Need Help? We are right here!
Need Help? We are right here!
Thanks for your Enquiry. Our team will soon reach out to you.
If you don't hear from us within 24 hours, please feel free to send a follow-up email to info@xecurify.com
Search Results:
×miniOrange supports Single Sign-on into your apps, to securely login for admins and users. miniOrange supports several different protocols for your applications, such as SAML, WS-FED, OAuth, OIDC, JWT, RADIUS, etc. Using Single Sign-on, users can use one set of credentials to login to multiple applications. This improves security, as it reduces avenues for phishing attacks, and also improves access to your application.
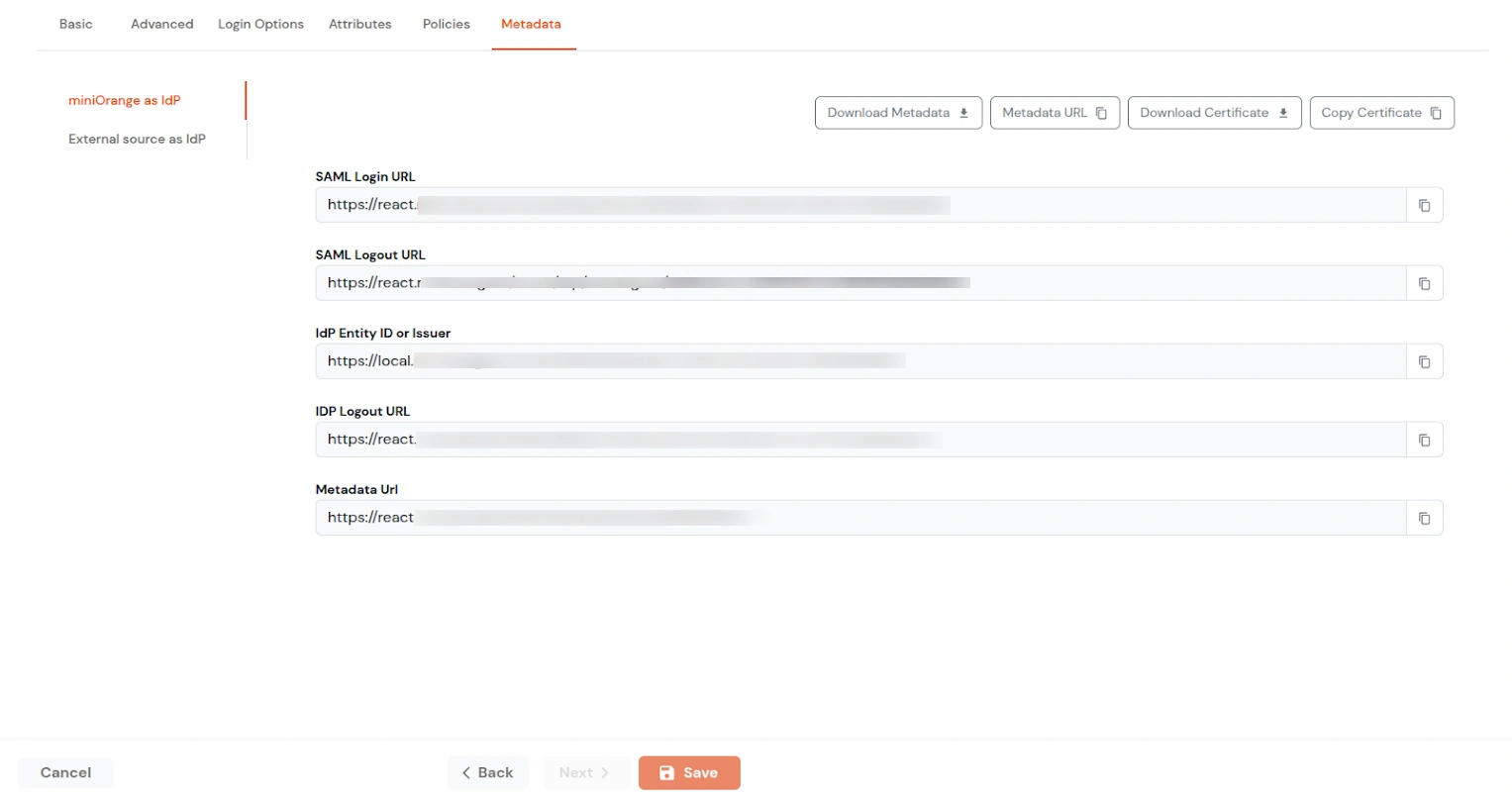
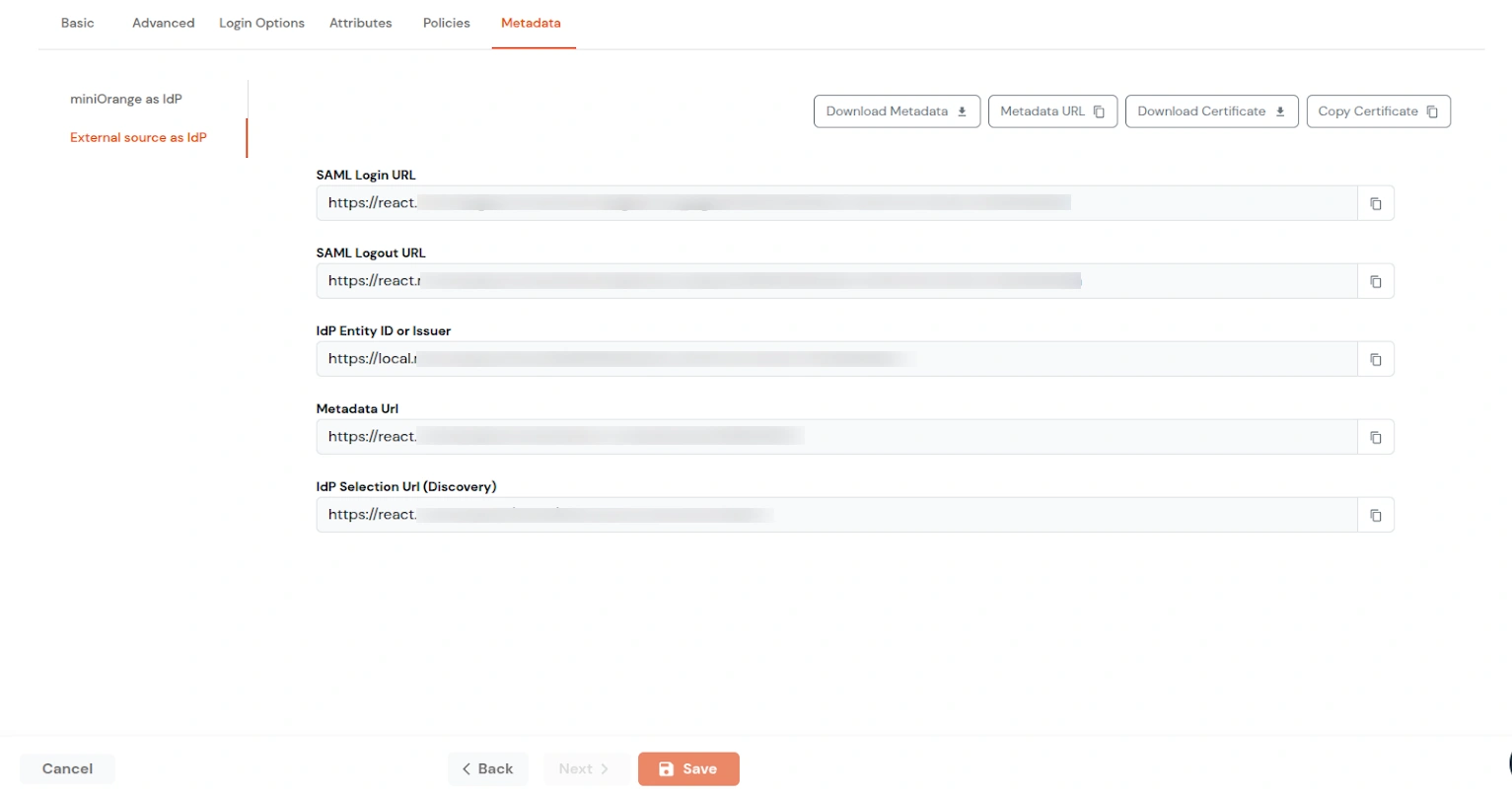
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML standard that allows secure web domains to exchange user authentication and authorization data. Using SAML, an online service provider (SP) can contact a separate online identity provider to authenticate users who are trying to access secure content. miniOrange