OAuth 2.0 Single Sign On (SSO) into Jira
Jira OAuth/OpenID app gives the ability to enable OAuth/OpenID Single Sign On for Jira Software and Jira Service Desk. Jira Software and Jira Service Desk are compatible with all OAuth/OpenID Providers. Here we will go through a guide to configure SSO between Jira and your OAuth/OpenID Provider. By the end of this guide, users from your OAuth/OpenID Provider should be able to login and register to Jira Software and Service Desk.
Video Setup Guide
Pre-requisites
Before proceeding with the integration of your OAuth/OpenID Provider and Jira, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
- Ensure that Jira has been installed and configured appropriately.
- Enable HTTPS on the Jira Server (optional, but recommended).
- Establish admin credentials for Jira.
- Obtain a valid Jira Server and Data Center License.
Download and Installation
Now, let’s look at how you can download and install the miniOrange Jira OAuth/OpenID Connect Single Sign On (SSO) plugin for your Jira Data Center.
- Log into your Jira instance as an admin.
- Navigate to the Settings Menu and click on Manage Apps.
- Next, click on Find new apps option on the left-hand menu of the page.
- Here, locate miniOrange Jira OAuth/OpenID Connect Single Sign On (SSO) plugin on Atlassian marketplace via search.
- Click on Try it free to begin a new trial of the plugin with a temporary license.
- When redirected to MyAtlassian, enter your information and click Generate license.
- Next, click Apply license.
Step 1: Set Up Custom OAuth Provider
- Register an OAuth application on your Provider by configuring the Callback URL provided in the plugin. The callback URL would be {oauth_client_base_url}/plugins/servlet/oauth/callback
- Collect the endpoints given below from your Provider to configure them in the plugin.
| Endpoints | Use |
|---|---|
| Client ID | Identify the application. |
| Client Secret | Authenticate the Authorization Server. |
| Scope | Limit an application's access to a user's account. |
| Authorization Endpoint | Identify a user or obtain an authorization code. |
| Access Token Endpoint | Allows an application to access an API. |
| User Info Endpoint | Access the user profile information. |
| Group Endpoint (optional) | Fetch groups of a user. |
| Logout Endpoint (optional) | Enter the Logout endpoint of your OAuth/OpenID Provider. Leave it blank if Logout endpoint is not supported by provider. |
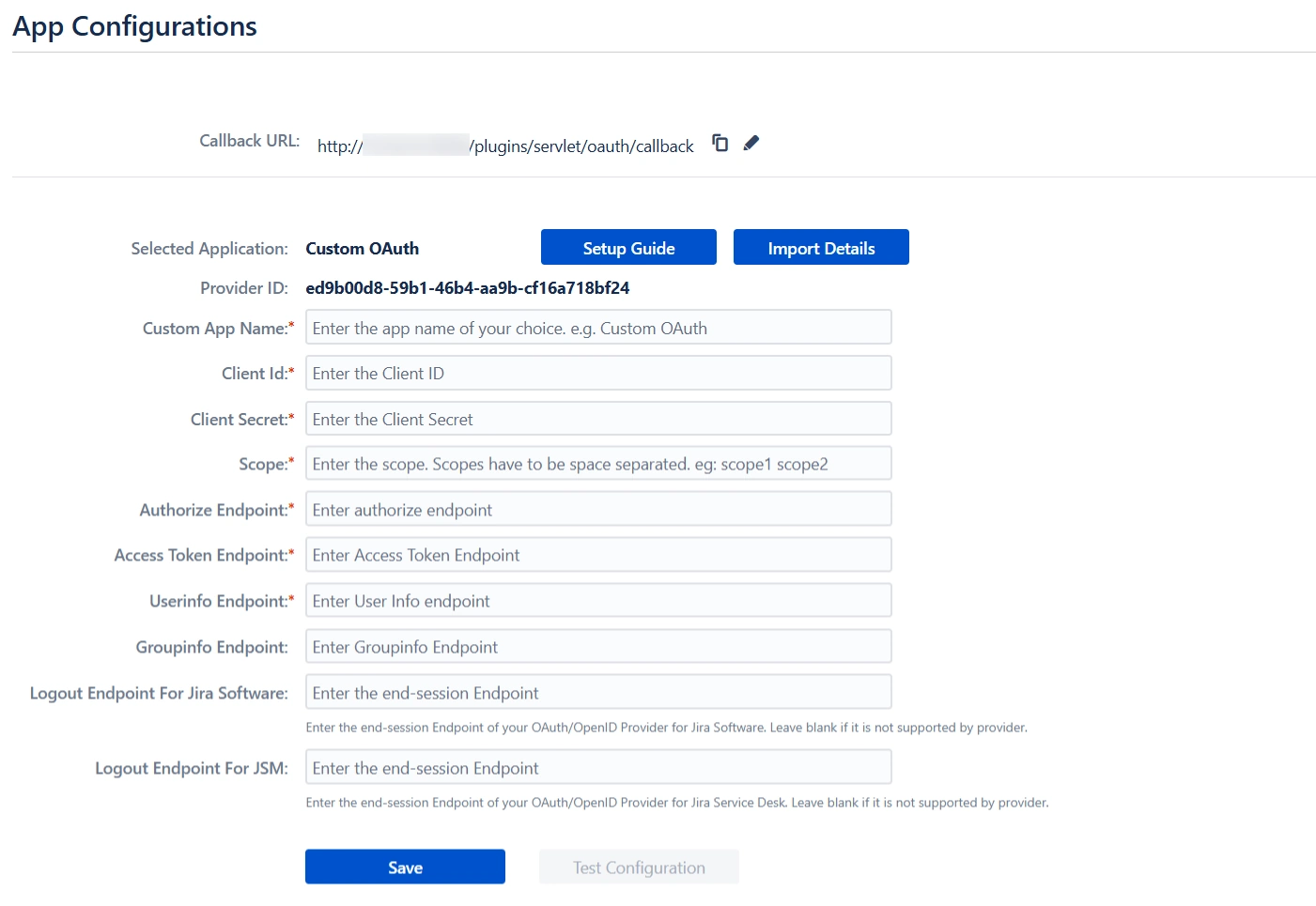
Step 2: Set Up Jira as OAuth Client
- Select Custom OAuth App from the dropdown list.
- Enter the App Name, Client ID, Client Secret and Scope.
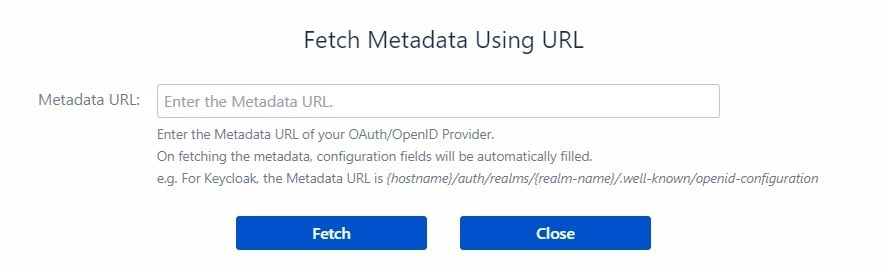
- Configure all the endpoints collected from the Provider (as mentioned in the Step 1) or if you have the Metadata URL of your Provider, then click on the Fetch Info by Metadata URL button for importing configurations.
