According to the 2025 Secure Network Access Report by Hughes, over 50% of organizations find securing remote network connectivity their biggest security challenge, and RADIUS has become the need of the hour. In our practical scenario of distributed work environments, careless network access can lead to costly breaches. RADIUS serves as a solution to prevent these security breaches because it enables IT teams to establish uniform security protocols and monitor user actions through one centralized system, which minimizes network access control vulnerabilities.
The RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) protocol operates as a networking standard that enables organizations to manage Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) functions for users who access network services through a centralized system. The security protocol operates as a network access controller which authenticates users and their devices before allowing them to access network resources, including Wi-Fi networks and VPNs and switches.
This blog aims to shed light on what RADIUS is, how it works, why we need it, and how to implement it in some practical applications. Also, it will help understand how miniOrange provides identity and access management solutions for network security applications using the RADIUS protocol.
What is RADIUS?
RADIUS operates as a client-server networking protocol that enables organizations to perform Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) functions for users who need to access remote networks. The system supports VPNs and wireless access points and Ethernet switches in addition to its original dial-up connection functionality. Networks implement RADIUS to perform user authentication and access control and activity tracking through Network Access Servers which connect to RADIUS servers.
Users establish their connection through a NAS device, which transmits Access-Request packets containing authentication data, including usernames and passwords or certificates, to the RADIUS server through UDP. The server authenticates user credentials through database resources, which include Active Directory and LDAP, before it sends either an Access-Accept or Access-Reject response or asks for more authentication details. The server grants access by sending attributes, which include IP addresses and session duration and VLAN and QoS configuration.
The RADIUS protocol operates through UDP ports 1812 and 1813 for authentication/authorization and accounting functions but legacy systems use ports 1645 and 1646. The system operates with two main packet types, which start AAA procedures through Access-Request packets and track usage data through Accounting-Request packets. The security mechanism uses MD5 hashing with shared secrets to protect passwords but it does not provide end-to-end encryption, which makes data vulnerable during proxy hops.