provides a solution to perform single sign-on (SSO) for applications supporting SAML protocol, like AWS, WordPress, Atlassian, Dropbox Enterprise, moodle, SAP, Zoho, zendesk, etc. The steps to configure SSO settings for SAML applications on miniOrange are as follows.
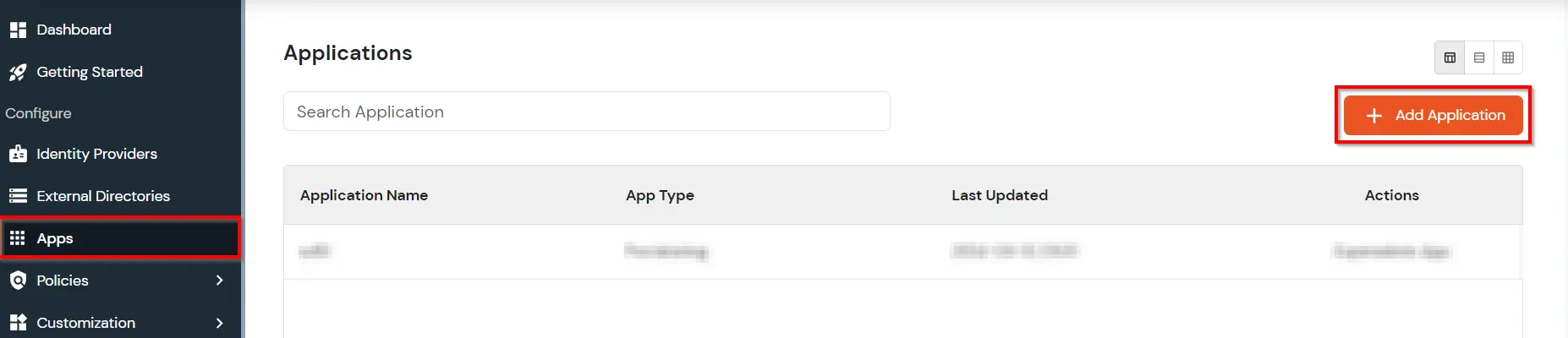
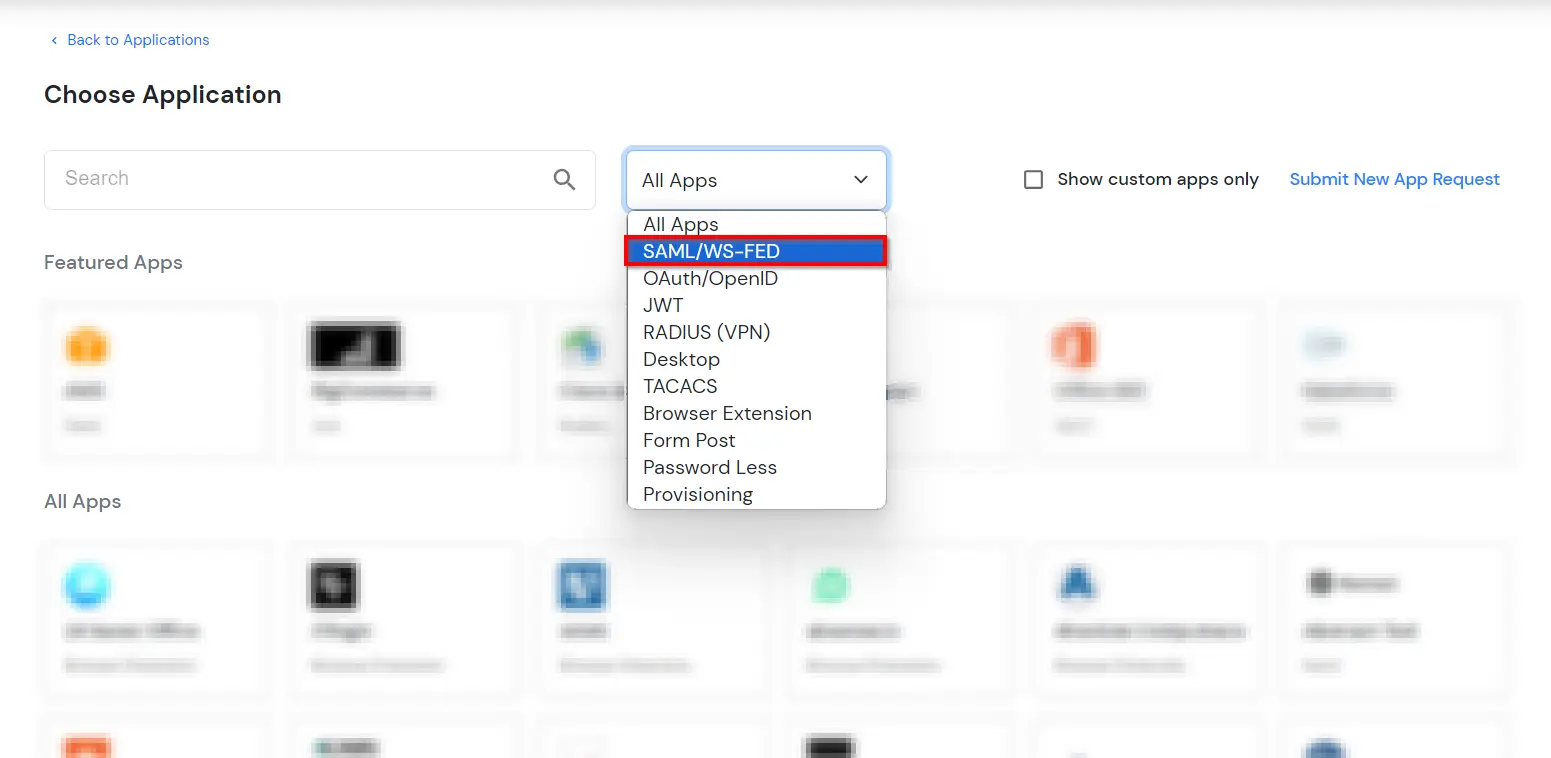
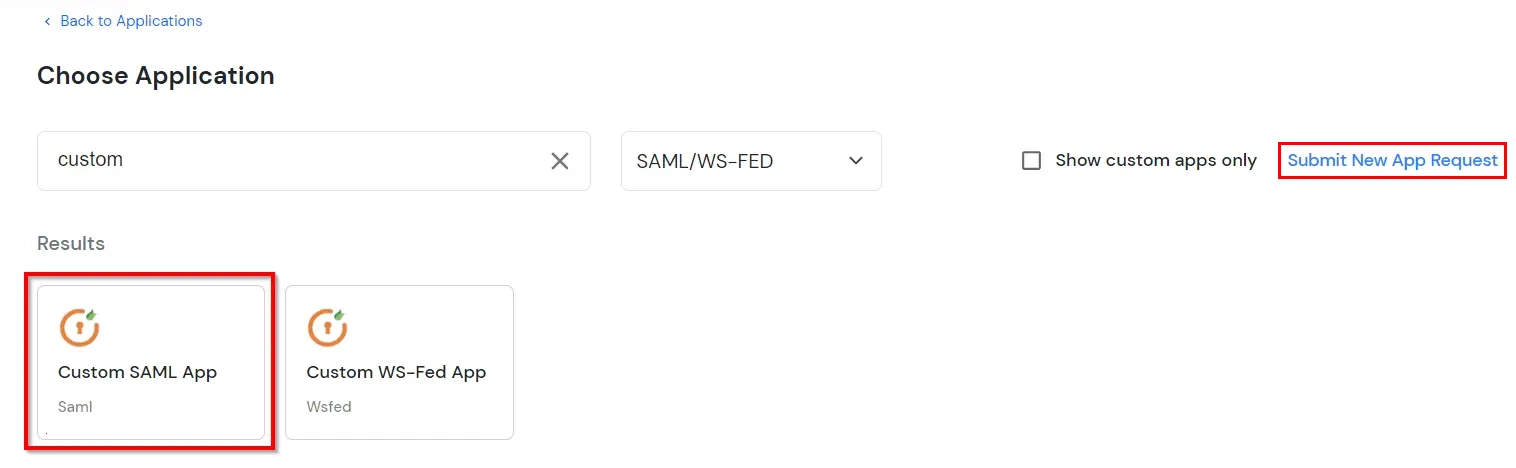
Note: You can configure your application using Manual Configuration or Import Metadata. Follow the steps below based on your preferred method.