- Enter the metadata URL and click on the Fetch option. All the Endpoints [like Authorize Endpoint, Access Token Endpoint, User Info Endpoint and Scope] will be configured automatically except Client ID and Client Secret.
- The format of metadata URL is {domain_name}/.well-known/openid-configuration
Here are a few examples of Providers along with their Metadata URLs. - Configure the Logout Endpoint if you want users to log out from Jira along with Provider. This setting is optional. Logout URL will destroy user’s session in Jira and Provider. You can also set redirect URL here, which specifies where to redirect after Jira logout.
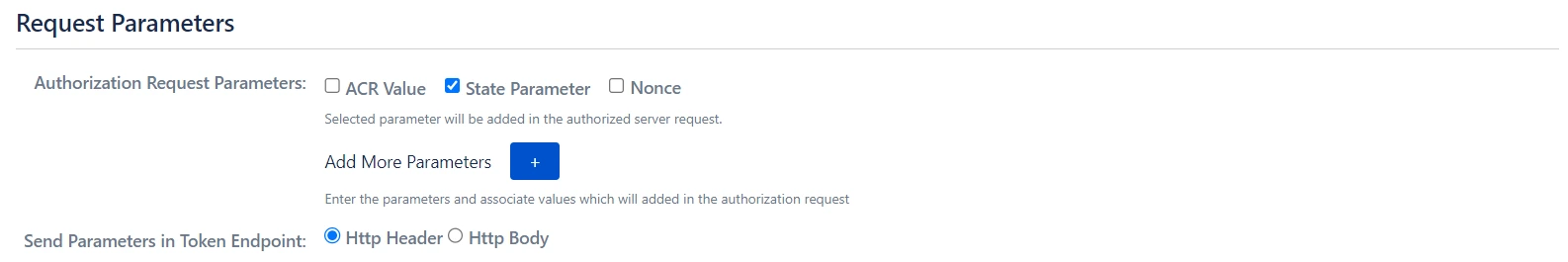
- Click on ACR Value Check checkbox if you want to add ACR Value parameter to the authorised server request. This setting is optional. The ACR value specifies the authentication method used by the Authorization Server and is used to enable the multi-factor authentication.
- Click on Nonce checkbox if you want to add the nonce parameter to authorised server request. The nonce parameter is used to validate the tokens received from the provider. Its purpose is to mitigate the replay attack.
- Select the Check State Parameter if required by your OAuth Provider. Using state parameter, a client application can validate that the response received from the provider is not altered in between.
- Click on Save button.
- Click on Test Configuration for verifying the entered details.

| miniOrange | https://login.xecurify.com/moas/.well-known/openid-configuration |
| Azure AD | https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/.well-known/openid-configuration |
| Okta | {domain_name}/.well-known/openid-configuration |
| Keycloak | {hostname}/auth/realms/{realm-name}/.well-known/openid-configuration |
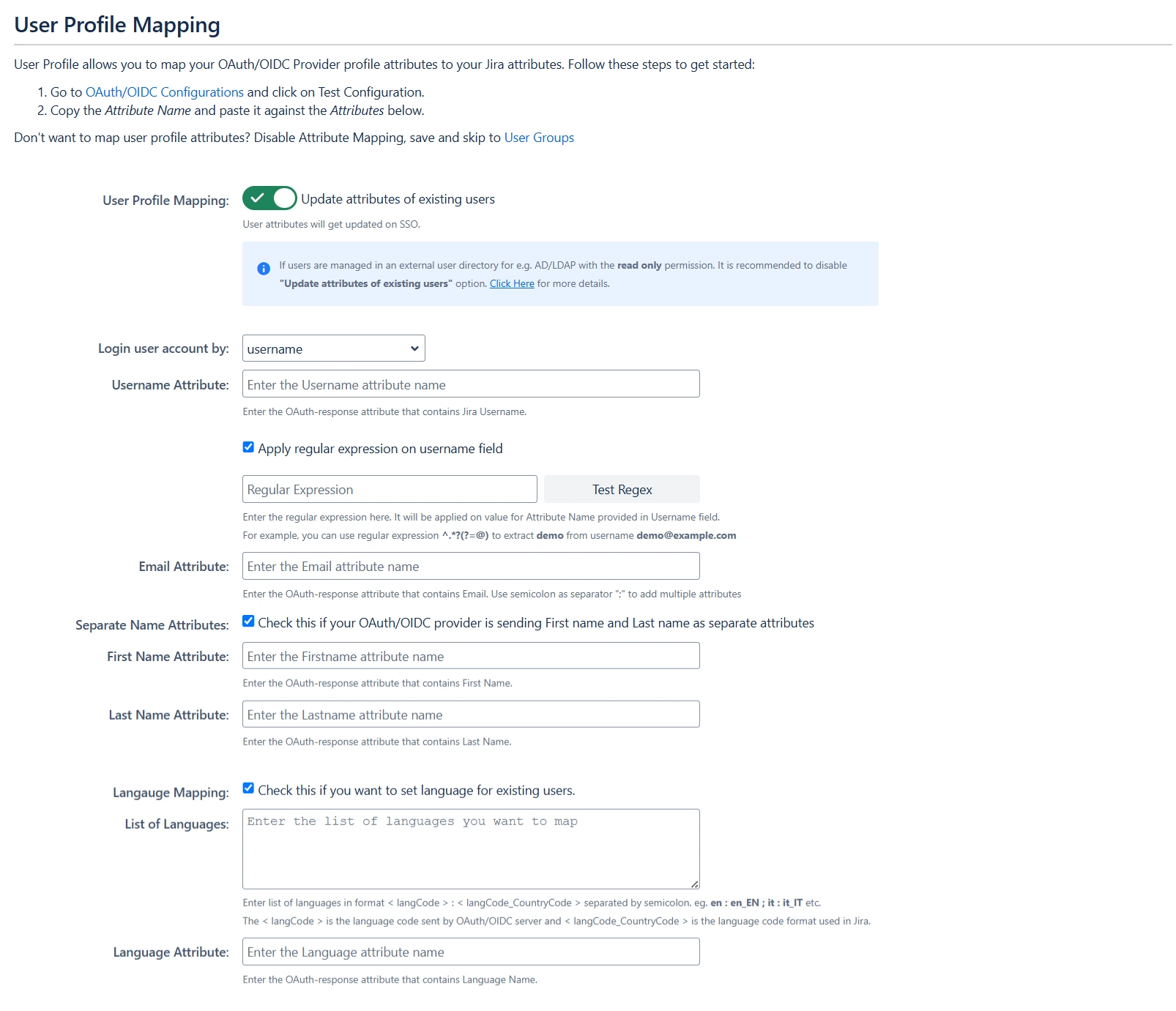
Step 3: User Profile Mapping
Navigate to the User Profile section in the left sidebar to set up user profile attributes for Jira. If your user directory is read-only, disable the User Profile Mapping option in this tab and proceed directly to the Matching a User step.
 3.1 Identifying Correct Attributes
3.1 Identifying Correct Attributes
- Access the App Configuration tab and click on Test Configuration.
- In the pop-up that appears, review the table displaying all values returned by your OAuth/OpenID Provider to Jira. If essential attributes like First Name, Last Name, Email, or Username are missing, adjust the settings in your OAuth/OpenID Provider accordingly.
- Once you've confirmed all values in the Test Configuration popup window, proceed to the User Profile tab.