RADIUS provides network management capabilities for big organizations through its Active Directory directory integration and RFC 2865/2866 standard support. The system allows users to make instant authorization updates through RFC 5176 extensions. The system faces two main security risks because UDP provides no guarantee of delivery, and each hop requires its own security measures.
Core Operation of RADIUS
RADIUS enables secure network access through its three essential operations, which include authentication, authorization, and accounting. The authentication process verifies user identities before authorization grants access rights, and accounting tracks all system activities. Network administrators depend on this "AAA" framework to defend their resources and track system usage.
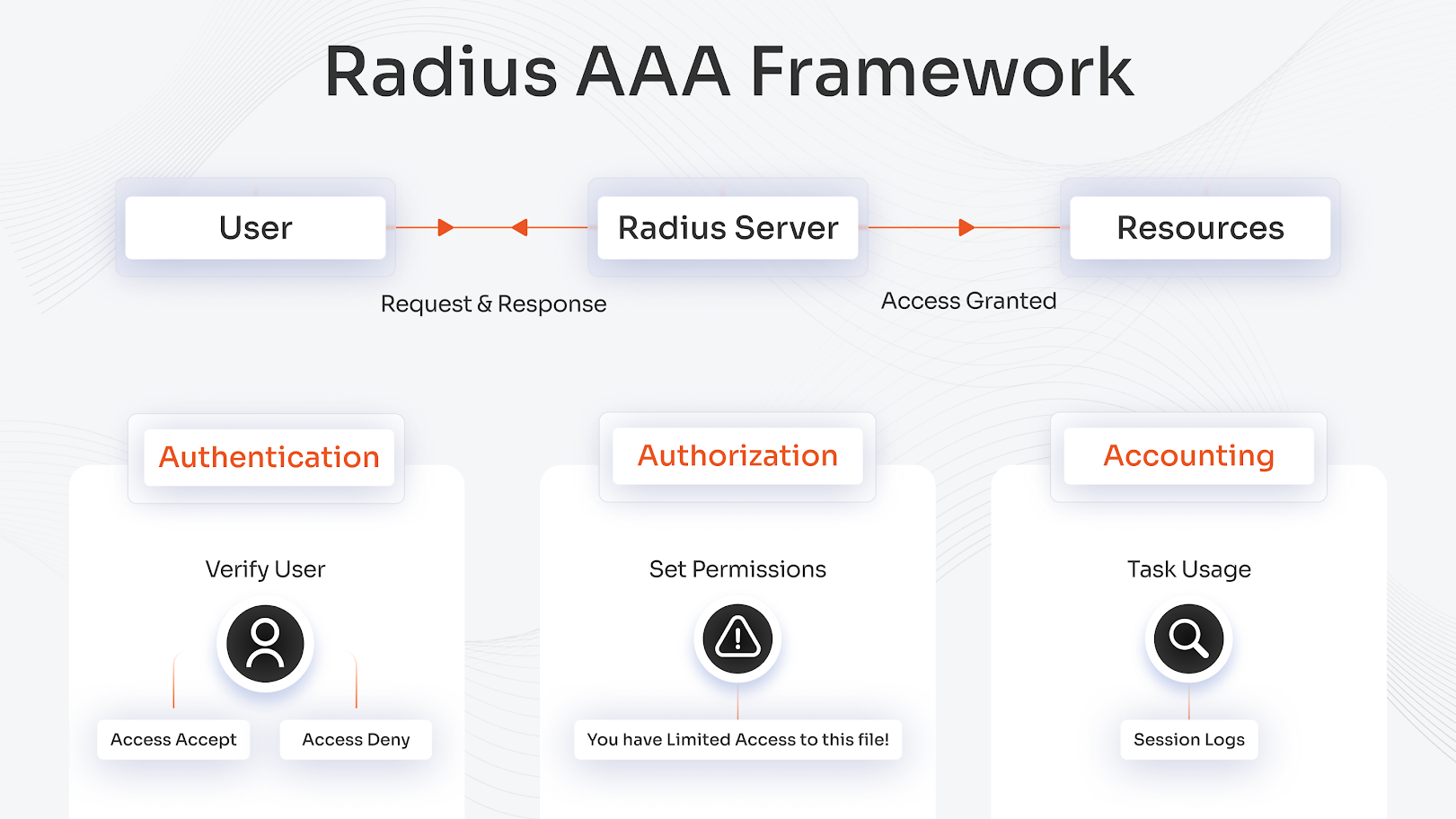
Authentication Verifies Identities
RADIUS client systems which include VPNs and Wi-Fi access points, allow users to authenticate their identities by entering their username and password. The RADIUS client encrypts authentication requests, which the RADIUS server uses to check user credentials against Active Directory or LDAP databases. The server sends "Access-Accept" when credentials match but sends "Access-Reject" to block unauthorized access. Modern security systems use RADIUS MFA as an additional authentication method to provide enhanced protection.
Authorization Sets Permissions
The RADIUS server performs role and policy checks for users after they complete their authentication process. The server determines which resources, including files and applications and network segments, users can access. The server provides authorization data to clients, which they must use to enforce access restrictions for security protection. The authorization process follows Zero Trust principles to restrict user access between different network segments.
Accounting Tracks Usage
RADIUS maintains session records, which include start and end times and all data transfer activities and disconnection events. The recorded data enables administrators to execute billing operations, conduct compliance verification, and detect unusual network traffic patterns. The accounting process starts at "Accounting-Start" and ends at "Accounting-Stop" to produce complete audit logs. The miniOrange system includes real-time alert functionality, which extends its logging capabilities.
Mastering RADIUS AAA operations enables you to construct secure networks that expand their capabilities while maintaining defense capabilities with the help of MFA software. Readers should proceed to miniOrange integration tutorials for implementing security solutions that will boost their protection measures.
How Does RADIUS Work?
RADIUS operates through three essential elements:
- Network Access Server (NAS) as the client,
- The RADIUS server and
- The user or device seeking access.