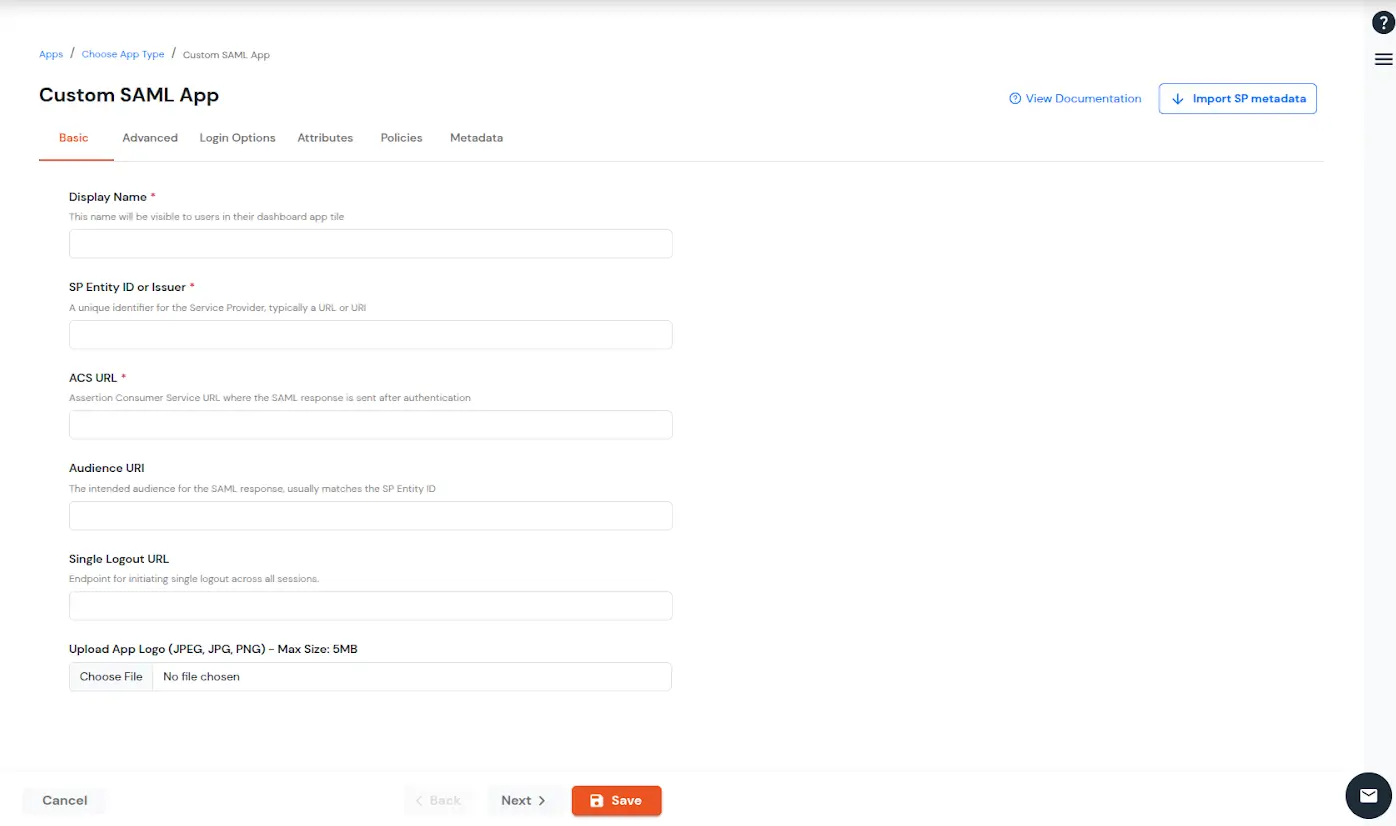
| Display Name (required) | Enter the Display name for your app as per your preference. |
| SP Entity ID or Issuer (required) | Is used to identify your app against the SAML request received from SP. The SP Entity ID or Issuer can be in either URL or in String format. |
| ACS URL or Assertion Consumer Service URL (required) | defines where the SAML Assertion should be sent after authentication. Make sure the ACS URL is in the format: https://www.domain-name.com/a/[domain_name]/acs. |
| Audience URL | As the name suggests, specifies the valid audience for SAML Assertion. It is usually the same as SP Entity ID. If Audience URL is not specified separately by SP, leave it blank. |
| Single Logout URL | The URL where you want the logout request to be consumed and where your users should be redirected after single logout from the applications. |
| Upload App Logo | Upload a logo for your application. |
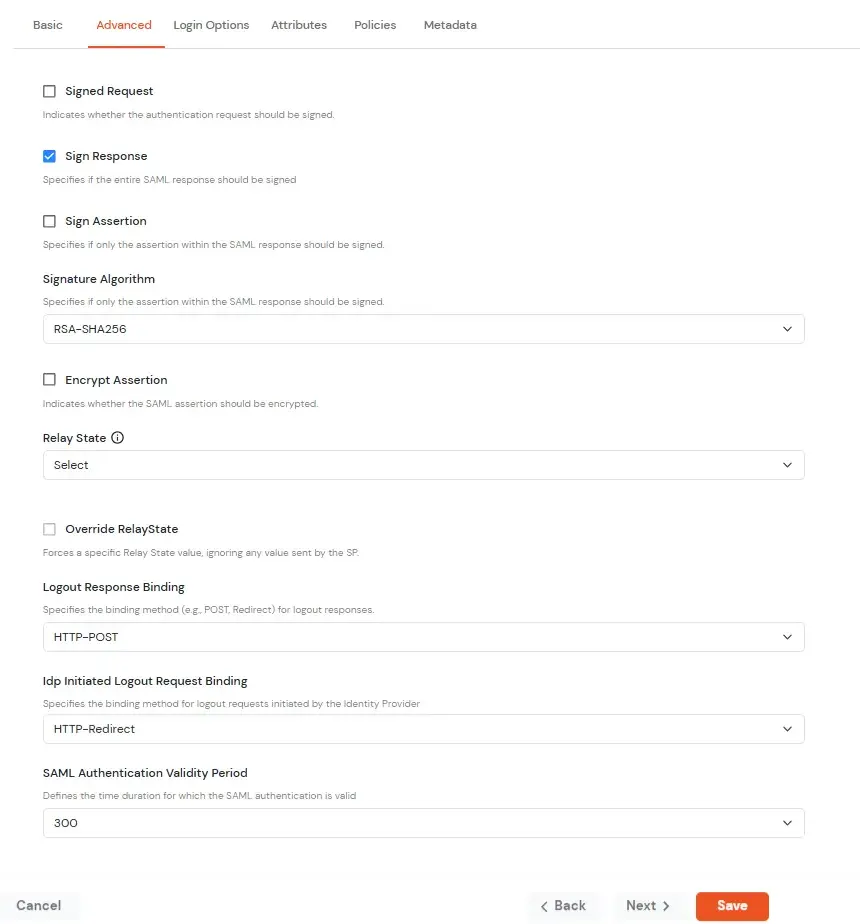
| Signed Request | Enable this to sign the saml request sent by SP. Provide the X509 certificate or upload the certificate. |
| Sign Response | Enable this if you want the entire SAML response to be signed. |
| Sign Assertion | Enable this if you want only the assertion within the SAML response should be signed. |
| Signature Algorithm | Select the algorithm that will be used to sign the SAML request/response. |