 3.2 Configuring Profile Attributes
3.2 Configuring Profile Attributes
- It's essential to set up both Username and Email if you allow user registration. Alternatively, you can restrict login to existing users by deselecting the Allow User Creation option in the Advanced SSO Options tab.
- You’ll be able to configure these rules in the Redirection Rules section.
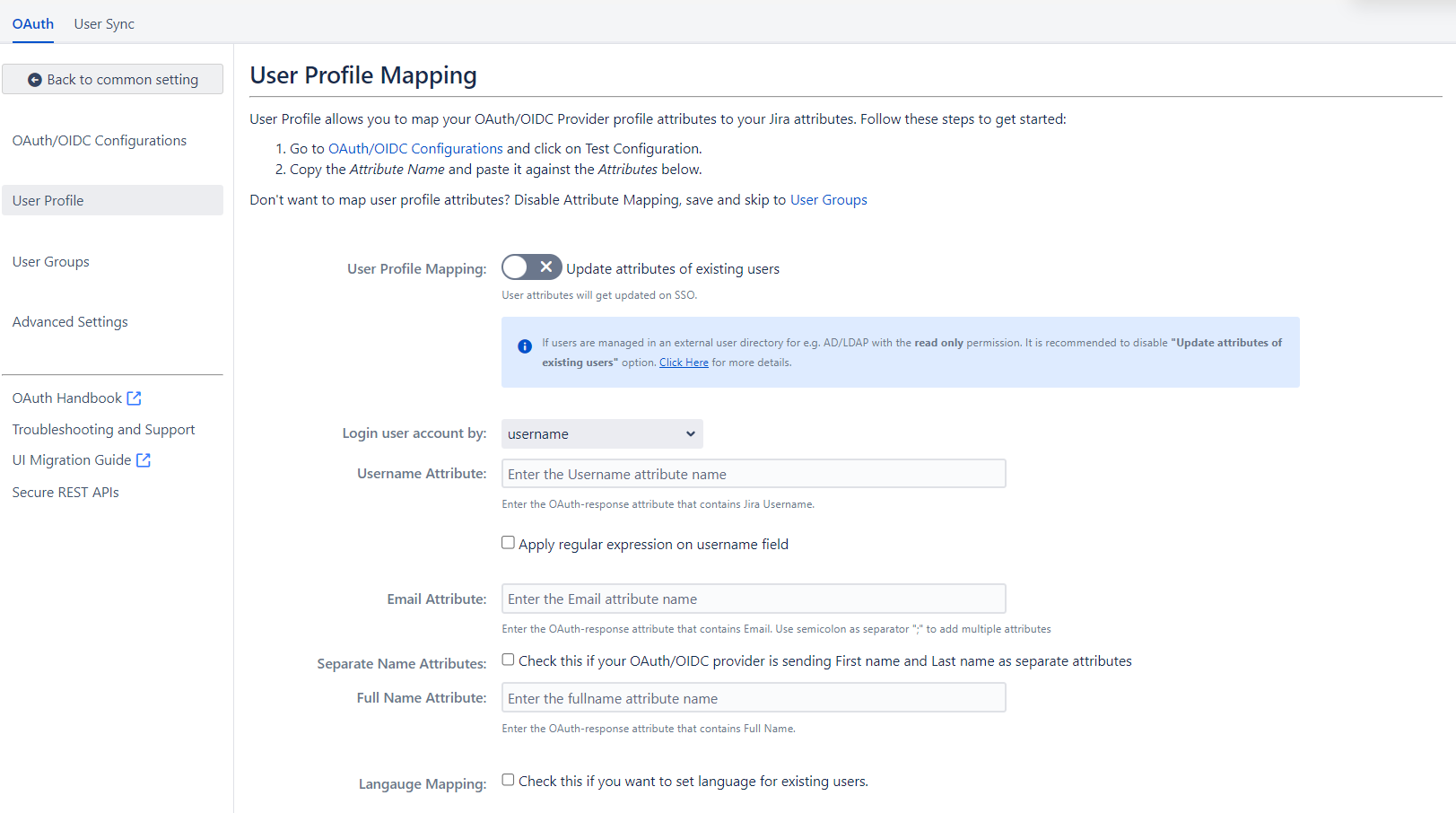
 3.3 User Attribute Matching
3.3 User Attribute Matching
When a user logs into Jira, data or attributes from the OAuth/OpenID provider are used to search for that user in Jira and facilitate login. To match the attributes:
- Navigate to the User Profile tab.
- Choose either Username or Email as the login for the Jira user account.
- Enter the attribute name from the OAuth/OpenID Provider that corresponds to the Username or Email as identified in the Identifying Correct Attributes step.
 3.4 Custom Attribute Mapping
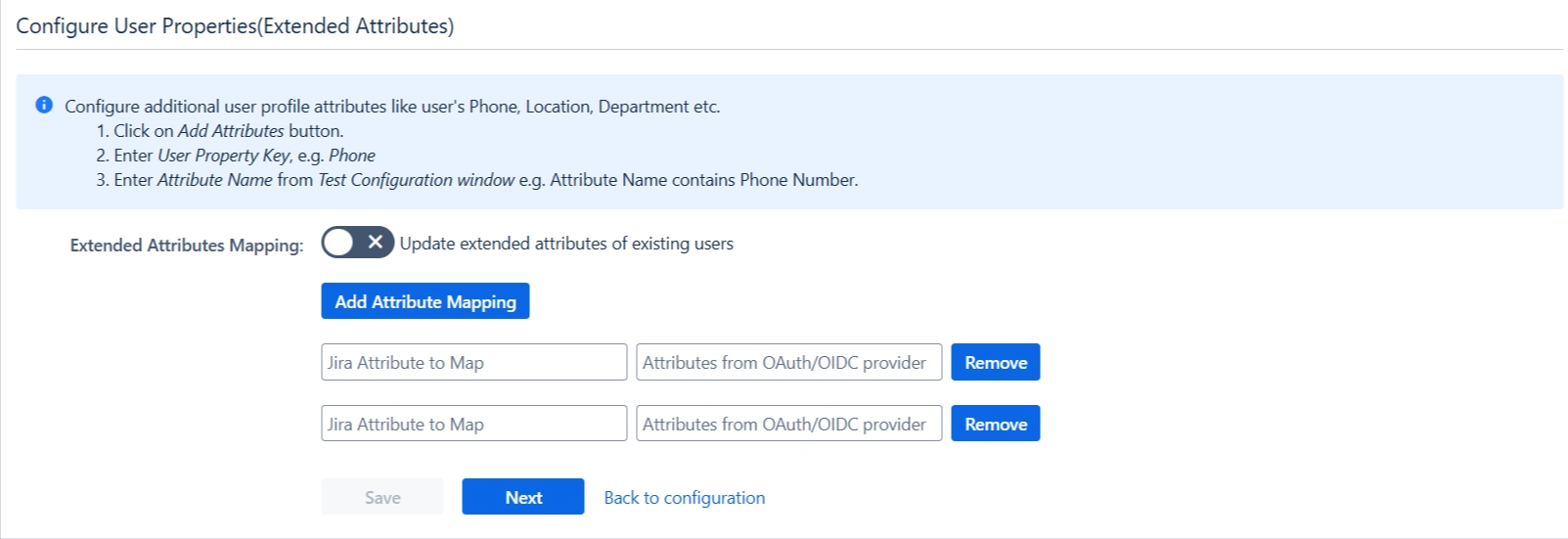
3.4 Custom Attribute Mapping
You can configure custom attributes received in the OAuth/OpenID response using the Configure User Properties(Extended Attributes) section.