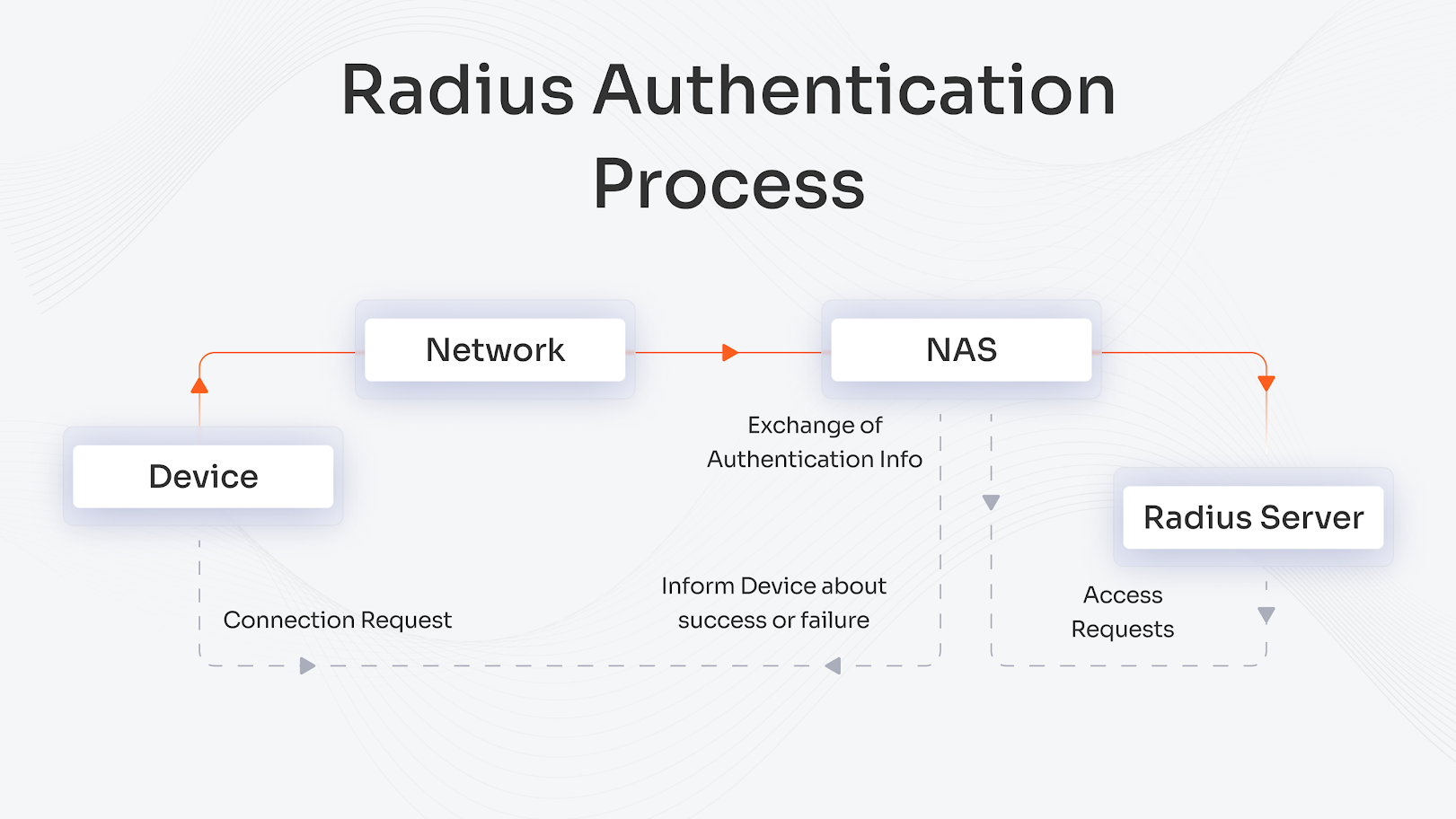
The NAS device sends an Access-Request packet with user information to the RADIUS server for authentication purposes. The server authenticates users through a two-step process that requires both verification of the shared secret and a database search for user information. The server generates three possible responses to access requests which include Access-Accept, Access-Reject, and Access-Challenge. The NAS system determines network access permission through its analysis of received responses.
The RADIUS protocol uses RFC 2865 to define multiple packet types, which include Access-Request, Access-Accept, Access-Reject, Access-Challenge, Accounting-Request, and Accounting-Response. The system protects user passwords through MD5 encryption, which encrypts them before transmission to prevent exposure.
While RADIUS utilizes MD5 as a hash function to encrypt passwords and verify responses from an authenticated user, it is also known that MD5 encryption is weak in terms of security. Since RADIUS combines shared secret keys with message data using MD5, security problems exist when MD5 is susceptible to collisions and length extensions, thus creating man-in-the-middle attack vulnerabilities (unless an organization implements the Message Authenticator Attribute using HMAC-MD5). Although Radius does protect passwords by encrypting them with MD5, organizations will have to add additional security elements to eliminate these potential vulnerabilities.
RADIUS in Network Security
RADIUS plays a crucial role in network security by centralizing authentication and access management, ensuring consistent protection across all network devices regardless of the vendor. It applies standardized access rules and continuously monitors user activity through a unified control system, helping organizations meet audit and compliance requirements effectively.
RADIUS also enables seamless access to directory services like Active Directory and LDAP, allowing organizations to rely on their existing authentication infrastructure while maintaining secure protocols. Its scalable design supports growing networks and diverse environments, while its authentication, authorization, and accounting functions reduce configuration errors and help security teams track user access for better incident response.
Practical Applications of RADIUS
Teams use RADIUS for secure network access in everyday operations. This protocol authenticates users and devices before they connect. It centralizes control and boosts security across enterprises.
