Organizations often struggle to securely handle access to their VPN (Virtual Private Network) or Wi-Fi, especially when the number of employees or devices increases.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) protocol steps in to solve this issue through a centralized AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) approach.
In this blog, we will be discussing the RADIUS protocol and the RADIUS client and server. We will also talk about RADIUS server authentication and how miniOrange, your trusted security software solution partner, can help you to elevate RADIUS server authentication.
Let’s have a look at this authentication solution now.
Understanding the RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service)
Here’s what you should know about the RADIUS before getting started on the complexities.
What is RADIUS Protocol?
RADIUS is a networking standard or protocol that works on a RADIUS server-client model, and it controls authorization and authentication of users. In simpler terms, it controls communication between the users, client, and server.
What is a RADIUS Server and RADIUS Client?
Here’s what you should know about the RADIUS server and RADIUS client before we move to the complexities of RADIUS server authentication and discover more about the RADIUS MFA.
- RADIUS Server: The primary functions of the RADIUS server include authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) of the users who are trying to access a network. Common RADIUS server products are Microsoft NPS, Cisco ISE, Open Systems Radiator, etc.
- RADIUS Client: Also known as NAS (Network Access Server), the RADIUS client functions as an intermediary between the user and the RADIUS server. It forwards user requests to the server. Usually, the RADIUS client takes credentials and forwards them to the RADIUS server. Common NAS products are wireless access points, such as dial-up equipment and the Linksys WRT54G.
What is RADIUS in Networking and Cybersecurity?
In networking and cybersecurity, RADIUS functions as a security guard that verifies who you are and what you can do, and also keeps track of everything you do over the network.
For example, imagine an organization of over 1000+ employees, where all of them connect over the office Wi-Fi. So, instead of setting up credentials for every router, the RADIUS server handles all the credentials.
When an employee tries to log in, the credentials are sent to the RADIUS server via the RADIUS client, and the server verifies the employee and sends back a response to either grant or deny access.
In cybersecurity and networking, the RADIUS server manages and controls several users and provides a central point to apply policies, authenticate users, and record activities.
This helps to amplify security levels and simplify the administration process, which is an essential facet for businesses, educational institutions, service providers, and other types of user bases.
What are the Types of RADIUS Servers
There are two major types of RADIUS servers, and they are as follows:
Synchronous Authentication Mode
- How it Works: In synchronous authentication mode, the user signs in using a password, a PIN, a token, or any other authentication method. The credentials are sent to the server via the client for validation. The RADIUS server then either accepts or denies the login.
- Example: An employee enters a password and a hardware token while logging into the office VPN. The user request is authenticated in a single step, and access is granted by the RADIUS server, provided that all the data is correct.
- Use Case: Synchronous authentication works in cases where two-factor authentication (2FA) is needed, such as setting up a new password.
Asynchronous Authentication Mode
- How it Works: The user authentication takes place in multiple steps. When a user logs in, the RADIUS server sends a challenge such as a one-time code or a puzzle. The user solves this challenge, and the response is sent back to the server, based on which the user is validated.
- Example: An employee logs into a protected database with credentials. The server sends a challenge, which the employee answers correctly. This challenge is usually a code created on mobile devices. Based on the employee’s answer, access is either granted or denied.
- Use Case: The asynchronous mode is used to secure critical databases of banks, healthcare organizations, or MNCs with the miniOrange MFA methods such as push notifications, SMS/email-based authentication, biometrics, and more.
What are the Components of RADIUS Authentication?
RADIUS authentication needs a few elements, which are as follows:
- RADIUS Server
- An Identity Provider (IdP), also known as a directory of user information.
- RADIUS Client
With these components, the RADIUS servers can control the network access efficiently, as they don’t have too much workload.
How Does RADIUS Authentication Work?