| Encrypt Assertion | Select this if you want to encrypt the assertion in SAML response and provide the algorithm and certificate for encryption. |
| Relay State | Enter the URL where you want the user to redirect after sign in to the application. |
| Override Relay state | Enable this to override the default relay state of the SP. |
| Logout Response Binding | A Logout Response is sent in reply to a Logout Request from SP. It could be sent by an Identity Provider or Service Provider. |
| IdP initiated Logout Request Binding: | A Logout Response is sent in reply to a Logout Request from the IdP dashboard. It could be sent by an Identity Provider or Service Provider.
|
| SAML Authentication Validity Period | The time for which the authentication should be considered valid and the user should be able to perform SSO. After that, the user will have to sign in again. |
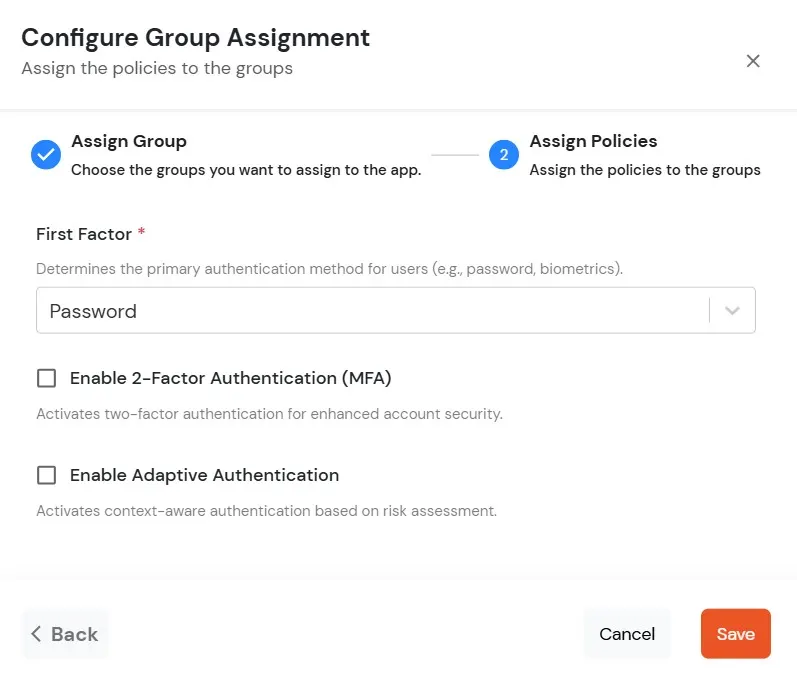
| Enable Shared Identity | This feature lets you control whether a specific application can be accessed by shared user or not. |
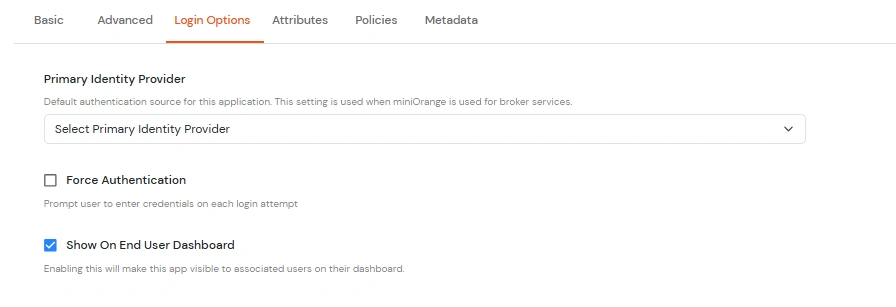
| Primary Identity Provider | Select the identity source from where you want the authentication to happen. You will see the list of all configured sources. |
| Force Authentication | Enable this to enforce authentication on each request to access the application. |
| Show On End User Dashboard | Disable this if you do not want the app to be visible for all users on end user dashboard. |
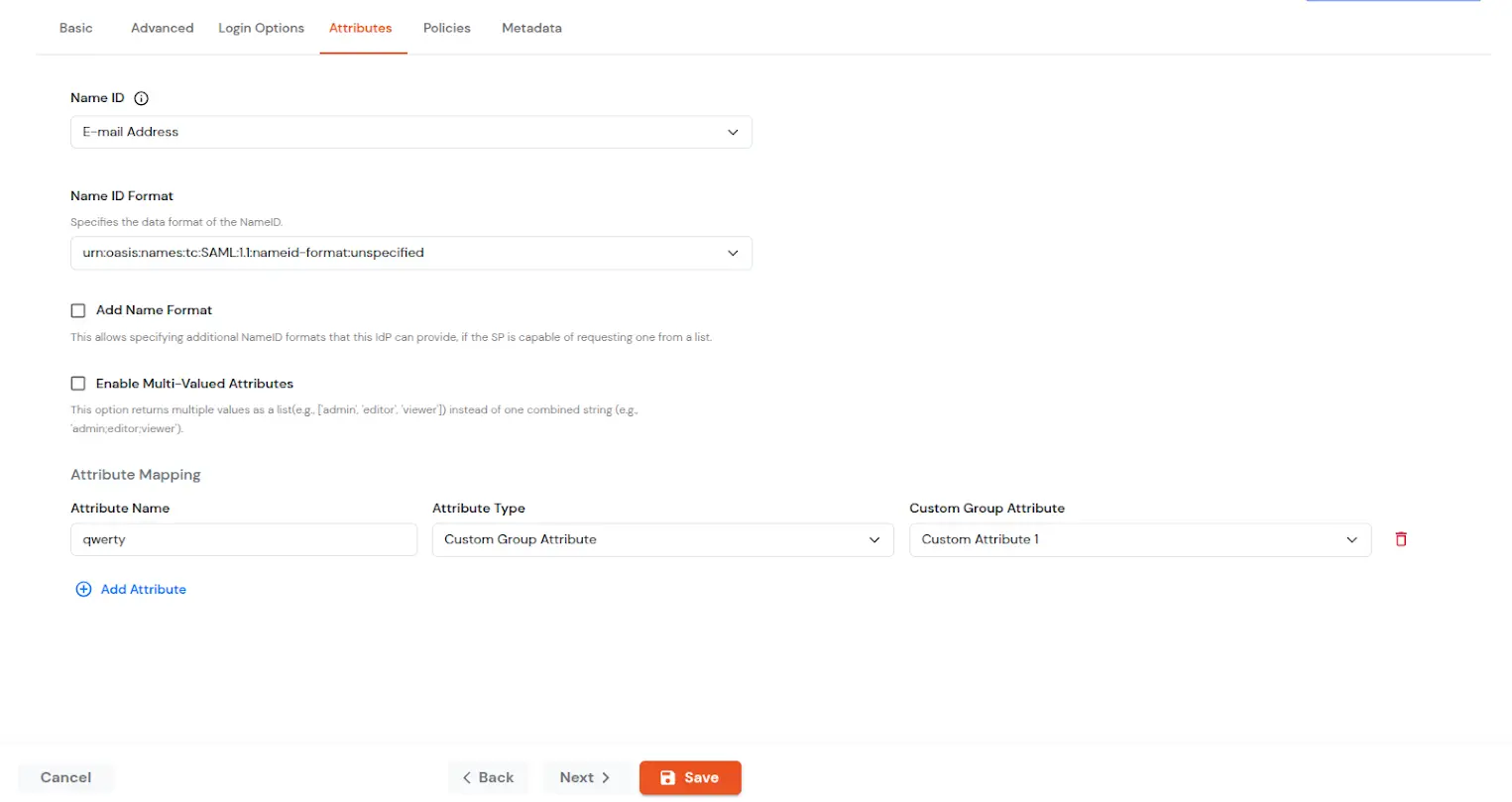