- Click on Add Attribute Mapping.
- Enter the attribute name( E.g. department) as User Property Key in the Select Jira Attribute to Map field.
- For each attribute, input the corresponding value retrieved from the Attributes from IDP tab in the Test Configuration window. For example, if the attribute name in the Test Configuration window is Department, enter Department as the Attribute Value.
- Additional attributes, such as location, can be added by selecting the Add Attribute Mapping option.
Step 4: User Group Mapping
As we proceed to configure user group attributes for Jira, you have the option to enable group mapping.
If you wish to do so, please ensure to select Enable Group Mapping in the User Groups tab. Alternatively, you can proceed directly to setting the default group.
 4.1 Setting the Default Group
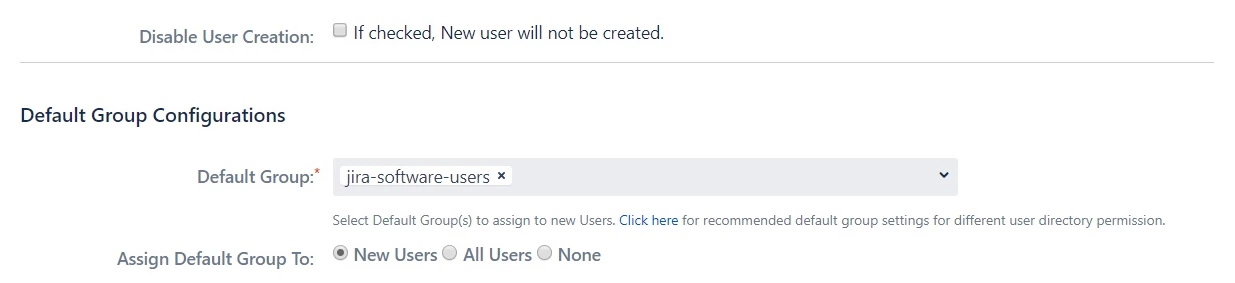
4.1 Setting the Default Group
- In the User Groups tab, select the default group for users. If no group is mapped, users are automatically added to this group.
- Using the Assign Default Group To option, you can assign default groups to all users or new users. Choose None if you prefer not to assign any default group to SSO users.
 4.2 Finding Group Attribute
4.2 Finding Group Attribute
- To identify group Attribute, go to the App Configuration tab and click on Test Configuration. Review the values returned by your OAuth/OpenID provider to Jira in the table. If group values are missing, adjust the settings in your OAuth provider to include group names.
- After reviewing all values in Test Configuration, proceed to the User Groups tab. Enter the Attribute Name of the group under Group Attribute.
- Check Disable Group Mapping option if you don't want to update groups of existing users.
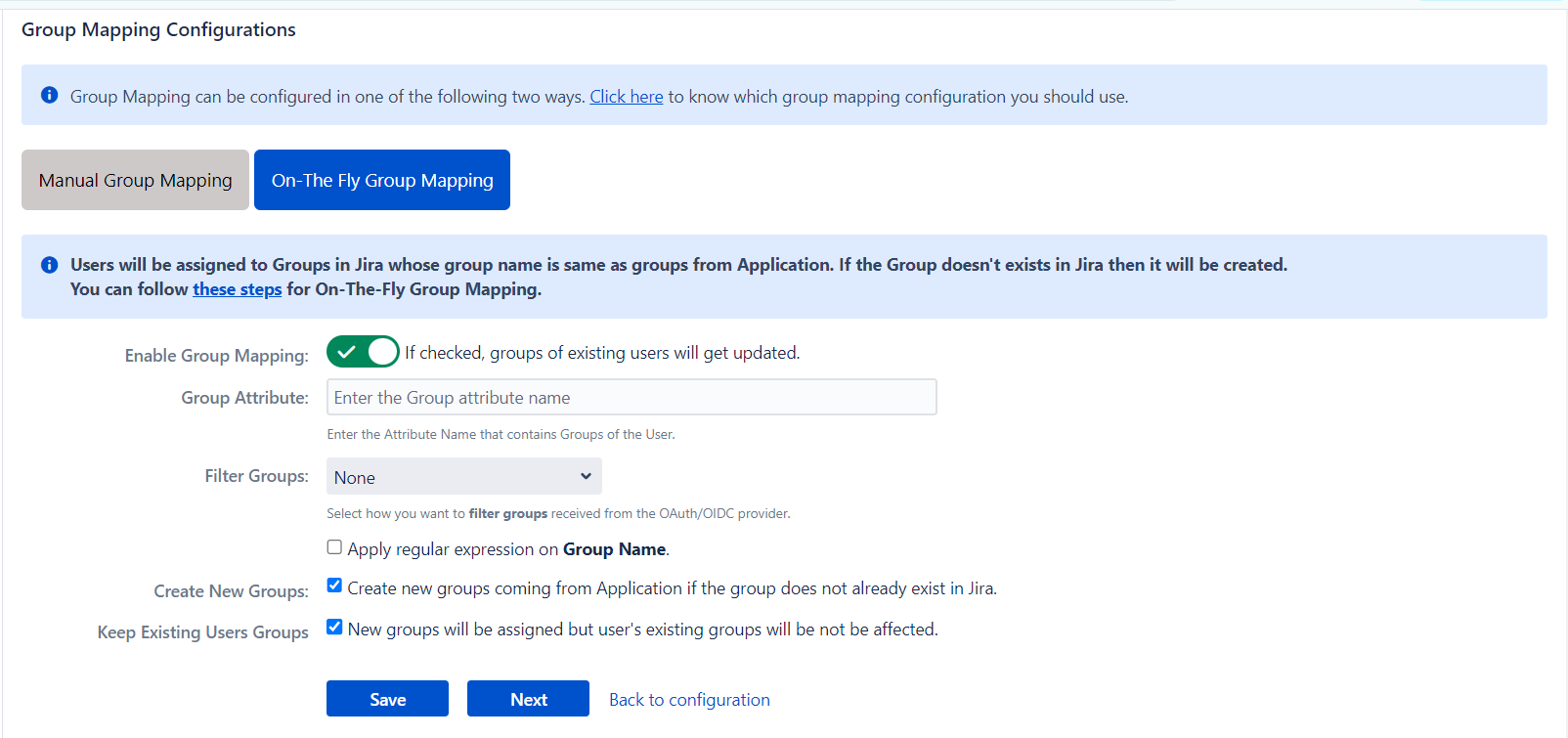
 4.3 Group Mapping
4.3 Group Mapping
Group mapping can be done manually or on the fly:
- Manual group mapping: If the names of groups in Jira are different than the corresponding groups in OAuth/OpenID Provider, then you should use Manual group mapping.
- On-The-Fly group mapping: If the names of groups in Jira and OAuth/OpenID Provider are same, you should use On-The-Fly group mapping.