RADIUS powers VPN connections for remote workers. Employees log in with credentials, and the server verifies them fast. Businesses cut breach risks with this setup.
Wi-Fi networks rely on RADIUS for enterprise-grade protection. It handles WPA2-Enterprise authentication in offices and campuses. Admins enforce policies like time-based access.
IT teams deploy RADIUS with Active Directory for seamless logins. It integrates with tools like miniOrange for MFA solution boosts. This combo strengthens Zero Trust models.
Cloud setups leverage RADIUS for hybrid environments. It secures Citrix or VPN gateways against threats. Companies scale access without weak points.
Key Benefits of RADIUS for Administrators
RADIUS operates as a core system that enables secure network access management. The system allows administrators to perform authentication and authorization and accounting functions through a centralized interface, which enables them to establish standardized policies and reduce system management complexity.
- The system gives administrators a single interface to manage all connected devices, handling authentication, authorization, and accounting centrally. This removes the need for configuring each device separately, enforces consistent network policies, reduces administrative work, and helps IT teams resolve access issues more quickly.
- The system enables fast user onboarding and offboarding across complex networks. Administrators can centrally automate role, permission, and access-level assignments, ensuring instant updates across all systems and reducing human errors while strengthening network security.
- The system generates complete authentication and session logs that support compliance with standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR. Continuous monitoring of user activities helps verify policy enforcement, detect unauthorized access attempts, and produce accurate compliance reports.
- The system provides real-time access data through built-in logging and accounting features. Administrators can monitor user connections, identify threats, and investigate incidents quickly, ensuring immediate visibility and strong protection for access control systems.
The RADIUS access management system improves operational performance while helping organizations meet better compliance standards.
Compliance and Oversight
The system provides enhanced compliance through its built-in AAA logging and audit capabilities. The system produces complete records of user actions during authentication and authorization processes, which enables administrators to monitor user activities and meet regulatory standards.
- The system records all authentication, authorization, and accounting events, which provides complete system visibility.
- The system produces reports that fulfill organizational governance requirements and outside regulatory standards.
- The system maintains a dependable audit trail that tracks all login attempts and access events.
The system enables organizations to boost their oversight capabilities through improved compliance management processes.
Limitations of RADIUS Protocol
RADIUS access control implementation requires administrators to know about its operational boundaries for successful deployment.
- The system operates through UDP, which results in unreliable network performance when network conditions become poor.
- The system performance deteriorates when authentication and authorization operations handle more than usual traffic volume.
- The exposure of systems to network-level attacks occurs when shared secrets receive insufficient protection.
Teams can enhance RADIUS security through appropriate configuration and encryption and traffic optimization methods when they understand its operational restrictions.
Getting Started with RADIUS Authentication
At the core of secure network authentication is RADIUS, which provides IT administrators with centralized management of users and their privileges to access resources. In addition to providing AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting) services, RADIUS ensures that only authenticated users and trusted systems have access to all types of resources (Wi-Fi, VPN, and RADIUS application gateways).
All IT professionals responsible for managing network security understand how RADIUS works, as it significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, creates audit trails for compliance purposes and allows you to implement very granular policy across all resources from a single location. Understanding RADIUS will allow you to better manage network security and provide a favorable user experience.
Do you need a simple yet modern approach to security? Solutions such as miniOrange include RADIUS support with additional features that cover multi-factor authentication, allowing you to prepare an easily scalable and strong cyberdefense system. Improve your RADIUS deployments and defend even the mightiest security breaches with the help of miniOrange IAM solutions today.
FAQs
What is the RADIUS protocol used for?
RADIUS serves as a protocol which verifies user identities and grants network access to Wi-Fi networks and VPNs and dial-up connections. Network access servers use a client-server architecture to request authentication services from RADIUS servers which operate as central authentication servers. The system enables administrators to access a single location for managing AAA function operations.
What's the difference between RADIUS and LDAP?
RADIUS operates through fast UDP communication on ports 1812 and 1813 to perform network access AAA functions. The LDAP protocol operates through reliable TCP connections on port 389 to manage directory information which contains user profile data and group membership details. The authentication process of RADIUS operates at high speed but LDAP performs better in query operations although its performance deteriorates when facing heavy traffic.
Is the RADIUS protocol still used?
Yes, RADIUS operates as a top authentication solution for enterprise networks because it delivers superior scalability for network access management. The encryption feature of RadSec provides enhanced security protection yet RADIUS continues to be the top choice for VPN and Wi-Fi network deployments because of its dependable operation.




Leave a Comment