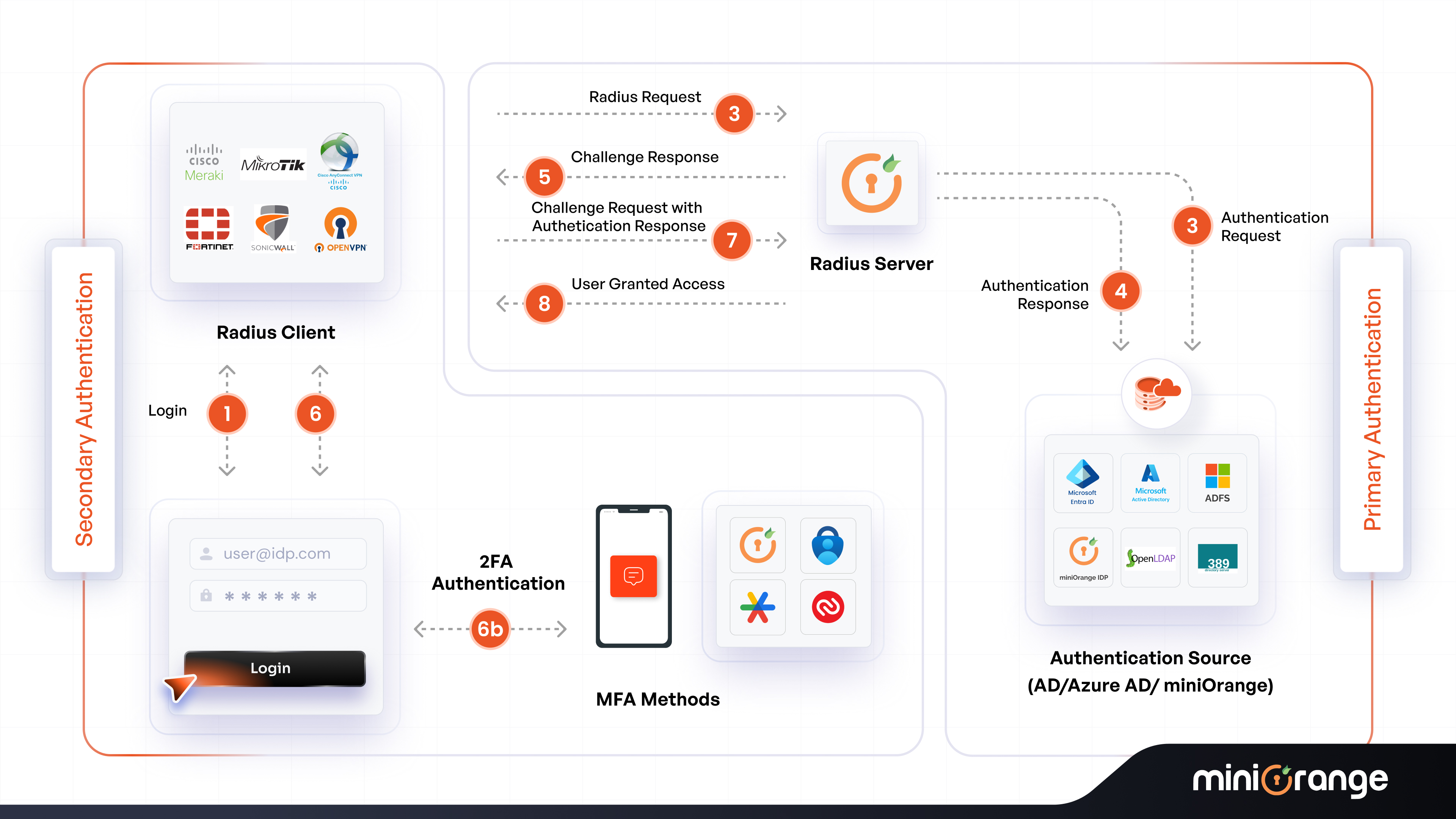
User Access Request
A user tries to sign in to a network, such as VPN, Wi-Fi, or any remote system, with their username and password. These credentials are received by the RADIUS client (VPN, Wi-Fi, or a remote service).
The client generates an access request encompassing the credentials, which are encrypted. This request is sent to the RADIUS server.
RADIUS Protocol Handshake
This is nothing but a way for the RADIUS client and the RADIUS server to communicate with each other through a series of requests and responses regarding whether to authenticate a user or not.
Both synchronous and asynchronous authentication modes can be a part of the RADIUS protocol handshake.
The AAA Framework Execution
The AAA framework stands for authentication, authorization, and accounting. And a combination of AAA and TACACS+ boosts security levels.