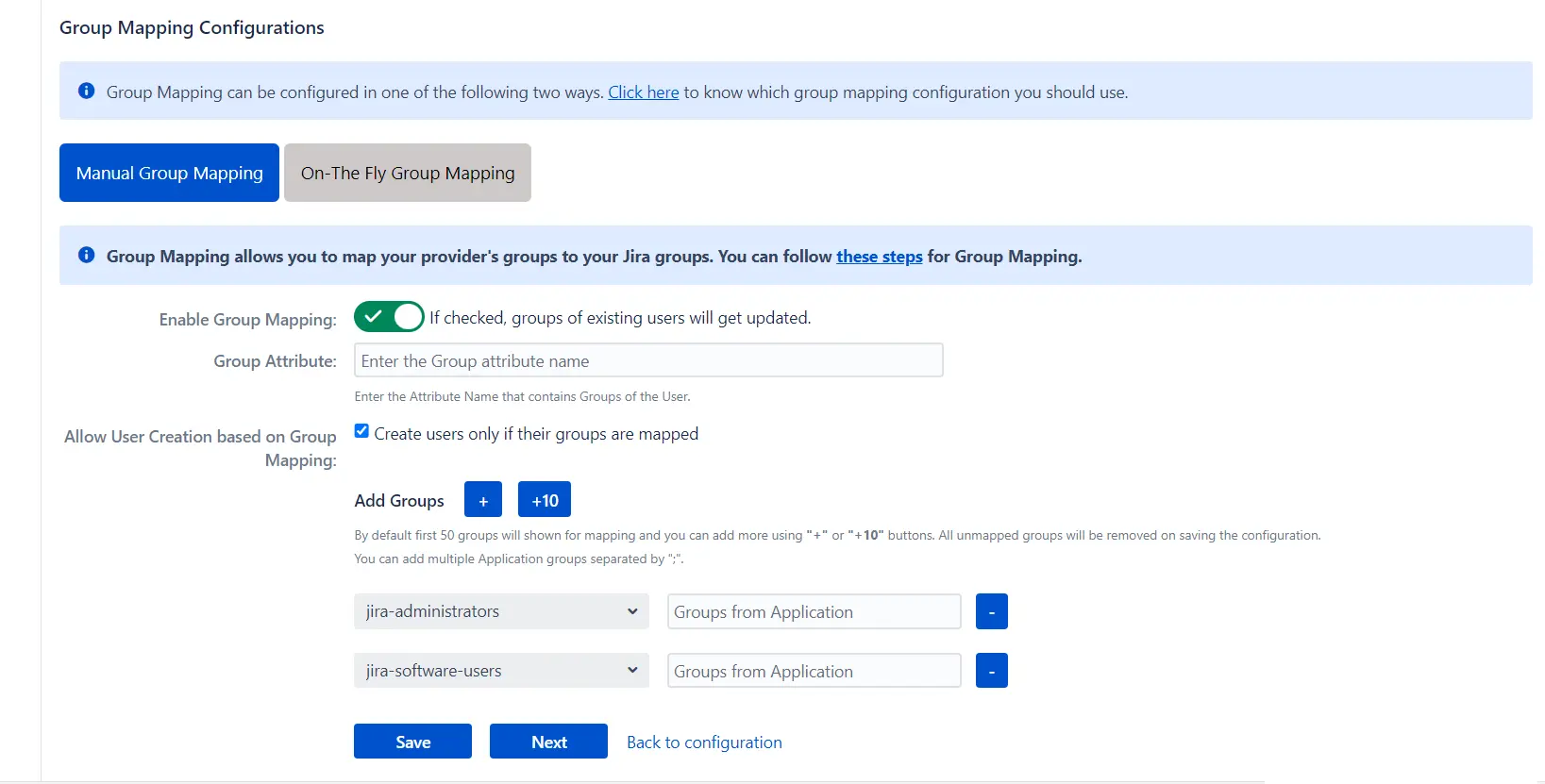
I. Manual group mapping
- Check the Allow User Creation based on Group Mapping option if you want new users to be created only if at least one of the user's OAuth/OpenID Provider groups is mapped to a group in the application.
- Select a Jira group from the dropdown list and enter the name of the OAuth/OpenID Provider group to be mapped in the Groups from Applications textbox.
- For instance, if you want all users in the 'dev' group of OAuth/OpenID providers to be added to jira-software-users, you will need to select jira-software-users from the dropdown and enter 'dev' against jira-software-users.
- You can use the '+' and '+10' buttons to add extra mapping fields, and the '-' button to delete mappings.
II. On-The-Fly group mapping
- If the group names in both Jira and the OAuth/OpenID provider match, opt for On-The-Fly group mapping.
- Check the Create New Groups option to create new groups from the OAuth/OpenID Provider if not found in Jira.
- Preserve existing user groups by selecting the Keep Existing User Groups option. Unticking this option will remove the user from a Jira group if it's not present in the OAuth/OpenID response.
- Deselect the Keep Existing User Groups option to prevent On-The-Fly group mapping from affecting locally managed Jira groups. Add those groups to the Exclude Groups field.
Step 5: Advanced SSO Configurations
- Enable PKCE to enhance security by adding an extra layer of protection to the OAuth flow, preventing authorization code interception attacks.
- Allow User Creation:- Enabling this will allow you to create new users through SSO.
- Directory for New User:- After a successful SSO, if the user is not found in JIRA , a new user account will be created in the selected user directory.
- Remote Directory Sync:- The user details will be synced from the remote directory on successful SSO only if the user exists in the remote directory.
- ACR Value: Requests additional information from the OpenID provider to determine the Level of Assurance for user authentication.
- State Parameter: Protects against CSRF attacks by sending a unique, non-guessable value with the authorization request, mandatory for certain providers.
- Add Custom Parameters: Allows the inclusion of extra parameters in the authentication request.
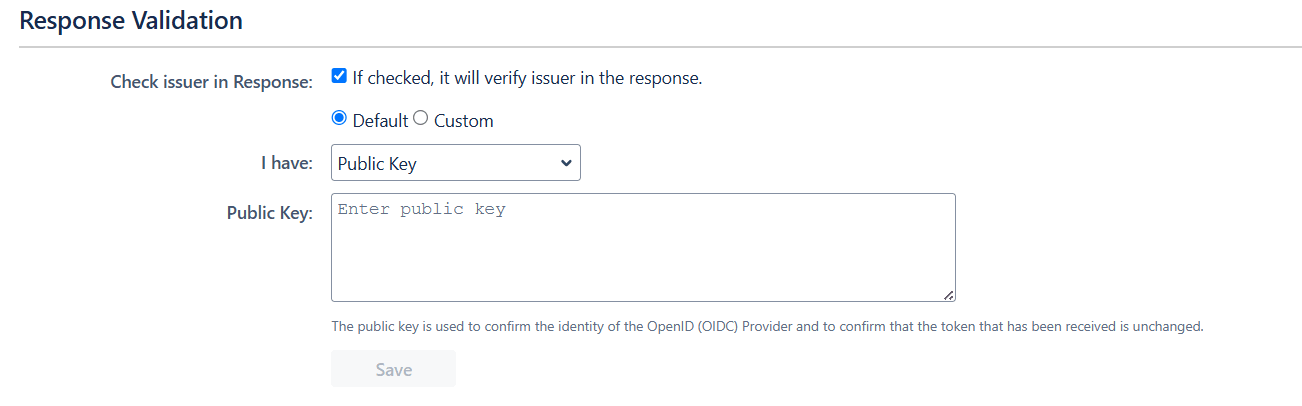
- Public Key: Used in asymmetric cryptography to decrypt signed tokens, verifying the identity of the OpenID provider and ensuring the tokens remain unchanged.
- JWKS Endpoint URL: Provides public keys used to validate JSON Web Tokens (JWT) issued by the authorization server for user authentication.

