannot gain remote VPN access, which substantially lowers the ability to gain unauthorized access and to breach your data.
How Does miniOrange Strengthen the Security of Your VPN?
miniOrange enhances security on the VPN level by serving as an authentication broker between your VPN solution and your identity store, making sure only the right users, at the right devices, at the right time can access your corporate network.
miniOrange will allow you to:
- Enforce MFA for every VPN log in - whether SSL VPN, IPsec VPN, client-based, or clientless.
- Integrate with on-prem Active Directory, LDAP and cloud identity providers.
- Establish one unified security layer over VPN vendors like Fortinet, Cisco, Palo Alto, SonicWall and CheckPoint.
- Deploy adaptive MFA policy based on location, device, time or risk factors.
- Meet audit requirements and regulatory compliance without hassle.
miniOrange helps you reduce the risks associated with weak passwords. It stops unauthorized logins and protects your critical systems from intrusions and cyber threats with 2FA at your VPN's core.
miniOrange 2FA for Fortinet FortiGate Login
Fortinet’s FortiGate VPNs are already providing secure remote access to thousands of enterprises around the world. By integrating miniOrange, you can quickly and easily add 2FA software protection to every user login to Fortinet’s FortiGate VPNs, protecting you from stolen credentials and brute-force attacks.
With miniOrange, you can enforce 2FA on logs of all three access points:
- SSL VPN Web Portal logins
- FortiGate admin panel access
- FortiClient VPN
Every user who logs in triggers a second-factor challenge (One Time Passwords, mobile push, or biometric authentication), making it impossible to use the stolen password alone. This way only authenticated individuals have access and your staff has an effortless, painless login.
Running miniOrange 2FA above Fortinet FortiGate closes the gaps left by allowing password-only logins to build stronger, compliant, and future-ready access control.
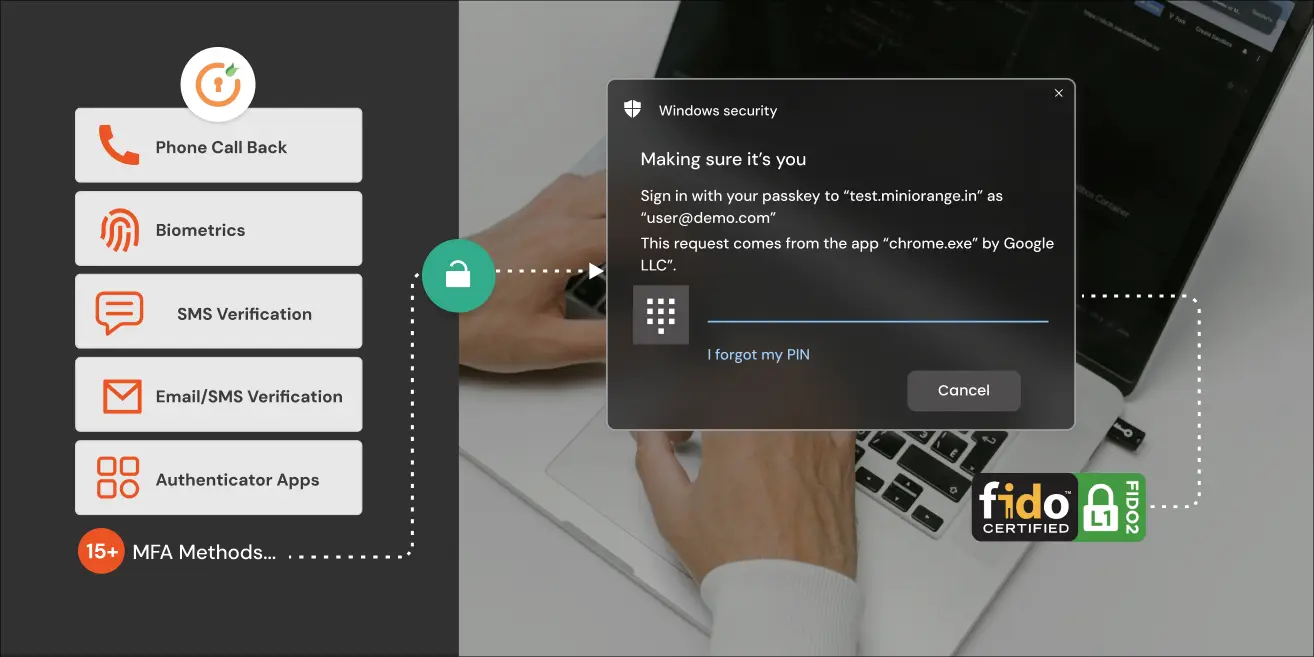
2FA/MFA Methods for Fortinet FortiGate Supported by miniOrange
miniOrange supplies 2FA for organizations relying on Fortinet FortiGate VPNs for strong authentication. This helps your organization balance your security, usability, and cost. Your users experience seamless, frictionless access, while you maintain a fortress-like defense against unauthorized logins.