We’ll dive into AAA frameworks here and then move on to TACACS+ in the later sections. Here’s how the AAA framework works:
1. The Authentication Process
In this process, the user/device identity is validated. Steps are as follows:
- User Request: Through a wireless connection (RADIUS Client), the user enters credentials, and an access request is generated.
- Request Goes to the RADIUS Server: The user credentials are sent to the server through the client.
- Verification: The credentials are verified against a central database such as an AD (Active Directory) or LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol).
- Response: An authentication response is sent from the server if the credentials match or don’t match.
- Access Granted: If the credentials match, then the user is permitted to access the resources.
Explore the Power of Adaptive Authentication
2. The Authorization Process
In this process, the server decides which resources the user can access, based on the policies. Here’s the complete process:
- Authentication: Once the user is authenticated, the server moves on to the authorization phase.
- Policy Verification: The RADIUS server checks the user’s roles and level of access, based on which it decides which resources the user can access, such as network areas, files, media, etc.
- Sending Authorization Notification: The server sends a notification (access granted or access denied) based on the user’s policies and permissions.
- Grant Access: In case the server sends a positive message, the user is permitted entry to the network.
Discover more about Authentication vs. Authorization
3. The Accounting Process
Here, user sessions are tracked and logged, which can be used for network management, auditing, and reporting. The steps for accounting are as follows:
- Request to Begin a Session: After the user is granted access to the network, the RADIUS client sends an ‘Accounting-Start’ packet to the server. This packet comprises user details such as session ID, user’s identity, and network access point.
- Tracking: The server tracks the user’s session details, such as data usage, session duration, and which resources were accessed. This produces an entire log of the user’s activities when they’re connected.
- Intermediary Updates: If the user sessions are prolonged, then the client may send updates in between the sessions.
- Session End: After the user logs out, the client sends an ‘Accounting-Stop’ packet to the server. This includes details such as time spent and data accessed.
- Data Reporting and Storage: The RADIUS server is a storehouse for all the data, which can be used by the admins for billing, auditing, and monitoring.
What are RADIUS Authentication Methods?
There are two main types of RADIUS authentication methods, which are as follows:
Credential-Based Authentication
The RADIUS server needs a directory like an AD to store user data, so it can check the credentials and related policies from there. Here are the steps involved in it:
- The user/device sends an authentication request to the RADIUS client (along with credentials).
- The client sends the request to the server.
- The server verifies the user credentials that are present in the directory.
- The server gives either an access denied or accepted message to the client, based on the results of the user authentication.
Certificate-Based Authentication
Certificate-based authentication is different, as it contains more information compared to the user credentials. It gives the server or an admin data such as session logs, giving more context of the user activities.
Here’s how the process flows:
- A user/device certificate is forwarded to the RADIUS client, which is transferred to the RADIUS server.
- The server starts checking the certificate to see whether it is still valid or not.
- After this, the server checks the CRL (Certificate Revocation List) to check whether the certificate has been revoked or not.
- In case the certificate is not revoked, the server confirms the user’s status in the directory.
Why is RADIUS Server Critical for Cybersecurity?
Here’s why the RADIUS server plays a crucial role in cybersecurity.
Prevents Unauthorized Access
The RADIUS server is backed by strong authentication protocols that validate users with their credentials. This approach drastically reduces the risk of malicious activities such as infiltration of remote networks, VPNs, or Wi-Fi.
The RADIUS server verifies every connection, so only the legitimate users are given permissions. This helps to mitigate risks such as man-in-the-middle attacks or data breaches.
Centralized Auditing
RADIUS servers track and monitor every user activity, such as session timeframes, login timings, data accessed, and more.
Auditing helps to create a digital trail that can be further used for cyberattack investigation, monitoring security, and checking regulatory compliance.
Benefits of Using RADIUS Server for Cybersecurity
Here are the top four benefits of using a RADIUS server for boosting cybersecurity for your business.
Centralized Identity Management
The RADIUS server facilitates a central database for user credentials, profiles, and policies to simplify identity management across the entire organization.
It is compatible with all users, reducing the risk of shared passwords over Wi-Fi. Moreover, the server enables granular access policies based on user roles and group memberships.
Enhanced Access Control with MFA
The RADIUS server integrates the miniOrange MFA solution during the network access step. It requires users to offer more than one form of authentication before granting a request.