Step 6: SSO Setting
The configurations within the SSO Settings tab are pivotal in shaping the user experience for Single Sign-On.
 6.1 Sign In
Settings
6.1 Sign In
Settings
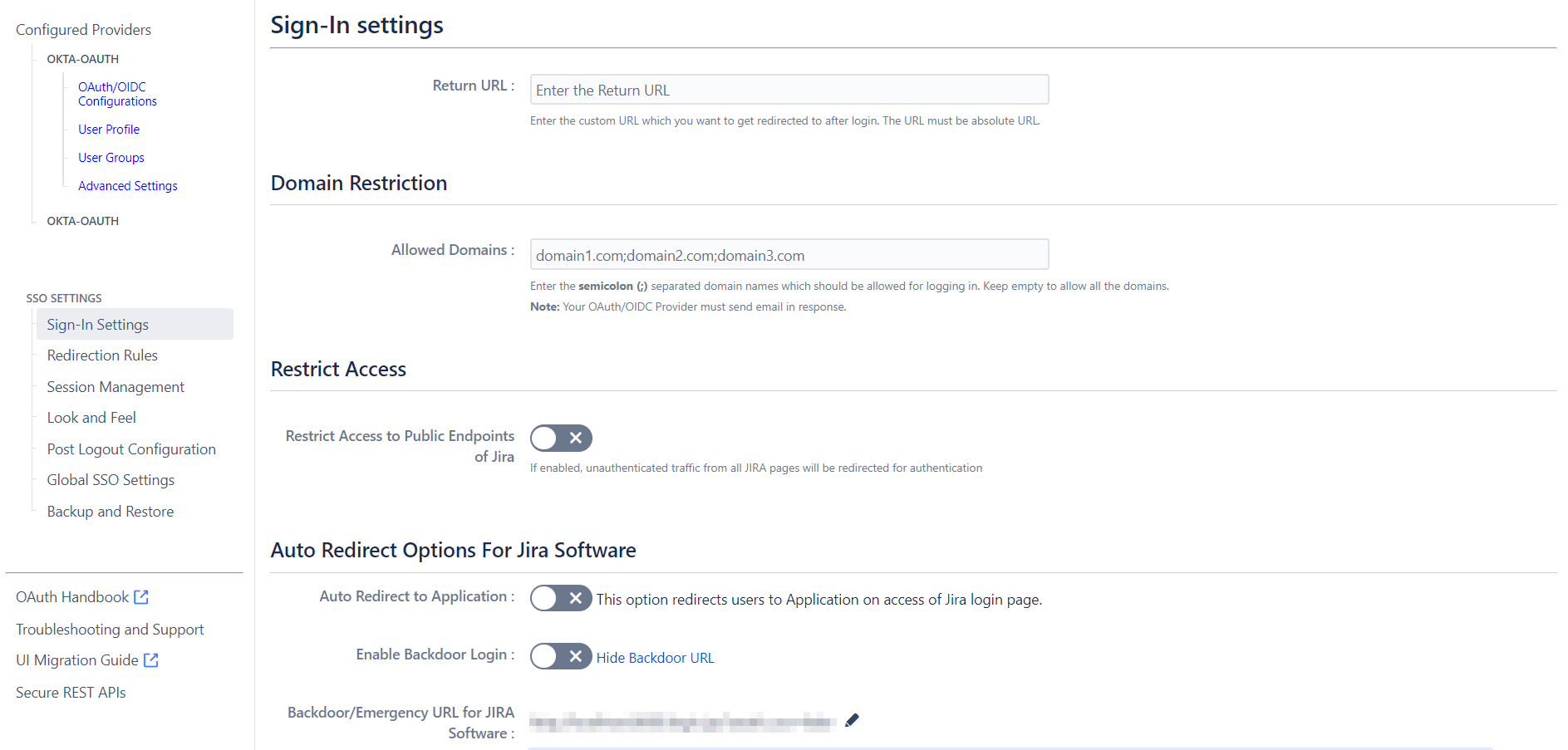
- Enable Auto Redirect to Application to redirect users to the OAuth/OIDC provider when accessing the Jira login page. You can set a delay before redirection.
- Next, toggle the Enable Backdoor Login option for emergency access using a backdoor URL. Restrict access to this URL for specific groups if needed.
- You can use Domain Restriction to allow login for specific user domains and configure multiple allowed domains (semicolon-separated).
- The Secure Admin Login option ensures the re-authentication of admin users before accessing pages with administrative permissions.
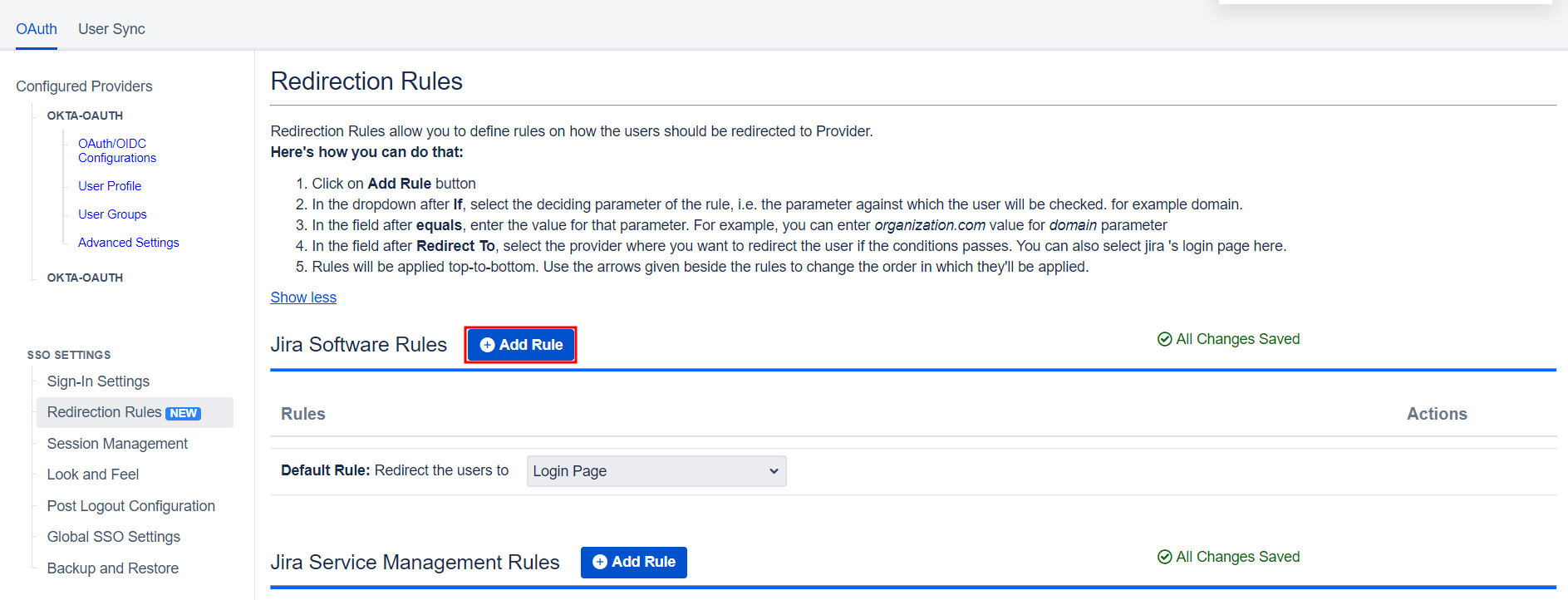
 6.2 Redirection Rules
6.2 Redirection Rules
- Redirection rules allow you to redirect users to login pages/providers based on their email domains, groups, or directories. This functionality is especially useful with multiple configured providers.