| NameID | NameID is the unique identifier for the authenticated user included in the SAML assertion. It allows the Service Provider to recognize and map the user to an account. Generally, NameID is a username or Email Address. |
| NameID format | Defines what type of identifier is used in the NameID (e.g., email, persistent, transient) so the SP can correctly map the user. If the SP does not request a specific format, the IdP can leave it unspecified and use a default. |
| Add Name Format | Name Format defines how attribute names are represented in a SAML assertion (e.g., as simple strings or URIs). It helps the SP correctly interpret attribute naming and ensures consistency between IdP and SP. |
| Enable Multi-Valued Attributes | Enabled:Commas (,) and semicolons (;) are treated as separators, so the attribute is split into a clean list. Example: roles = ['admin', 'editor', 'viewer']. Disabled:Commas and semicolons are not treated as separators, so the attribute stays as one combined string. Example: roles = "admin;editor;viewer". |
| Attribute Mapping | You can Add Attributes to be sent in SAML Assertion to SP. The attributes include user’s profile attributes such as first name, last name, full name, username, email, custom profile attributes, and user groups, etc. |
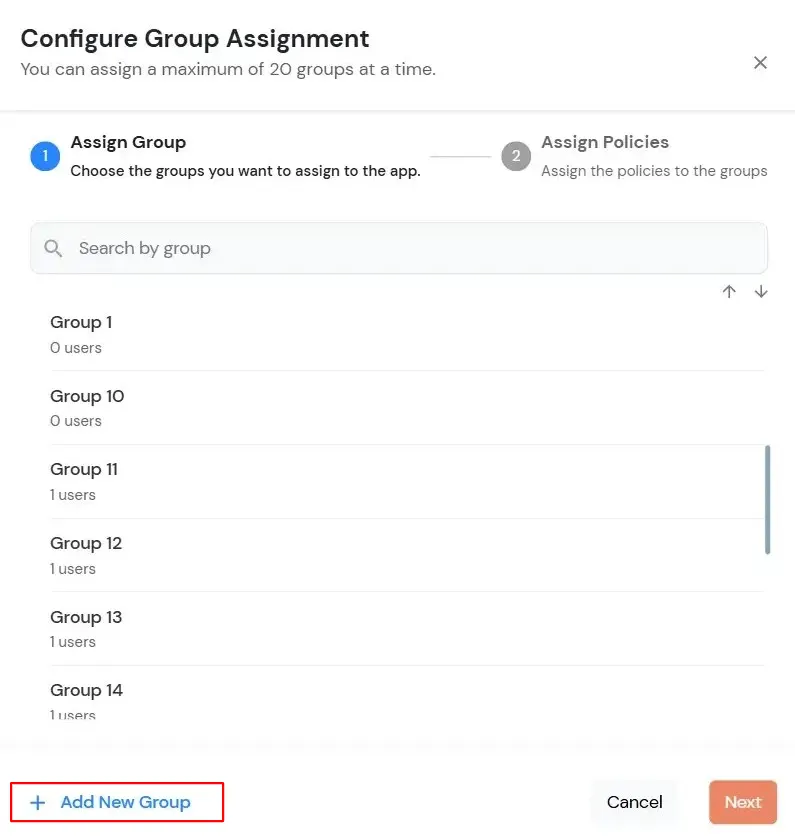
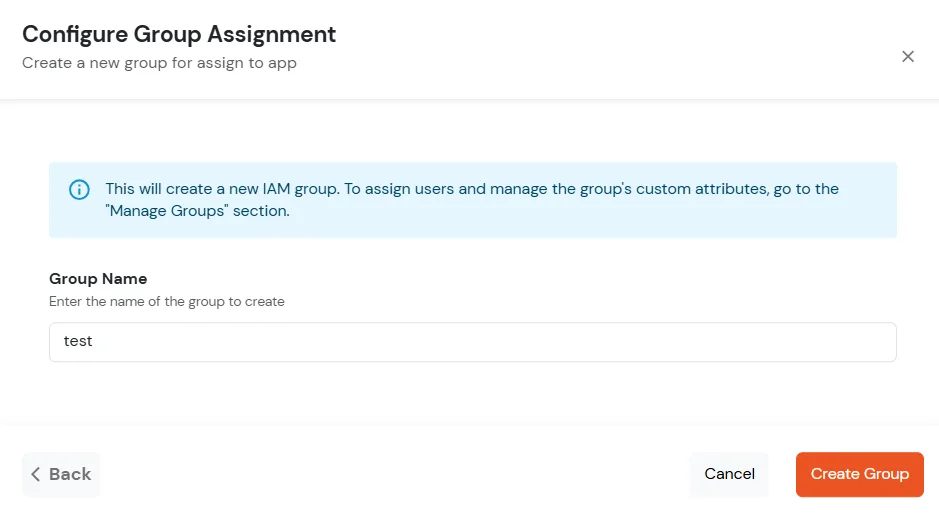
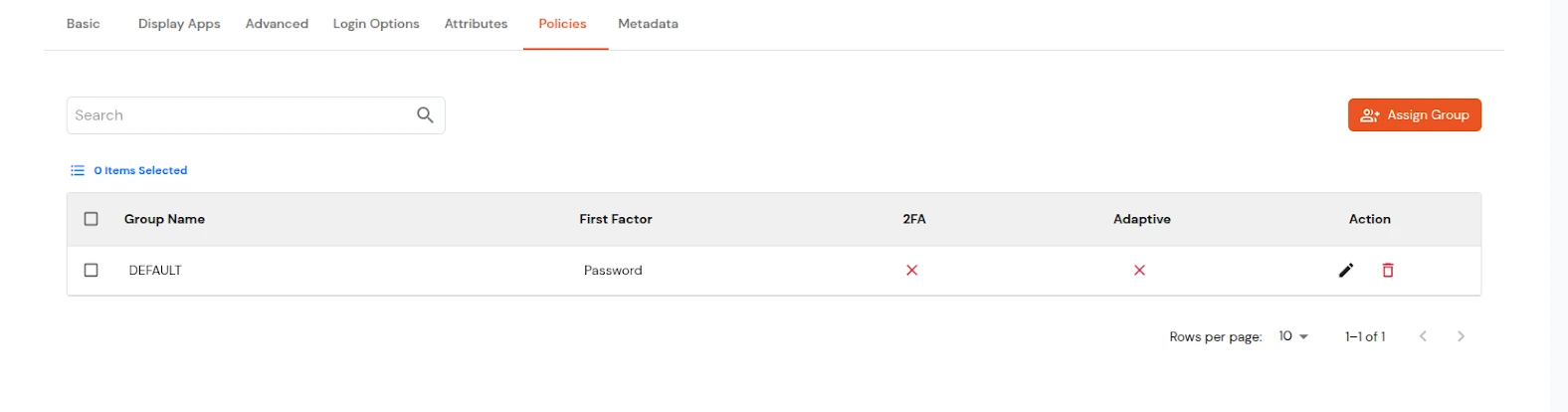
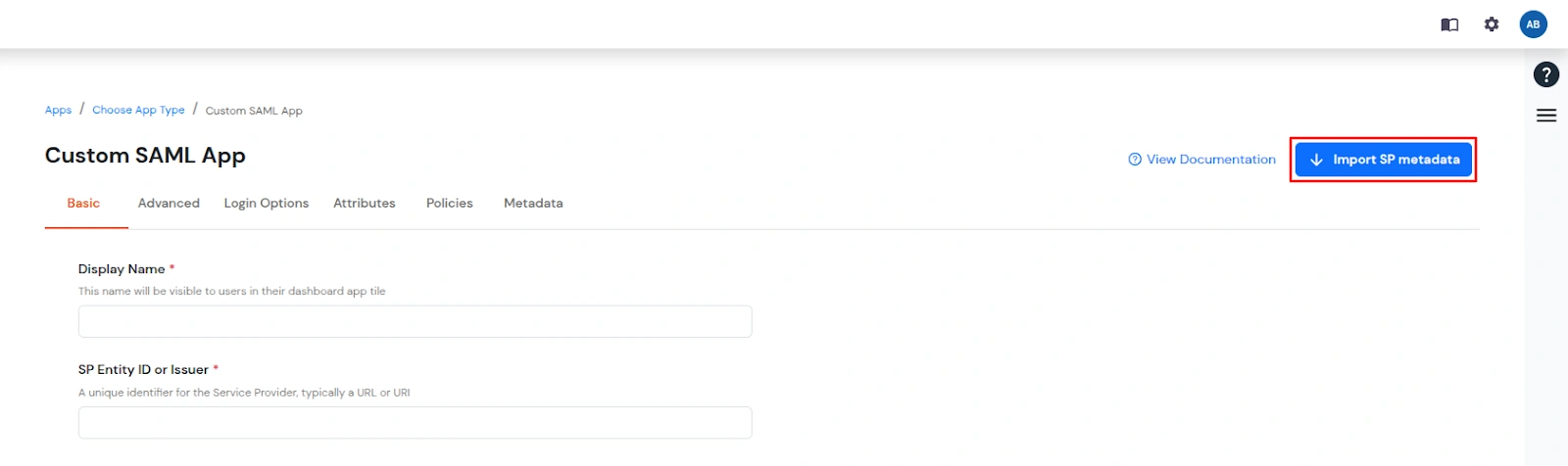
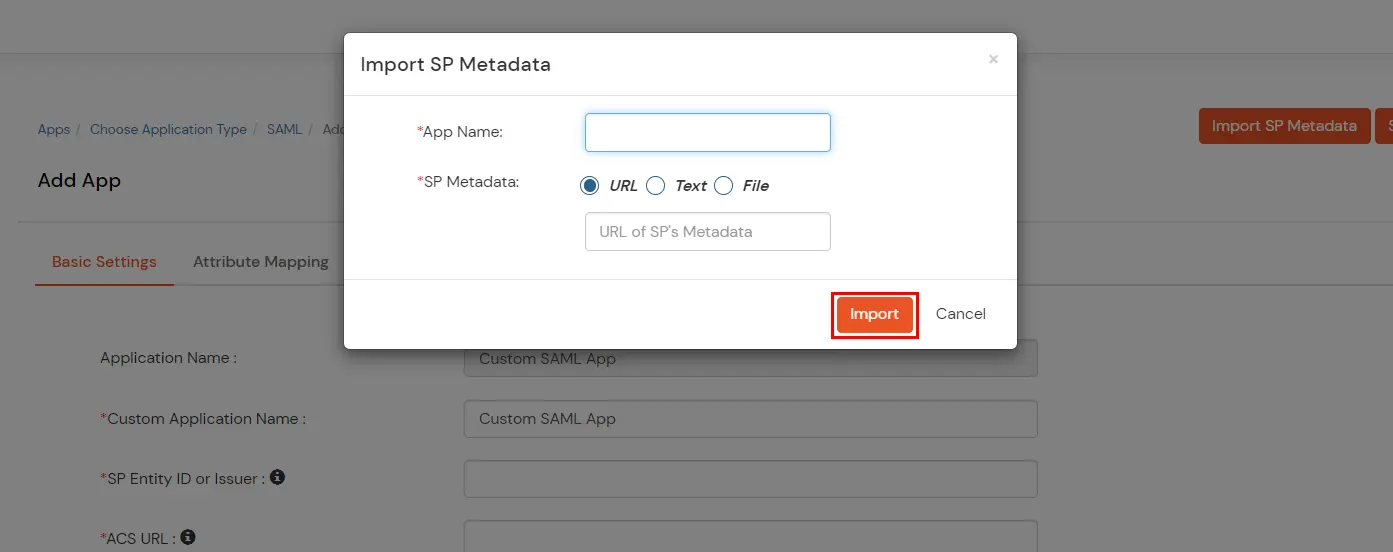