Here are the 2FA/MFA options for Fortinet using miniOrange:
- Mobile & app-based — Push notifications, authenticator applications, QR code logins, and TOTP codes.
- Hardware tokens — Secure OTP tokens, YubiKeys, and other FIDO2 keys for a physically-anchored assurance.
- Biometrics — Finger print or Face ID using the miniOrange mobile app.
- SMS/Email OTPs (one-time passcodes) — OTPs are discretely delivered to recipient phones or inboxes.
- Voice call verification — Automated voice calls delivering login codes.
- Adaptive MFA — Risk-based challenges triggered by unusual login habits (new device, odd location for user, or suspicious time of the day).
As stated, miniOrange offers a comprehensive mix of authentication methods, which means organizations can increase the security of their FortiGate VPN without degrading user experience. You choose the best method for your teams—all while remaining compliant and able to continue staffing resilience against active threats.
Getting Started with your VPN Security using 2FA
Protecting remote access and sensitive data consists of more than just a VPN. To create protection during this increasing cybersecurity threat environment, you need to supplement your password with strong authentication breaches from stolen credentials that can wreak havoc on your organization. miniOrange can augment identity verifications on any VPN, even Fortinet, with adaptive multi-factor authentication and actionable compliance monitoring without sacrificing user experience.
Want to plug the leakages in your VPN security? Reach out today or take a free trial to see how miniOrange can enhance access security, eliminate internal credential theft, and future-proof the VPN structure you have in place.
Give your VPN the 2FA advantage with miniOrange. Schedule a meeting with us today
FAQs
What value does two-factor authentication bring to your VPN?
2FA sets up an extra security layer for VPN access by mandating a second factor besides passwords. This extra layer makes your account much more impenetrable and helps reduce unauthorized access and data breaches.
Can 2FA stop hackers from accessing a VPN if they have stolen my password?
Yes. Even if a hacker has stolen a password, they cannot log into the VPN without the second factor (such as OTT, or push approval). Many credential thefts rarely consist of attacks such as "SIM swapping." 2FA will block the bulk of these attacks.
What 2FA methods work best for VPNs such as Fortinet FortiGate?
The best 2FA methods are push notifications, OTPs from authenticator apps, hardware tokens, or email codes. Push notification-based 2FA offers the most balanced secure capability with user convenience.
How does miniOrange add 2FA to existing VPN solutions?
miniOrange integrates as a RADIUS server and does two things: it validates your existing password against a directory of some sort (Active Directory is popular) and adds a second factor to complete the log in (OTP, Push, or Hardware Token), and the VPN partner (Fortinet, Cisco, Palo Alto, etc.) can all be audited, and numerous directory types are supported.
Will adding 2FA to a VPN have an adverse effect and impact complexity for users?
2FA adds an extra step; however, the contemporary methods of verification (push, choice, OTP), keep this process simple. With communication, and possibly training for your team, the resistance from the user shown be minimal and added security will not be compromised.


Leave a Comment