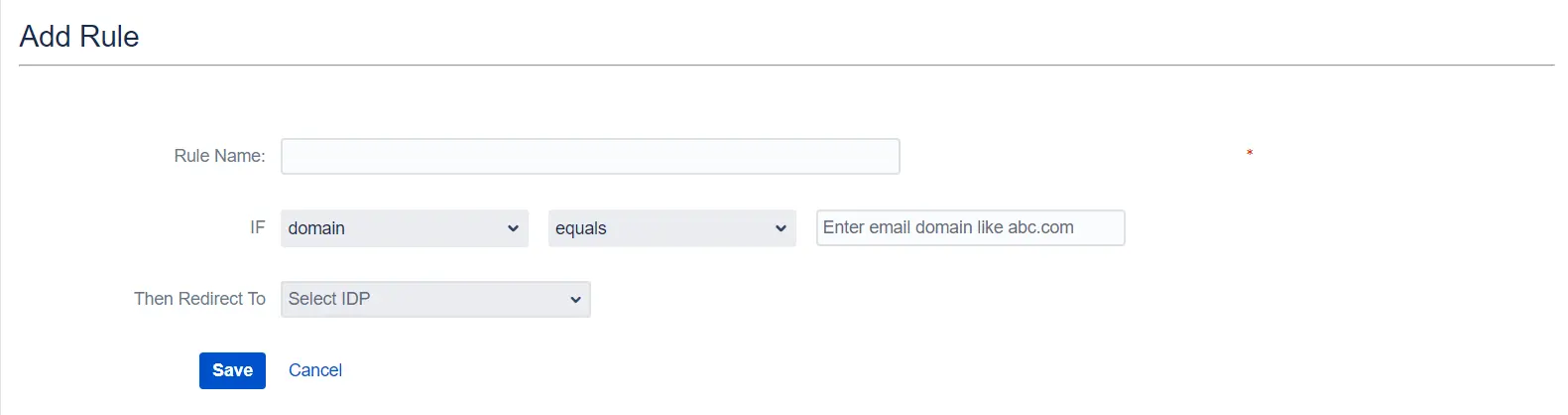
- To create a new rule, go to the Redirection Rules tab and click Add Rule.
- Next, give the rule a name and set the conditions for redirection. Click Save once you’re done.
- You can also set a default rule if no other rule conditions are met.
- Once you set a redirection rule, users who fulfill its conditions will be shown a login form, prompting them to input their username/email address. You can set domain-based rules for directing users to specific providers as well.
 6.3 Global SSO
Settings
6.3 Global SSO
Settings
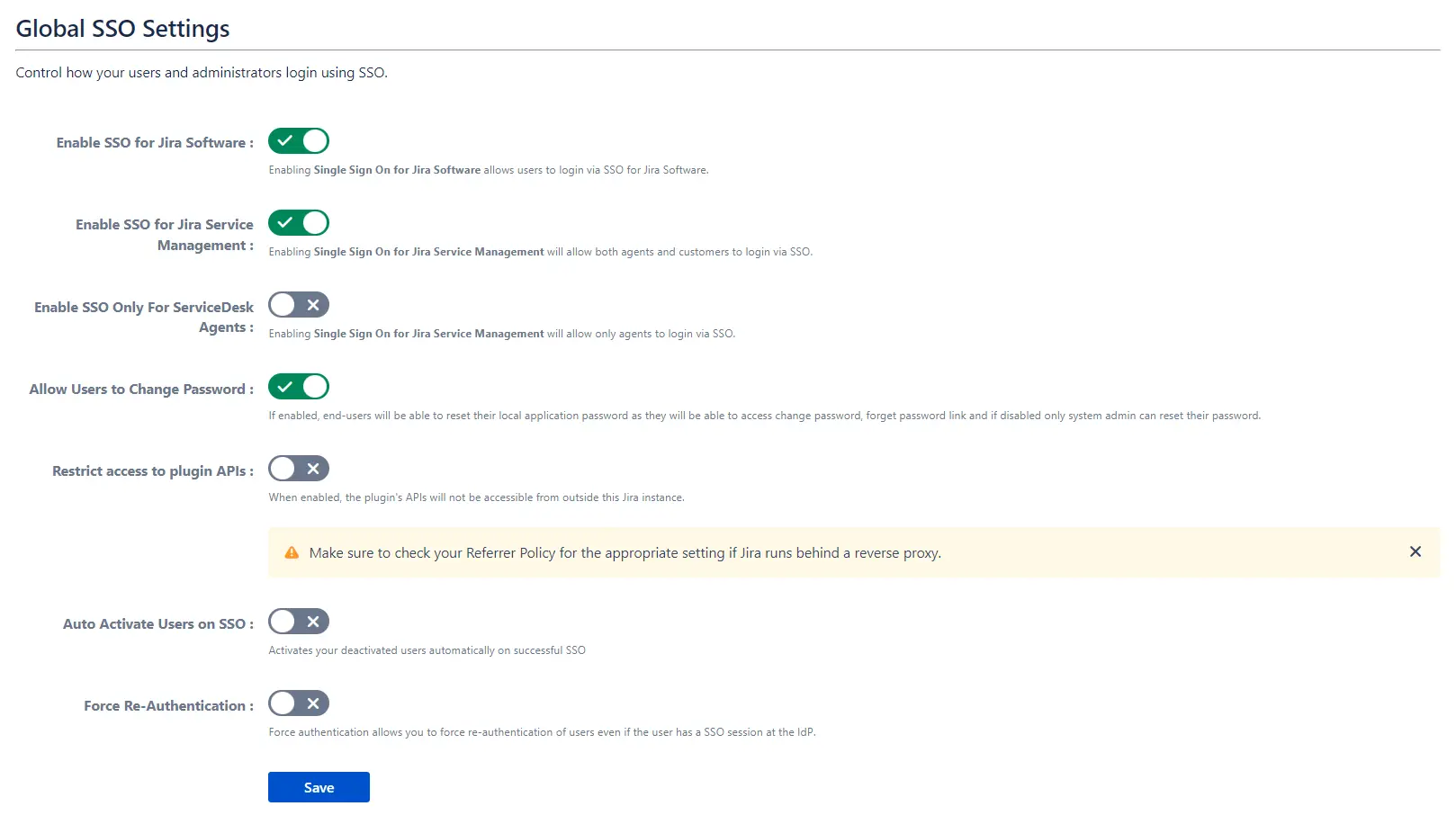
- You can enable/disable SSO for Jira Software and Service Desk from the Global SSO Settings tab.
- If enforcing SSO for Service Desk Agents only, select Enable SSO Only For Service Desk Agents.
- You have the option to activate SSO for both Jira software and service desk by selecting Enable SSO for Jira Software and Enable SSO for Jira Service Desk respectively.
- The app also gives you options to adjust additional settings like Allow Users to Change Password, Restrict Access to Plugin APIs, and Auto Activate Users on SSO.
- To keep users logged in until explicitly logged out, you can enable Remember Me-Cookie in the Session Management tab.
