Need Help? We are right here!
Need Help? We are right here!
Thanks for your Enquiry.
If you don't hear from us within 24 hours, please feel free to send a follow-up email to info@xecurify.com
Search Results:
×Active Directory (AD) is a database and a set of services that connects users to the network resources they require to complete their tasks.
The database (or directory) contains critical information about your environment, such as the number of users and computers present, as well as who is authorized to do what. For example, the database could contain 100 user accounts with information such as each person's job title, phone number, and password. It will also keep track of their permissions. The services manage a large portion of the activity in your IT environment. They specifically ensure that each person is who they claim to be (authentication), usually by checking the user ID and password they enter and limiting their access to only the data they are authorized to use (authorization). Active Directory (AD) Authenitcation is a windows system used for centralized management of user roles and permissions. AD contains a group policy feature through which this can be achieved.
AD supports multiple protocols through which authentication of the organization’s users can be done. The two main of these are Kerberos and LDAP.
The following are the main advantages of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS):
miniOrange supports user authentication from external directories such as Active Directory, LDAP, OpenLDAP, and OpenDS, among others. We have directory integration solutions that are simple and easy to use for both cloud and on-premise applications. This on-demand integration service enables user authentication, user provisioning, de-provisioning, and application usage reporting. The fact that miniOrange's directory integration is simple to set up is an important aspect of this service. MiniOrange also supports thousands of applications and provides an Single Sign-on (SSO) mechanism for users in the integrated directory.

To set up Active Directory (AD) Authentication, you can follow the steps here.
Authentication in Active Directory entails more than just the verification of a username and password. miniOrange AD authentication includes the following components:
The first component of AD authentication service that we provide at miniorange is Self-service password reset which allows users to change or reset their passwords without the involvement of an administrator or help desk. If a user forgets his password, the miniOrange solution can be used to generate a new one for him.
The second component of the AD authentication service that we provide at minorange is MFA. MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) is a type of authentication in which a user must provide additional multi-factors in order to gain access to specific resources. In this context, resources refer to a website, an application, a network, or a VPN.
Rather than simply asking for a username and password, MFA (Multi-Factor authentication) adds additional verification factors (OTP, push notifications, fingerprint, etc. 15+ MFA methods) that indirectly halt cyber attackers' activities such as phishing, Malware, and so on, providing a high level of assurance and security. Simply put, you must convince the system or online service of your identity multiple times before the system can determine whether you have the rights to obtain the data services that you are attempting to retrieve.
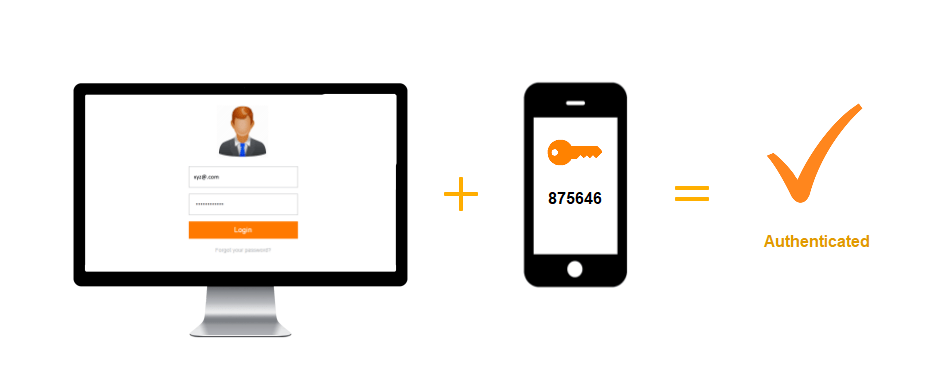
The goal of using MFA is to create a layered defence so that even if one factor (username-password) is stolen or a targeted cyber attacker has at least one more barrier to overcome before successfully breaking into the actual targeted device.
One of the most amazing components of the AD authentication service that miniorange will provide you is password-less authentication. Users can log in without having to remember a password using passwordless connections. To login to the application, users simply enter their username and pass the 2-factor authentication by entering an OTP or receiving push notifications. This provides people with a simple and convenient way to sign in and access data from anywhere.
Passwords are also a major vulnerability because users reuse passwords and can share them with others. An attacker cannot easily replicate 2-factor authentication methods. miniOrange provides ways to natively authenticate using passwordless methods to simplify the sign-in experience for users and reduce the risk of attacks.