| Signed Request | Enable this to sign the saml request sent by SP. Provide the X509 certificate or upload the certificate. |
| Sign Response | Enable this if you want the entire SAML response to be signed. |
| Sign Assertion | Enable this if you want only the assertion within the SAML response should be signed. |
| Signature Algorithm | Select the algorithm that will be used to sign the SAML request/response. |
| Encrypt Assertion | Select this if you want to encrypt the assertion in SAML response and provide the algorithm and certificate for encryption. |
| Relay State | Enter the URL where you want the user to redirect after sign in to the application. |
| Override Relay state | Enable this to override the default relay state of the SP. |
| Logout Response Binding | A Logout Response is sent in reply to a Logout Request from SP. It could be sent by an Identity Provider or Service Provider. |
| IdP initiated Logout Request Binding: | A Logout Response is sent in reply to a Logout Request from the IdP dashboard. It could be sent by an Identity Provider or Service Provider.
|
| SAML Authentication Validity Period | The time for which the authentication should be considered valid and the user should be able to perform SSO. After that, the user will have to sign in again. |

| Primary Identity Provider | Select the identity source from where you want the authentication to happen. You will see the list of all configured sources. |
| Force Authentication | Enable this to enforce authentication on each request to access the application. |
| Show On End User Dashboard | Disable this if you do not want the app to be visible for all users on end user dashboard. |

| NameID | NameID is the unique identifier for the authenticated user included in the SAML assertion. It allows the Service Provider to recognize and map the user to an account. Generally, NameID is a username or Email Address. |
| NameID format | Defines what type of identifier is used in the NameID (e.g., email, persistent, transient) so the SP can correctly map the user. If the SP does not request a specific format, the IdP can leave it unspecified and use a default. |
| Add Name Format | Name Format defines how attribute names are represented in a SAML assertion (e.g., as simple strings or URIs). It helps the SP correctly interpret attribute naming and ensures consistency between IdP and SP. |
| Enable Multi-Valued Attributes | Enabled:Commas (,) and semicolons (;) are treated as separators, so the attribute is split into a clean list. Example: roles = ['admin', 'editor', 'viewer']. Disabled:Commas and semicolons are not treated as separators, so the attribute stays as one combined string. Example: roles = "admin;editor;viewer". |
| Attribute Mapping | You can Add Attributes to be sent in SAML Assertion to SP. The attributes include user’s profile attributes such as first name, last name, full name, username, email, custom profile attributes, and user groups, etc. |