 6.4 Look and
Feel
6.4 Look and
Feel
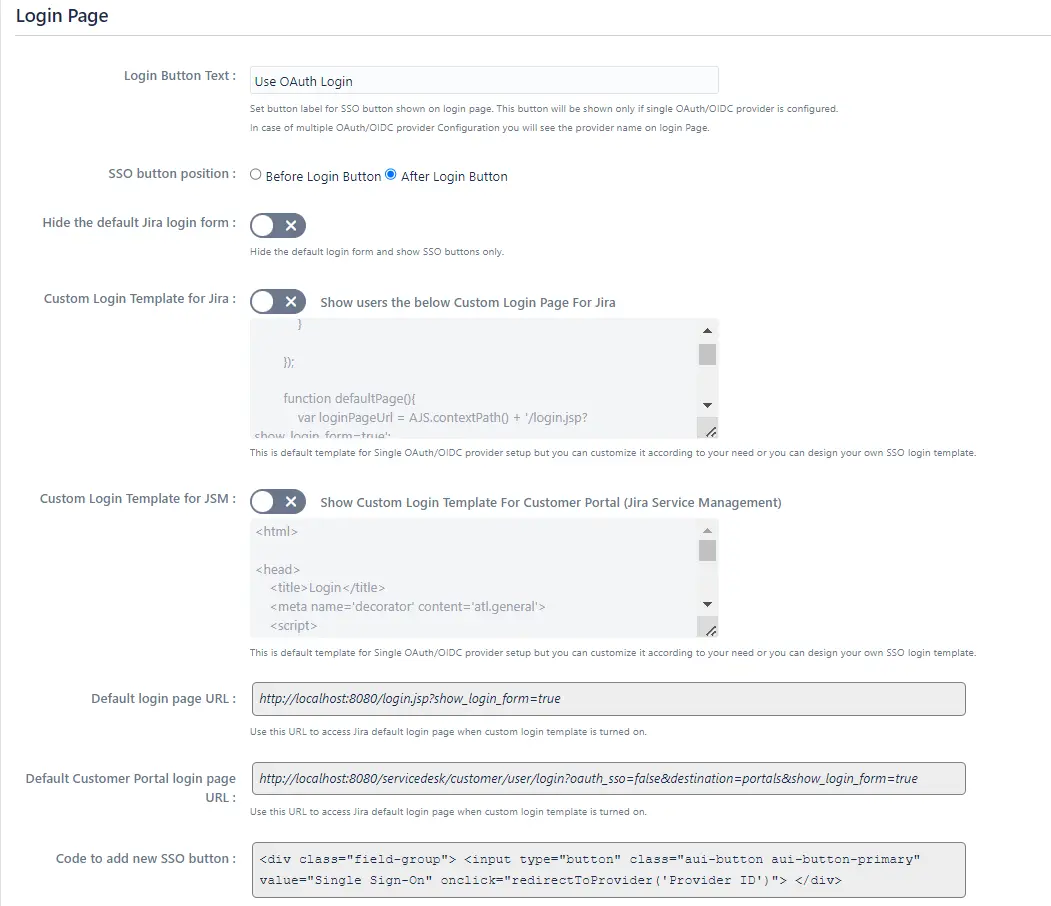
- You can customize the appearance of your login page and error messages from the Look and Feel tab.
- The plugin has provisions for modifying the default login button text and designing the login page using customisable templates.
- You can also set a Custom Logout URL from the Post Logout Configuration tab to redirect users to a specific screen after they logout.
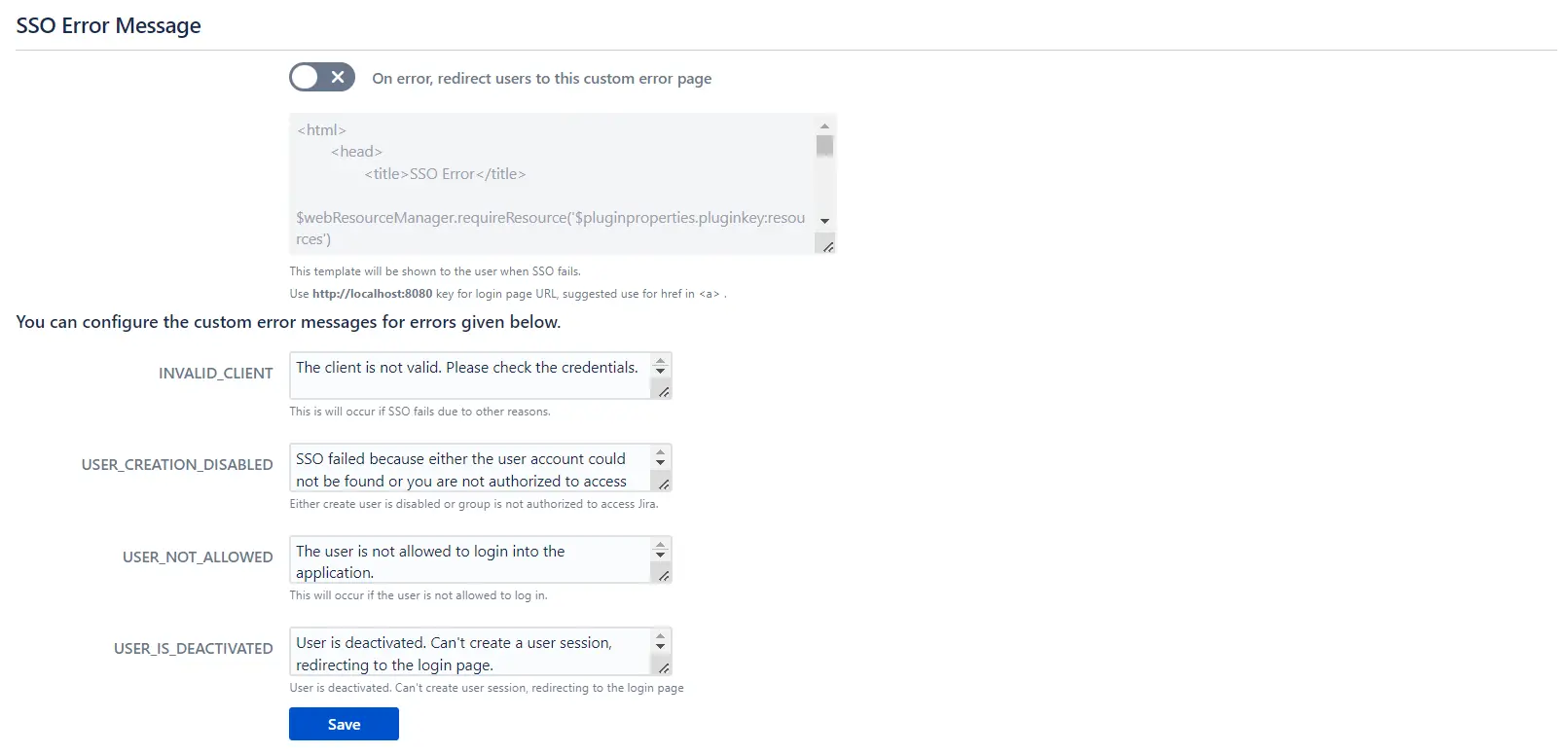
- The SSO Error Message section allows you to customize the error message displayed to users.
Configure SCIM with OAuth
Additional Resources
Did this page help you?

 Try it for free
Try it for free