Common MFA methods include OTP, facial recognition, push notifications, and more. Also, phishing-resistant MFA helps to keep the network secure from phishing-based attacks such as email phishing, spear phishing, whaling, smishing, and more.
Discover the Basics of Multi-Factor Authentication Today
Scalability Across Devices and Networks
The server has the ability to support large businesses and organizations without needing any substantial infrastructure changes. It is also compatible with multiple systems such as VPNs, routers, switches, LDAP, AD, and more in the pipeline, making it a flexible solution.
Regulatory Compliance
Meeting compliance standards is a necessity to avoid unwanted penalties and fines that could cost organizations tons of money and reputation damage. RADIUS implementation helps to meet the regulatory standards.
Some of the recommended compliances are HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and more along these lines.
Use Cases of RADIUS Server for Enterprise Security
Here are the top four use cases where the RADIUS server shines and leaves an everlasting impression.
RADIUS for VPN Access Control
With a RADIUS server, enterprises can authenticate users trying to log into a VPN to achieve secure remote access, allowing only authorized users into the network. This helps to maintain consistent authentication policies for remote and local access. Moreover, enterprises can secure VPN with MFA solutions for better network security.
The miniOrange 2FA solution for Palo Alto GlobalProtect is easy to set up and also scalable. It connects with the Palo Alto VPN server to add an extra layer of security.
RADIUS for Wireless Network Security (802.1X)
Enterprises can make use of a RADIUS server to secure their Wi-Fi via 802.1X authentication. It checks devices or users prior to allowing network access to the users. This prevents unauthorized wireless connections and safeguards sensitive information.
RADIUS in Firewall and Device Authentication
A RADIUS server authenticates switches, firewalls, and access points, enabling central access control. This is necessary to connect only the trusted devices to the network.
RADIUS for Remote Workforce and Cloud Access
Enforce secure authentication for cloud platforms and remote employees with a RADIUS server. It integrates with IdPs, adaptive MFA, SSO, and more software to offer a scalable and centralized authentication solution, which is suitable for cloud and hybrid settings.
RADIUS and TACACS+
TACACS+ stands for Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus. it segregates authentication, authorization, and accounting, making it possible to use other protocols such as LDAP, PAP (Password Authentication Protocol), and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol), to name a few.
These protocols are primarily used for authentication, but can also be used for accounting or authorization.
On the other hand, RADIUS combines authorization and authentication, making it impossible to use them separately.
So, RADIUS vs. TACACS+, which one is a better choice? Well, it depends on what your end goal is and how you are using protocols.
How miniOrange Enhances RADIUS Server Security
Amplify the RADIUS server security by integrating the miniOrange MFA software into the RADIUS server authentication flow.
So, the users trying to access resources via networks such as Wi-Fi, VPNs, routers, firewalls, and switches offer extra verification aspects, other than their credentials.
These verification aspects (MFA solutions) include push notifications, OTP, biometric verification, and more.
Contact us to know more about these MFA products, or start a 30-days free trial today.
Conclusion
Amongst various methods of authentication, the RADIUS server is a one-of-a-kind security facet that makes use of context-based authentication, AAA, and keeps up with compliance. This allows enterprises to safeguard their networks, limiting them to only the authorized users.
Integrating it into your everyday business can help you keep potential cybercriminals away, preventing major breaches and suspicious activities.
FAQs
What is RADIUS in networking?
In networking, a RADIUS server verifies the users who are trying to access networks such as wireless access points, VPNs, firewalls, etc.
How is RADIUS different from other protocols?
RADIUS combines authentication and authorization in a central system, which is absent in protocols such as TACACS+.
Is RADIUS secure for enterprise networks?
Yes, it is secure for enterprise networks because it helps to avert unauthorized access by validating users against trusted sources such as an AD, where the entire user data is stored.
What is the RADIUS protocol used for?
The RADIUS protocol is used to handle network access by authenticating, authorizing, and accounting.
Is RADIUS authentication scalable for growing businesses?
Yes, RADIUS server authentication is highly scalable, as it is compatible with large networks and can be easily integrated with identity providers.
Which type of businesses benefit the most from using RADIUS authentication?
Businesses that are operating remotely or have a hybrid setting, and those that need a wireless connection to manage multiple devices.




Leave a Comment